bioTM is an integrative software package that allows users to data mine PubMed literature at scale.
Whenever a user inputs a query on PubMed, they often see thousands of publications that are related to their search. In an ideal scenario we would be able to read all of these entries, but this is often times impractical. bioTM can sample large quantities of scientific abstracts (n = 500 - 2,000) and data mine them to generate potentially important keyword or bio-concept relationships spanning the literature. By using an automatic text extraction framework that combines natural language processing (NLP) and association rules learning, users can generate broad or highly-specific outputs of text relationships that serve as reflection of current scientific evidence and/or understanding of specific biomedical topics.
- Windows, Mac, or Linux
- R Version (4.2.2 or latest version)
- Python virtual environment with spaCy and a spaCy english-language model
- R studio (Suggested)
- Package installation
library(devtools)
devtools::install_github('dandycodingpipe/pubAssociationFinder')
library(bioTM)
library(tidyverse)
- Virtual environment installation (REQUIRED)
Windows
python -m venv /path/to/directory
path\to\venv\Scripts\activate.bat
pip install spacy
python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm
Mac
virtualenv path/to/venv
source path/to/venv/bin/activate
pip install -U pip setuptools wheel
pip install -U spacy
python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm
Save the path to your activated virtual environment because it will be used to activate spaCy on R.
If you are done using the tool it is recommended to deactivate and remove the virtual environment from your computer.
This function is the fastest way to apply text mining to PubMed. Depending on your computer and the amount of abstracts retrieved, results can be generated in about 3-10 minutes.
keywords <- easyKAF("pulmonary arterial hypertension","pubmed", "C:/Users/Chris/OneDrive/2023/Systox/venvJune19", "en_core_web_lg")
- Limited to a maximum of 1,500 abstracts
- Databases available are "pubmed" and "pmc"
- Mines relationships with a minimum support, confidence, and p-value of 1%, 75%, and p<0.005)
- For more customization options see the manual function calling guide
bioTM contains functions that help classify, visualize, and export (coming soon) results so that users can conveniently survey the biomedical topic that was queried.
meshTerms <- matchMeSH(keywords, c("lead"))
aopRisks <- matchAOP(keywords, "aop-wiki-xml-2023-04-01.xml")
- matchMeSH which classifies rules using the Medical Subject Headings database according to (Anatomy, Organism, Disease, Chemicals and Drugs, Analytical, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Techniques, and Equipment, etc.) through exact-string matching
- matchAOP which classifies a set of 5,000 rules using the AOP-wiki database quarterly downloads according to AOP-classes (stressor, key-event, biological process, biological-object, AOP) through fuzzy-string matching (>75% similarity threshold). It is the user's responsability to download and place the xml file in the current directory.
This function generates more specific toxico-genomic data by using abstracts that are pre-annotated by PubTator for bio-named entities or bio-concepts. Depending on your computer and the amount of abstracts retrieved, results can be generated in about 10-20 minutes.
concepts <- PubTator("pulmonary arterial hypertension")
results <- bioCAF(concepts, "gene", 0.001, "C:/Users/Chris/OneDrive/2023/Systox/venvJune19", "en_core_web_lg")
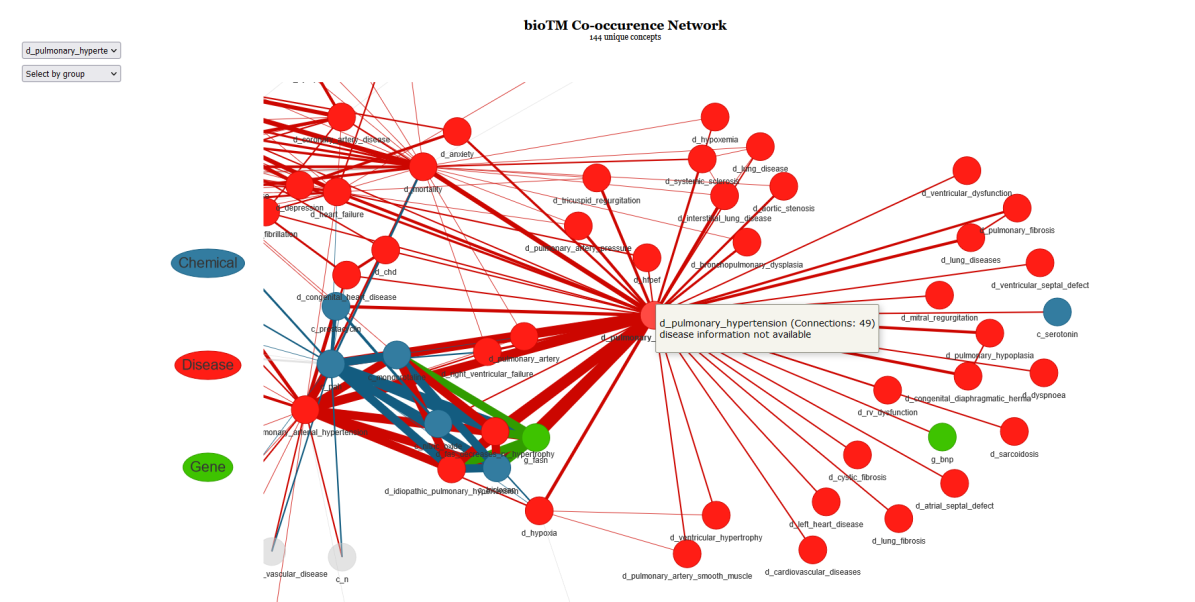
#NEW!
viz <- systox(results, "layout_nicely")
viz
- Limited to a maximum of 2,000 abstracts
- Support is controlled by the user but confidence and p-value thresholds are fixed at (60% and p<0.05)
- Currently only pre-annotated PubTator abstracts are supported
# 1. Retrieval
retrieved <- pubRetrieve(query, 1500, database)
# 2. Natural language processing
preProcessed <- pubParse(retrieved, method = "POS", composite = "n", venv_path, lang_model, 0.2)
# 3. Unsupervised machine learning
rules <- pubMine(preProcessed, 0.01, 0.75, 0.005)
# 3.1 (Optional) Pruning large-rule set
filt_rules <- which(rules$lift <= 2)
rules <- rules[-filt_rules,]
Be conscious of your hardware limitations as this software can create significant computational load with parameters that call many articles or mine large rulesets.
When retrieving abstract data, PubMed is limited to 2,000 texts while EuropePMC can reliably retrieve up to 20,000 for certain queries.
Contributors names and contact info
ex. Christian A. Hernandez-Fajardo ex. Linkedin
- 0.0.2
- Addition of a co-occurence network construction and visualization function (systox) with instructions for html export in the documentation.
- 0.0.1
- Alpha release (does not include co-occurence network visualization or export functions)
bioTM is not intended to provide specific medical advice or diagnosis. The software only provides users with information to better survey health risks, genetics, diagnosed disorders, and advances in medicine and biotechnology that are frequenting in the scientific community. Results from bioTM are not medical advice and you should consult with a qualified health professional for diagnosis and/or answers to personal questions.
This tool was developed for the Systox group (Unit T3S) at the Université Paris Cité as a means of exploring new methods for leveraging scientific research for the discovery of adverse outcome pathways.
A special thanks to Karine Audouze, Florence Jornod, and Mingji Kim for their supervision and expertise.
Complementary tool:
-
Wei, C. H., Kao, H. Y., & Lu, Z. (2013). PubTator: a web-based text mining tool for assisting biocuration. Nucleic acids research, 41(Web Server issue), W518–W522. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt441
-
Chih-Hsuan Wei and others, PubTator central: automated concept annotation for biomedical full text articles, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 47, Issue W1, 02 July 2019, Pages W587–W593, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz389