Atari Tempest Lite is a retro browser game built with JavaScript and Canvas. Inspired by Tempest, a 1981 arcade game by Atari, it calculates vectors on the fly to render three-dimensional surfaces.
| Control | Action |
|---|---|
| Point mouse | Move blaster to segment |
| Click mouse | Shoot bullet |
| ← key | Move blaster clockwise |
| → key | Move blaster counter-clockwise |
| Space key | Shoot bullet |
- Eliminate all red flippers (150 points each).
- Avoid flippers & enemy bullets.
- Flippers are harmless mid-flip.
- If a flipper reaches the rim, it still can be shot from the adjacent segment.
- Time your shots carefully!
- Enemy bullets are destructible.
- However, they're not worth any points.
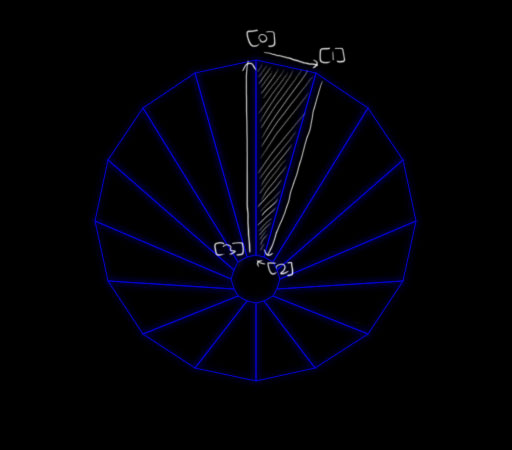
Each tube shape is stored as a multi-dimensional array of coordinates for the rim and the pit.
Game.TUBE_CIRCLE = [
[
[256, 60], [316, 73], [368, 108], [403, 160], [416, 221], [403, 281], [368, 334], [315, 368], [256, 381], [195, 368], [143, 334], [108, 281], [95, 221], [108, 160], [143, 108], [195, 73], [256, 60]
],
[
[256, 255], [264, 257], [273, 262], [277, 270], [280, 279], [277, 289], [273, 296], [264, 301], [256, 303], [247, 301], [238, 296], [234, 289], [231, 279], [234, 270], [238, 262], [247, 257], [256, 255]
]
];
Game.TUBE_SHAPES = [
Game.TUBE_CIRCLE, Game.TUBE_SQUARE, Game.TUBE_STARBURST, Game.TUBE_CROSS, Game.TUBE_PEANUT, Game.TUBE_CLOVER, Game.TUBE_CELTIC, Game.TUBE_HEART
];Upon starting the game or advancing levels, the tube coordinates are converted into quadrilaterals and pushed to an array this.tubeQuads.
defineTubeQuads(tubeShape) {
this.tubeQuads = [];
for (let i = 0; i < tubeShape[0].length - 1; i++) {
this.tubeQuads.push([
tubeShape[0][i],
tubeShape[0][i + 1],
tubeShape[1][i + 1],
tubeShape[1][i],
]);
}
}Afterwards, each quadrilateral is rendered for each animation frame using Canvas's lineTo function.
drawTubeQuads(context, color) {
context.shadowColor = color;
context.shadowBlur = Game.SHADOW_BLUR;
context.strokeStyle = color;
for (let i = 0; i < this.tubeQuads.length; i++) {
const tubeQuad = this.tubeQuads[i];
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(...tubeQuad[0]);
context.lineTo(...tubeQuad[1]);
context.lineTo(...tubeQuad[2]);
context.lineTo(...tubeQuad[3]);
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}
}The Blaster has four instance variables pertaining to movement:
this.gamethis.xPos(0to119)this.targetPos(0to119, ornull)this.changingXPos(-7,0, or7)
The canvas has a mousemove listener that iterates through each tube quadrilateral and determines if the mouse position is inside the quadrilateral.
for (let i = 0; i < this.tubeQuads.length; i++) {
const boundary = this.tubeQuads[i];
if (Util.isInside(point, boundary)) {
this.blasters[0].targetXPos = Game.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS * i + this.xPosInTubeQuad(point, boundary);
}
}If so, then the relative lateral position within the quadrilateral is calculated. This xPosInTubeQuad plus the xPos for the current quadrilateral is passed as targetPos to the Blaster.
class Game {
...
xPosInTubeQuad(point, boundary) {
return Math.floor(Game.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS * Util.xFractionInTubeQuad(point, boundary));
}
...
}
class Util {
...
xFractionInTubeQuad(point, tubeQuad) {
const distBack = Util.distanceToLine(point, tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[3]);
const distForward = Util.distanceToLine(point, tubeQuad[1], tubeQuad[2]);
const distTotal = distBack + distForward;
return distBack / distTotal;
},
...
}If this.targetPos is not null (in case of keyboard input), the blaster chooses the shortest of the two paths from this.xPos to this.targetPos (clockwise/counterclockwise) and sets its direction this.changingXPos accordingly.
move() {
if (this.targetXPos) {
const numXPos = this.game.tubeQuads.length * Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS;
if (this.xPos <= this.targetXPos - Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS) {
if (this.targetXPos - this.xPos < numXPos / 2) {
this.changingXPos = Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS;
} else {
this.changingXPos = -Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS;
}
} else if (this.xPos >= this.targetXPos + Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS) {
if (this.xPos - this.targetXPos < numXPos / 2) {
this.changingXPos = -Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS;
} else {
this.changingXPos = Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS;
}
} else {
this.changingXPos = 0;
this.changeXPos(this.targetXPos - this.xPos);
this.targetXPos = null;
}
}
if (this.changingXPos !== 0) {
this.changeXPos(this.changingXPos);
}
...
}Finally, the Blaster wraps around if necessary and plays a sound if it has reached a new segment.
changeXPos(increment) {
const oldXPos = this.xPos;
this.xPos += increment;
const numXPos = this.game.tubeQuads.length * Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS;
if (this.xPos < 0) {
this.xPos += numXPos;
} else if (this.xPos >= numXPos) {
this.xPos -= numXPos;
}
if (Math.floor(oldXPos / Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS) !== Math.floor(this.xPos / Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS)) {
this.game.blasterMoveSound.currentTime = 0;
this.game.blasterMoveSound.play();
}
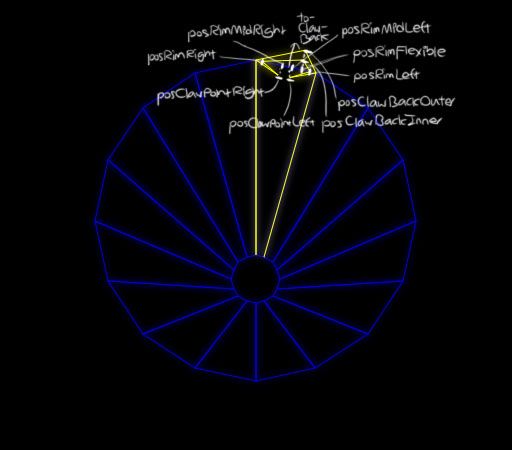
}The Blaster coordinates are defined based on:
- The rim of the current quadrilateral, i.e. the line from
tubeQuad[0]totubeQuad[1] - The relative lateral position within the current quadrilateral, i.e.
this.xPosInTubeQuad
this.xPosInTubeQuad === this.xPos % Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS
drawBlaster(context, tubeQuad) {
const posRimFlexible = Util.weightedMidpoint(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], (this.xPosInTubeQuad + 1) / (Blaster.NUM_BLASTER_POSITIONS + 1));
const posRimLeft = Util.weightedMidpoint(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], 0.9);
const posRimMidLeft = Util.weightedMidpoint(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], 0.6);
const posRimMidRight = Util.weightedMidpoint(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], 0.4);
const posRimRight = Util.weightedMidpoint(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], 0.1);
const toClawBack = Util.orthogonalUnitVector(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], 10);
const posClawBackOuter = Util.addVector(posRimFlexible, toClawBack, 2);
const posClawBackInner = Util.addVector(posRimFlexible, toClawBack);
const posClawPointLeft = Util.addVector(posRimMidLeft, toClawBack, -1);
const posClawPointRight = Util.addVector(posRimMidRight, toClawBack, -1);
context.strokeStyle = Blaster.YELLOW;
context.shadowColor = Blaster.YELLOW;
context.shadowBlur = Blaster.SHADOW_BLUR;
context.beginPath();
context.moveTo(...tubeQuad[0]);
context.lineTo(...posClawBackOuter);
context.lineTo(...tubeQuad[1]);
context.lineTo(...posClawPointLeft);
context.lineTo(...posRimLeft);
context.lineTo(...posClawBackInner);
context.lineTo(...posRimRight);
context.lineTo(...posClawPointRight);
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}The appearance of a Flipper is determined entirely by its position along two axes:
this.xPosthis.zPos
The first step in drawing a Flipper is to break up this.xPos into two components:
- The index of the tube segment it occupies
- The flipper's relative lateral position within the tube segment
draw(context) {
this.xPosInTubeQuad = this.xPos % Flipper.NUM_FLIPPER_POSITIONS;
this.tubeQuadIdx = Math.floor(this.xPos / Flipper.NUM_FLIPPER_POSITIONS);
const tubeQuad = this.game.tubeQuads[this.tubeQuadIdx];
...
}A quadratic easing function is used to simulate 3D perspective with this.zPos.
class Flipper extends MovingObject {
...
draw(context) {
...
const easeFraction = Util.easeOutQuad(this.zPos / Flipper.MAX_Z_POS);
...
}
...
}
const Util = {
easeOutQuad(fraction) {
return 1 - Math.pow(fraction - 1, 2);
},
}The "baseline" position of the flipper is calculated by extending inward from the tube rim segment, using easeFaction as a scalar.
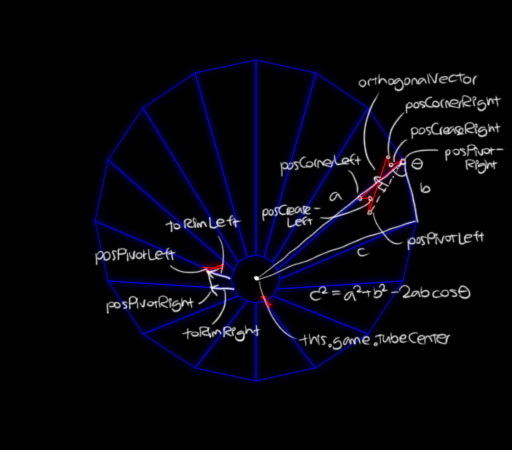
draw(context) {
...
const toRimRight = Util.vector(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[3], easeFraction);
const toRimLeft = Util.vector(tubeQuad[1], tubeQuad[2], easeFraction);
let posPivotRight = Util.addVector(tubeQuad[0], toRimRight);
let posPivotLeft = Util.addVector(tubeQuad[1], toRimLeft);
...
}This is where it gets fun. Based on whether a flipper is arriving from or departing to an adjacent tube rim segment, it must rotate its "baseline" position around either the posPivotLeft or the posPivotRight. Fortunately, this simplifies to two cases, based on whether this.xPosInTubeQuad is above or below the middle point midFlip.
Next, in order to render the rest of the bowtie shape, an orthogonalUnitVector must be calculated from the "baseline", and this must also rotate around the pivot point.
Then, the theta by which the flipper must rotate is equal to the angle formed from the triplet of points comprising the rim tube segment and the center of the entire tube pit, with the angle facing outward from the center.
draw(context) {
...
let orthogonalVector;
const orthogonalHeight = 15 * (1 - 0.9 * easeFraction);
let theta;
const midFlip = Math.floor(Flipper.NUM_FLIPPER_POSITIONS / 2);
if (this.xPosInTubeQuad > midFlip) {
theta = Util.theta(tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1], this.game.tubeCenter) * 2;
theta *= -(this.xPosInTubeQuad - midFlip) / Flipper.NUM_FLIPPER_POSITIONS;
orthogonalVector = Util.orthogonalUnitVector(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, orthogonalHeight);
posPivotRight = Util.rotateAroundPoint(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, theta);
orthogonalVector = Util.rotateAroundPoint(orthogonalVector, [0, 0], theta);
} else {
theta = Util.theta(this.game.tubeCenter, tubeQuad[0], tubeQuad[1]) * 2;
theta *= -(this.xPosInTubeQuad - midFlip) / Flipper.NUM_FLIPPER_POSITIONS;
orthogonalVector = Util.orthogonalUnitVector(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, -orthogonalHeight);
posPivotLeft = Util.rotateAroundPoint(posPivotLeft, posPivotRight, theta);
orthogonalVector = Util.rotateAroundPoint(orthogonalVector, [0, 0], theta);
}
...
}At this point, the coordinates can be calculated, and the flipper can finally be drawn.
draw(context) {
...
const posCornerRight = Util.addVector(Util.weightedMidpoint(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, 0.1), orthogonalVector);
const posCreaseRight = Util.addVector(Util.weightedMidpoint(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, 0.2), orthogonalVector, 0.5);
const posCreaseLeft = Util.addVector(Util.weightedMidpoint(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, 0.8), orthogonalVector, 0.5);
const posCornerLeft = Util.addVector(Util.weightedMidpoint(posPivotRight, posPivotLeft, 0.9), orthogonalVector);
context.moveTo(...posPivotRight);
context.lineTo(...posCornerLeft);
context.lineTo(...posCreaseLeft);
context.lineTo(...posPivotLeft);
context.lineTo(...posCornerRight);
context.lineTo(...posCreaseRight);
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}