sql-lock is a distributed lock manager for NodeJS, which works with the help of a MySQL Server.
There are a lot of use cases that require an exclusive access to a resource. In a distributed system, with several containers running the same piece of code in parallel, achieving this can get quite difficult.
sql-lock solves this problem, by allowing you to get distributed locks in your code from a MySQL server.
- On initialization it creates a table
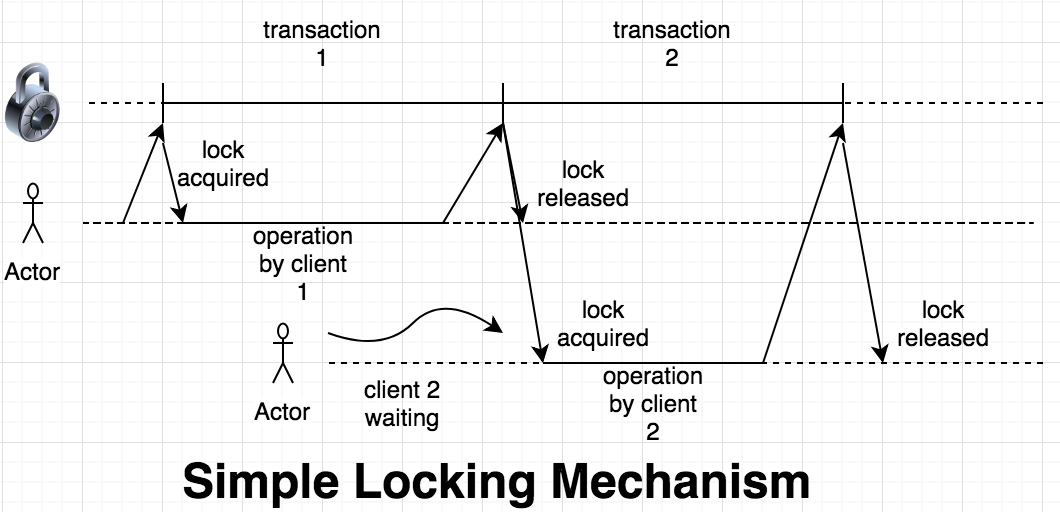
lockingscontaining a columnid. - Whenever someone tries to get a lock, a transaction is started in MySQL and an entry is created with
idequal to lock key. - This gives a row lock to the transaction, which prevents someone from trying to get the same lock again.
- To release the lock, the transaction is committed and the row deleted. Anyone else trying to get a lock with same lock key can then proceed.
- More information can be found in our blog posts -
- MySQL Server
- NodeJS > 6
npm install sql-lock
const sqlLock = require('sql-lock');
sqlLock.initialize(MysqlURI, { locking_ttl: 30000 });- MysqlURI - MySQL connection string - Eg
mysql://travis@127.0.0.1:3306/test. - Options:
- locking_ttl - Default timeout for your locks (in ms)
This will automatically create a table named locking in the database.
const sqlLock = require('sql-lock');
const lockReleaser = await sqlLock.getLock('lock_key', 3000);
await someAsyncWork();
lockReleaser(); //Release lockThis code gets a lock on the key lock_key which is released when either lockReleaser function is called or the lock times out.
If someone else tries to get a lock with the same key, they will have to wait till the first lock is released.
getLock accepts two parameters -
- lockKey: string - mandatory
- TTL: number - timeout in ms for the lock. If not given, the TTL given during initialization is considered as the timeout.
Contributions are welcome. Please create a pull-request if you want to add new features, test-support or enhance the existing code.