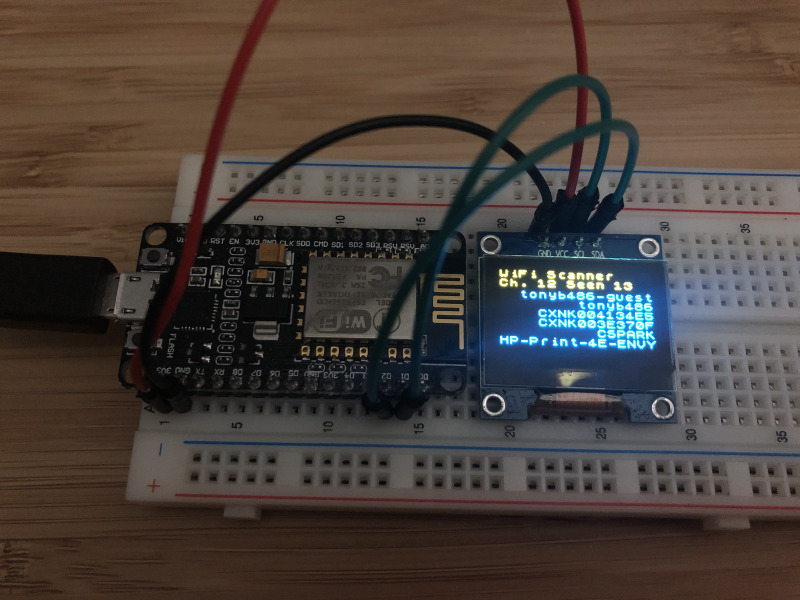
This is a little passive WiFi scanner for ESP8266 boards, specifically the NodeMCU (ESP-12E) with an inexpensive SSD1306-based OLED display.
It works by listening for 802.11 beacon packets on channels 1-14, extracting the ESSID and the BSSID, and sorting them based on RSSI.
It's different from a standard WiFi scan in that it doesn't send out inquiries, it just listens for those beacons that are already in the air, checking each channel in sequence.
The code is meant to be extremely simple, and was a way for me to learn the very basics of using an inexpensive ESP8266-based board, and the structure of an 802.11 beacon packet, which is parsed in the simpliest way possible, though not the most robust way.
This was inspired by the ESP8266 Mini Sniff project, which contains a far more complete 802.11 frame parser. I wound up writing my own parser for simplicity and as a learning exercise.
The little device itself is also useful in tracking down WiFi APs, as they're constantly being sorted by RSSI, making it possible to roam until the targeted network is first on the list.
I used the Arduino IDE to build and upload the code to the board. Configure the IDE to use the ESP8266 board type by following the instructions here.
Once you've added the board manager URL, installed the board in the board manager, and selcted the board type, in my case NodeMCU 1.0 (ESP-12E), you should be able to verify (compile) code, and upload it to the board.
Next, select "Include Library" from the "Sketch" menu, and add the "ACROBOTIC SSD1306" module. If you're using a different kind of screen, you'll need to modify the source code.
Finally, add the C code in sketch.c from this repository, upload, and run!