Schematics are generators that transform an existing filesystem. They can create files, refactor existing files, or move files around.
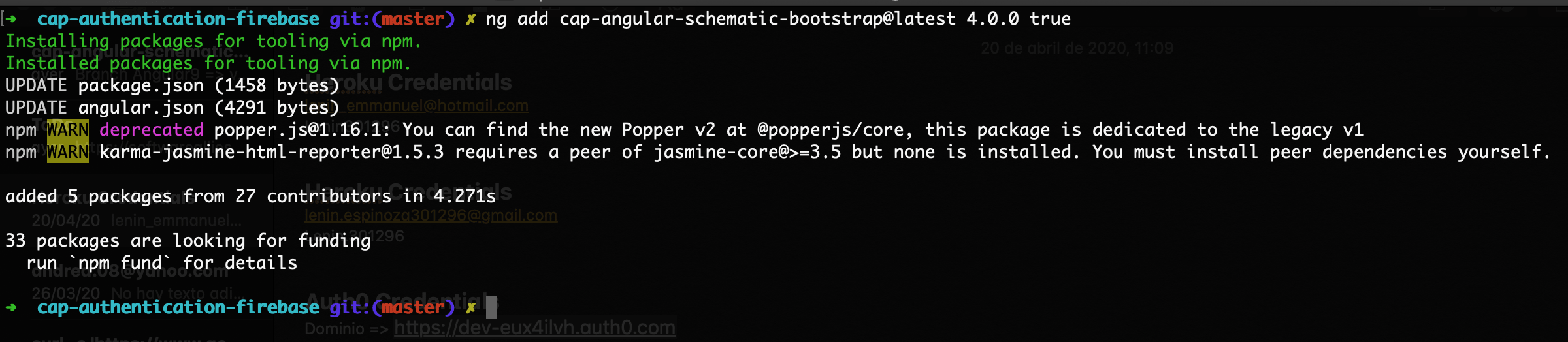
cap-angular-schematic-auth-firebase use bootstrap's classes, You can use a CAP product to configure and install bootstrap to your project the installation is as follows cap-angular-schematic-bootstrap.
ng add cap-angular-schematic-bootstrap@latest 4.0.0 true
To run the schematic you have to execute the following command on your terminal. Note the schematic only works within an angular project.
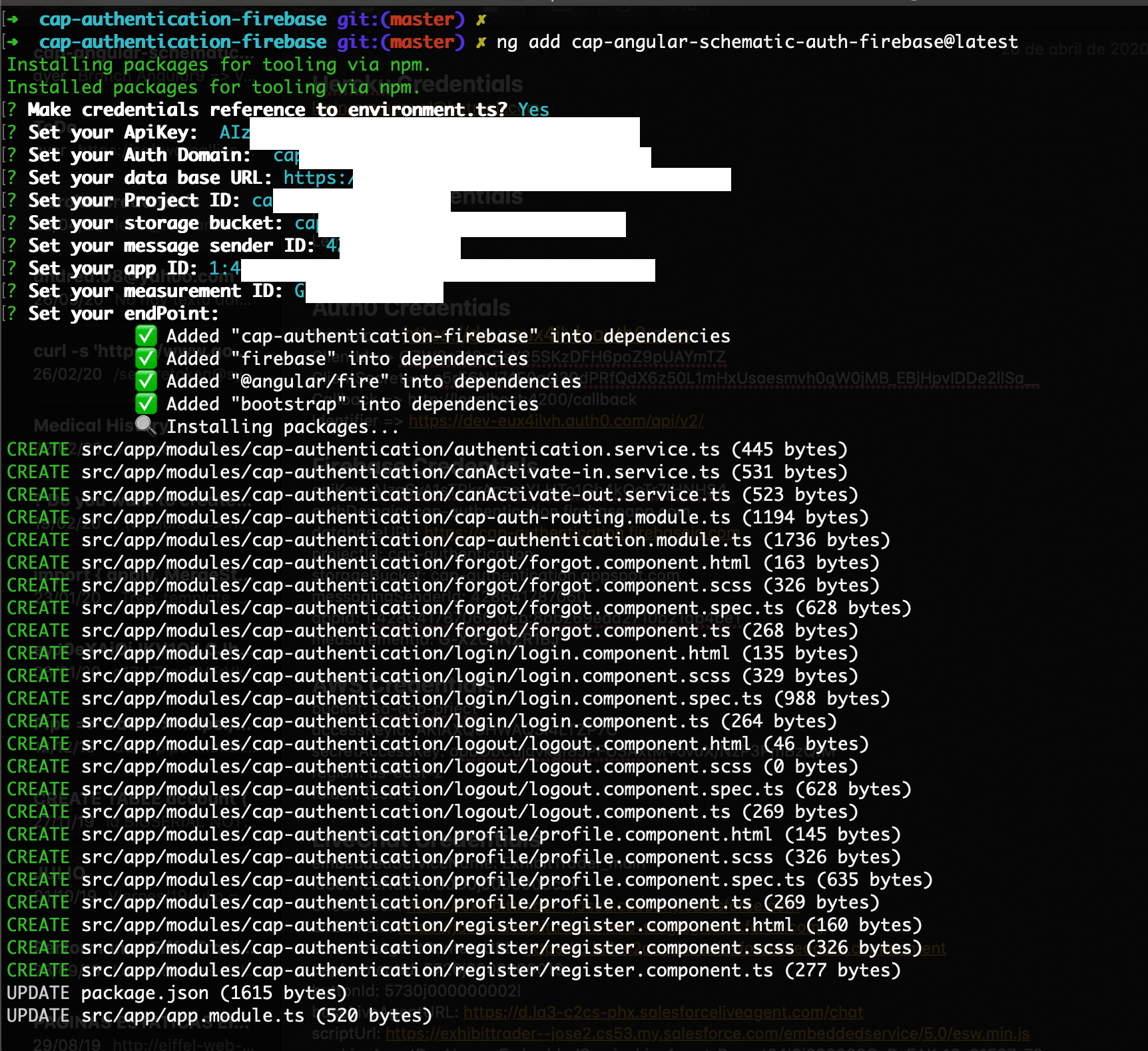
ng add cap-angular-schematic-auth-firebase
We must have previously created a project on Firebase platform and enabled authentication methods such as Email/password, Facebook and Google. We will need the credentials in our firebase application right away that the schematic will ask for
- Set your ApiKey: < your-ApiKey >
- Set your Auth Domain: < your-Domain >
- Set your data base URL: < your db-URL >
- Set your Project ID: < your-Project-ID >
- Set your storage bucket: < your-storage-bucket >
- Set your message sender ID: < your-sender-ID >
- Set your app ID: < your-app-ID >
- Set your measurement ID: < your-measurement-ID >
Next, the Schematic will create a component for each of the authentication actions along with the routing configuration.
modules
|
cap-modules
|-- forgot/
|-- login/
|-- logout/
|-- profile/
|-- register/
|-- routing.ts
|-- service.ts
|-- module.ts
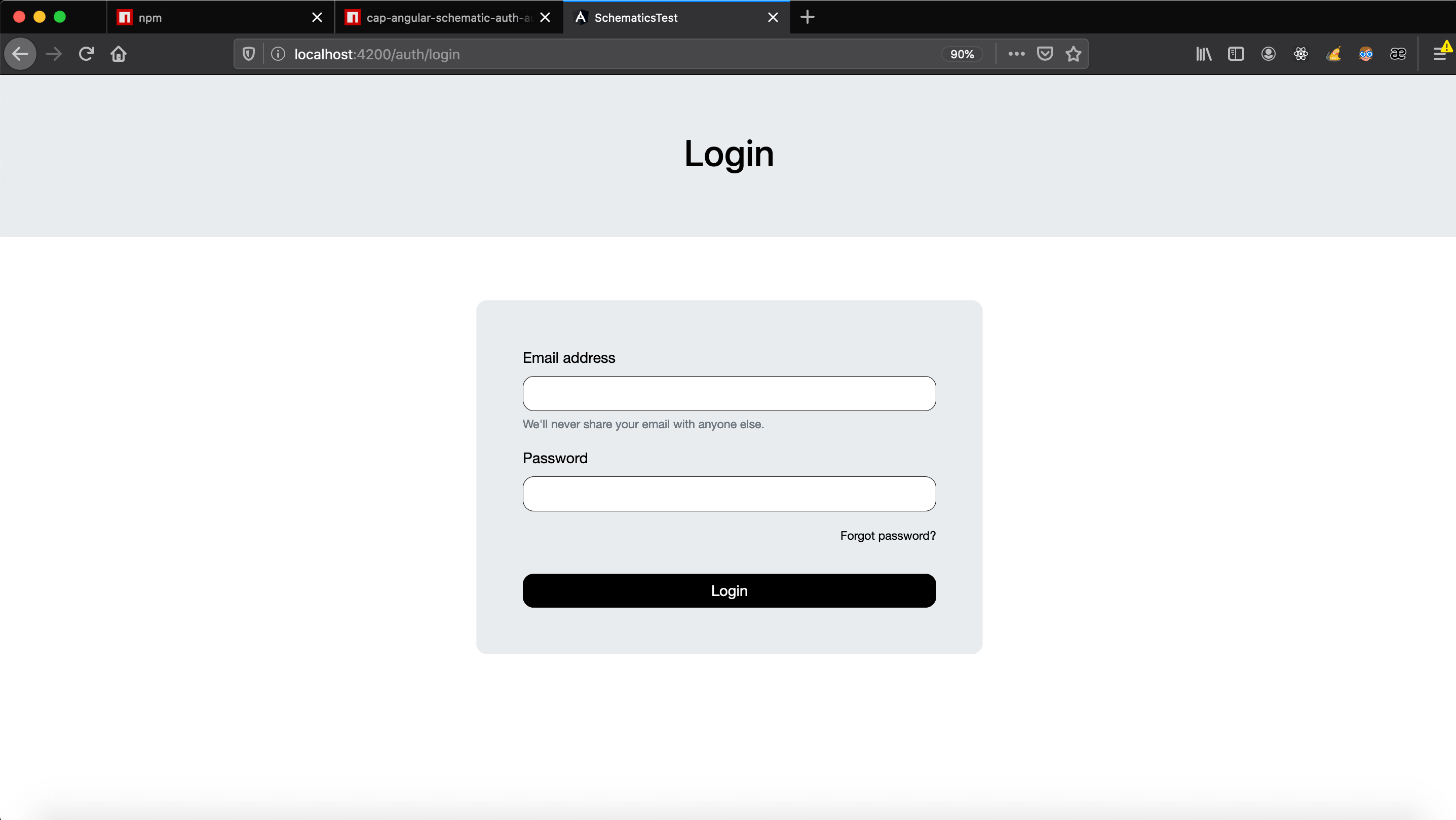
Now you can run your server from your angular project that we just modified and open the browser at http://localhost:4200/ and navigate on the different routes of the components of this schematic.
- Login
/auth/login
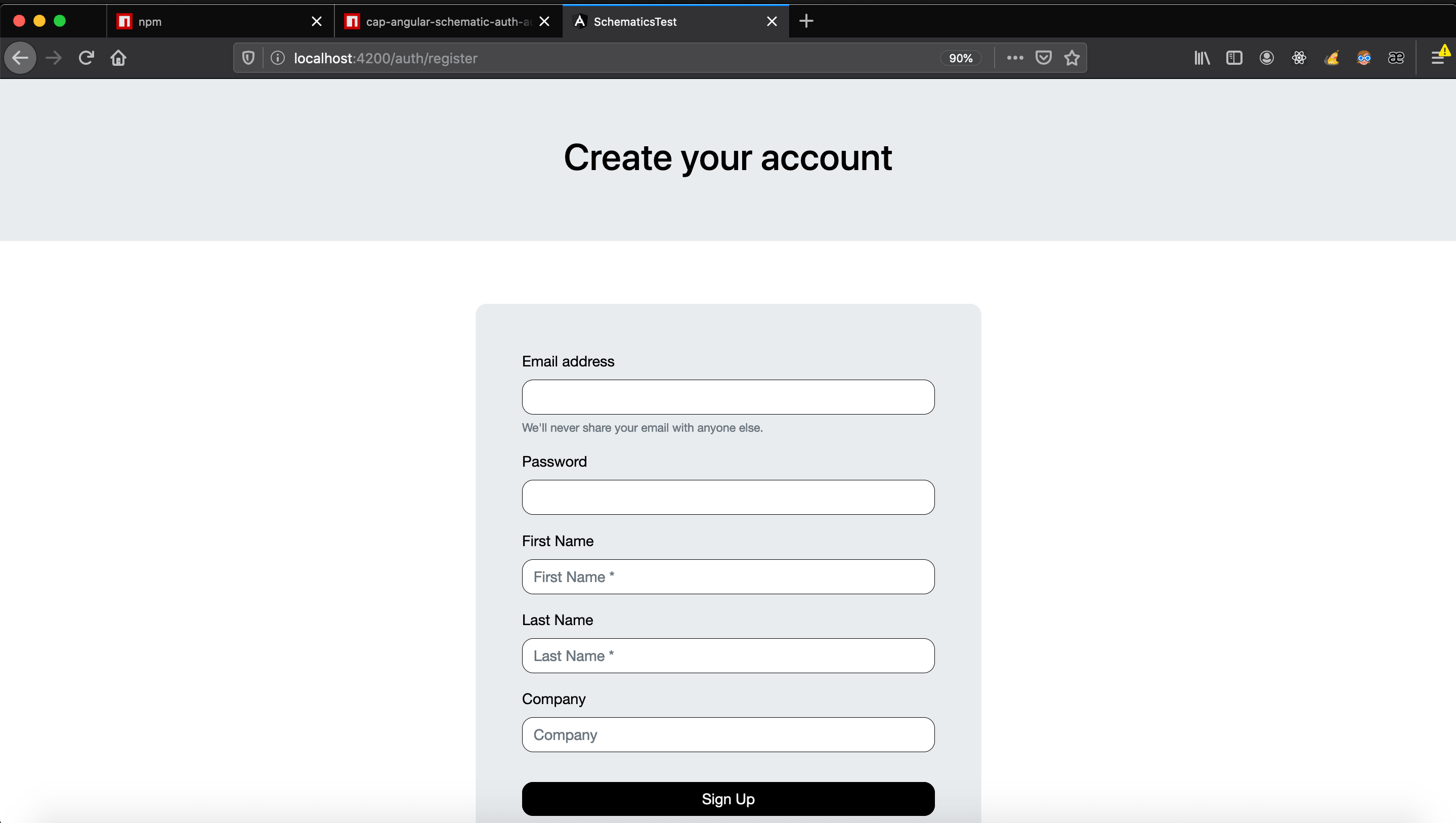
- Register
/auth/register
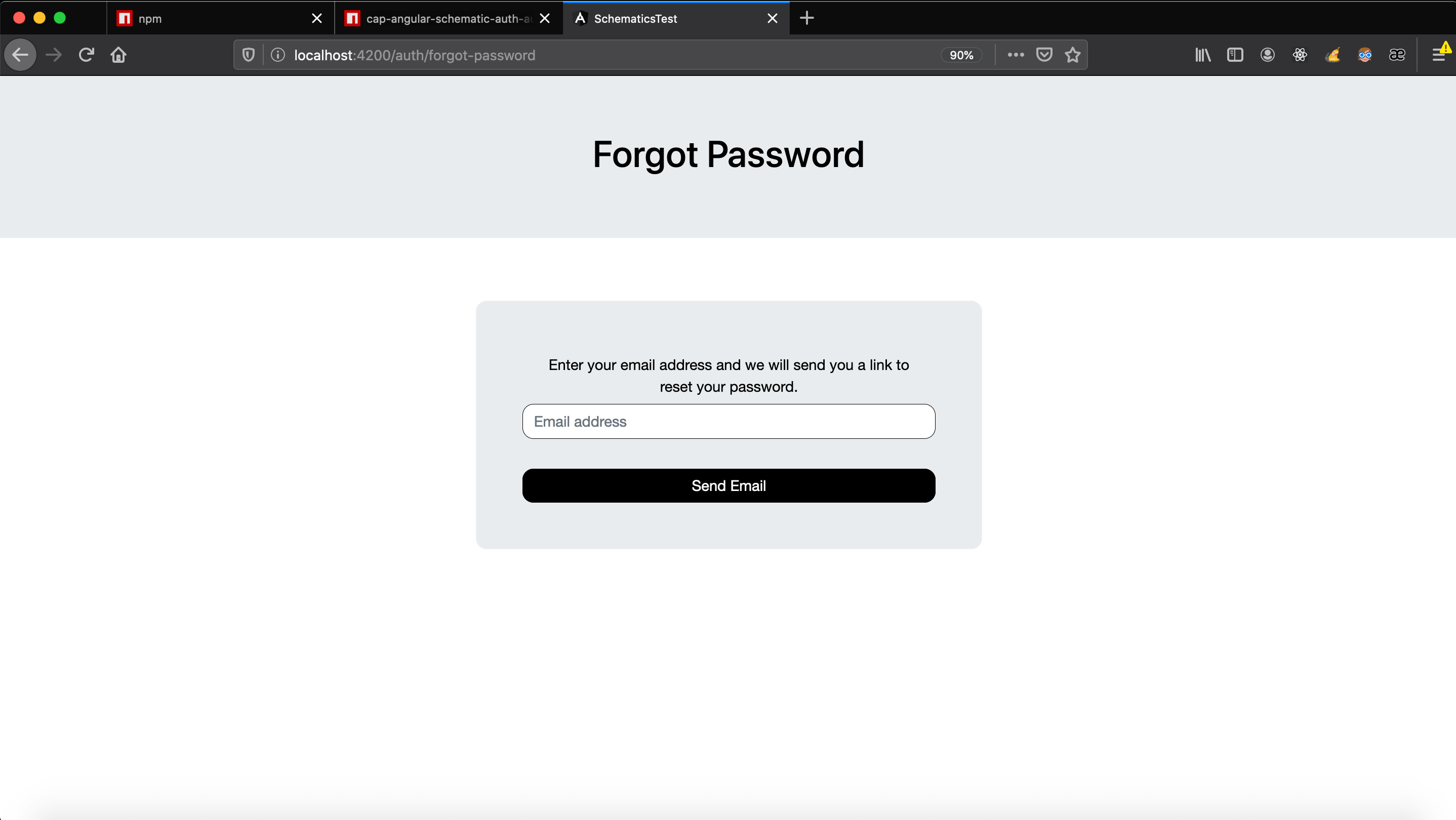
- Forgot
/auth/forgot-password
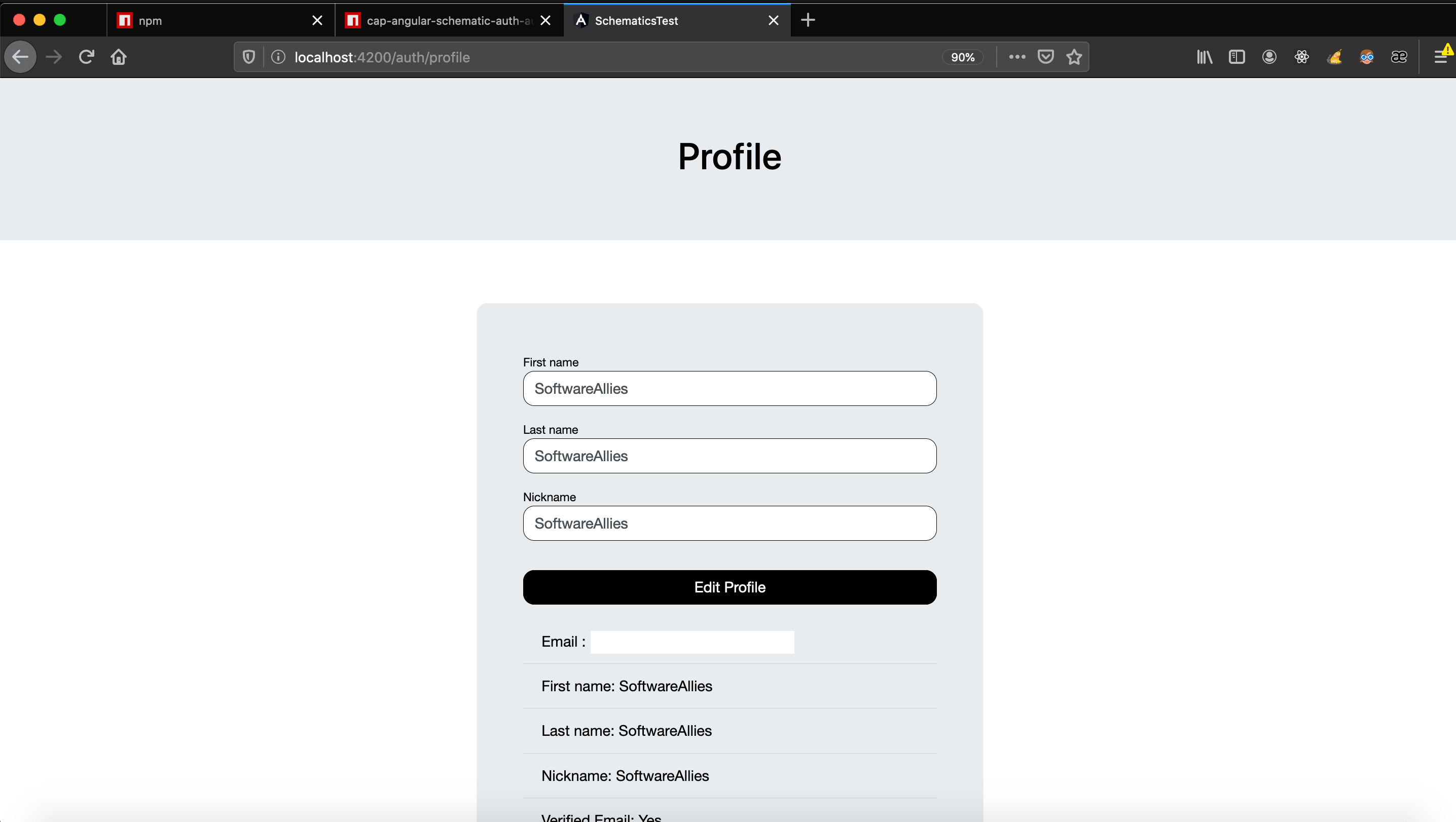
- Profile
/auth/profile
- LogOut function
import { AuthenticationService } from 'cap-authentication';
export class Component implements OnInit {
constructor (public authenticationService: AuthenticationService) { }
logoutFunction() {
this.authenticationService.signOut() // Return to home page
}
}
In order to edit and create classes that affect the components above, a class will have to be overwritten globally! all kinds and styles will have to go in the src/styles.scss file. with Pseudo-classes we will be able to modify the styles of the components, the component structure will be illustrated immediately to be able to access with scss each one of the nodes.
You can see an example of how to edit this module with your design styles.scss.
<div class="box">
<div>
<form>
<!-- Register -->
<!-- Login -->
<!-- Forgot -->
<div class="form-group">
<label></label>
<input class="form-control">
<small class="form-text text-muted"></small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label></label>
<input class="form-control">
<div class="form-control-feeback text-danger text-center">ErrorMessage</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group form-check">
<small class="form-text text-right">
<a routerLink="#"> goTo </a>
</small>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary btn-block"></button>
<!-- Register -->
<!-- Login -->
<!-- Forgot -->
<!-- Profile -->
<!-- Profile -->
<div class="row">
<div class="col-12">
<div class="form-group">
<small class="form-text"></small>
<input class="form-control"/>
<small class="form-text"></small>
</div>
<div class="form-control-feeback mb-2 text-success text-center">
</div>
<button class="btn btn-info btn-block btnSubmit"></button>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-12">
<ul class="list-group list-group-flush">
<li class="list-group-item">{{}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Profile -->
<!-- Profile -->
</form>
</div>
</div>