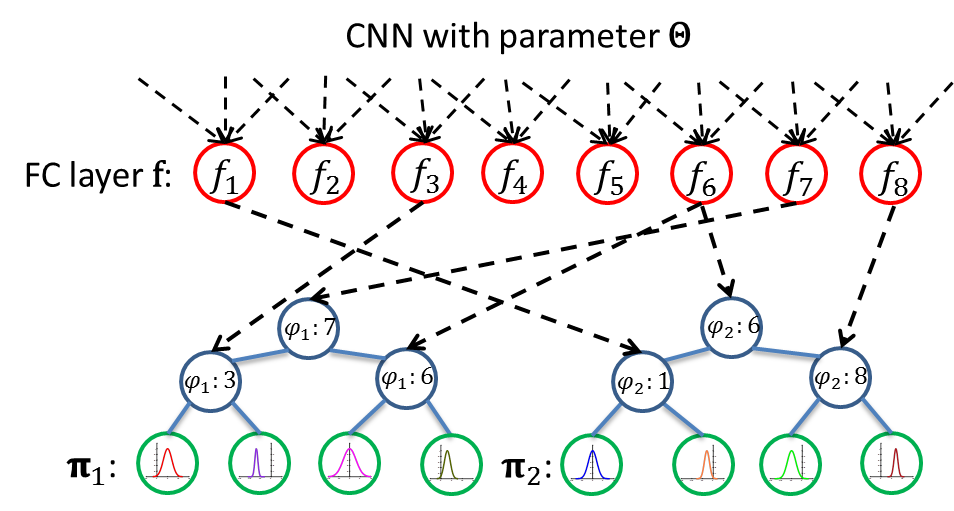
Age estimation from facial images is typically cast as a nonlinear regression problem. The main challenge of this problem is the facial feature space w.r.t. ages is heterogeneous, due to the large variation in facial appearance across different persons of the same age and the non-stationary property of aging patterns. In this paper, we propose Deep Regression Forests (DRFs), an end-to-end model, for age estimation. DRFs connect the split nodes to a fully connected layer of a convolutional neural network (CNN) and deal with heterogeneous data by jointly learning input-dependant data partitions at the split nodes and data abstractions at the leaf nodes. This joint learning follows an alternating strategy: First, by fixing the leaf nodes, the split nodes as well as the CNN parameters are optimized by Back-propagation; Then, by fixing the split nodes, the leaf nodes are optimized by iterating a step-size free and fast-converging update rule derived from Variational Bounding. We verify the proposed DRFs on three standard age estimation benchmarks and achieve state-of-the-art results on all of them. For detailed algorithm and experiment results please see our CVPR 2018 paper.
A quick demo of using the proposed DRFs for age estimation. In this example, we adopt VGG16 model and simply replace the softmax loss layer with the proposed DRFs. To run the demo, do the following steps:
-
Download the Morph dataset. The Morph dataset is not free availabel, but you can request for it from here.
-
Download pre-trained VGG model VGG_ILSVRC_16_layers.caffemodel.
-
Create a symbolic link to the Morph dataset with the name 'data/morph'
ln -s 'the absolute path for the Morph dataset' data/morph
or change the testdir and traindir in run.py. -
Create the train set list and test set list
python split.py -
Start training and testing
python run.py
If you have different Caffe version than this repo and would like to try out the proposed DRFs layers, you can transplant the following code to your repo.
(util)
- include/caffe/util/sampling.hpp
- src/caffe/util/sampling.cpp
- include/caffe/util/neural_decision_util_functions.hpp
- src/caffe/util/neural_decision_util_functions.cu
(training)
- include/caffe/layers/neural_decision_reg_forest_loss_layer.hpp
- src/caffe/layers/neural_decision_reg_forest_loss_layer.cpp
- src/caffe/layers/neural_decision_reg_forest_loss_layer.cu
(testing)
- include/caffe/layers/neural_decision_reg_forest_layer.hpp
- src/caffe/layers/neural_decision_reg_forest_layer.cpp
- src/caffe/layers/neural_decision_reg_forest_layer.cu
Tips:
- Make sure that the names of the NeuralDecisionRegForestWithLoss layer and the NeuralDecisionRegForest layer in the train_net and test_net prototxts are the same, so that the learned leaf nodes can be loaded in the testing stage.
- In our implementation, we use L2 norm as the loss function rather than the negative log likelihood loss described in the paper, to avoid observing negative loss during training (because probability density can be larger than 1). Since we assume each leaf node is a normal distribution, minimizing L2 norm is equivalent to minimizing negative log likelihood loss.
- In GPU code, we only implement the case that the target is one-dimensional data.
Please cite the following paper if it helps your research:
@inproceedings{shen2018DRFs,
author = {Wei Shen and Yilu Guo and Yan Wang and Kai Zhao and Bo Wang and Alan Yuille},
booktitle = {Proc. CVPR},
title = {Deep Regression Forests for Age Estimation},
year = {2018}
}
If you have any issues using the code please email us at shenwei1231@gmail.com, gyl.luan0@gmail.com