Human activity recognition is the problem of classifying a sequence of data from sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes etc. into well-defined movements. These sequences are generally recorded using specialized harness of sensors or by embedded sensors in smartphones. Sensor-based activity recognition integrates the emerging area of sensor networks with novel data mining and machine learning techniques to model a wide range of human activities.
Existing researches often use statistical machine learning methods to manually extract and construct features of different motions from time series data based on sliding windows of fixed sizes and then training machine learning models such as ensembles of decision trees. However, in the face of extremely fast-growing waveform data with no obvious laws, the traditional feature engineering methods are becoming more and more incapable. Additionally, Feature engineering required a lot of expertise in the field.
With the development of deep learning technology, we do not need to manually extract features and can improve the performance in complex human activity recognition problems. So, someone who is not an expert is the field of activity recognition could train a very good model to as it required no feature engineering. These models provided state-of-the-art results on very challenging activity recognition tasks.
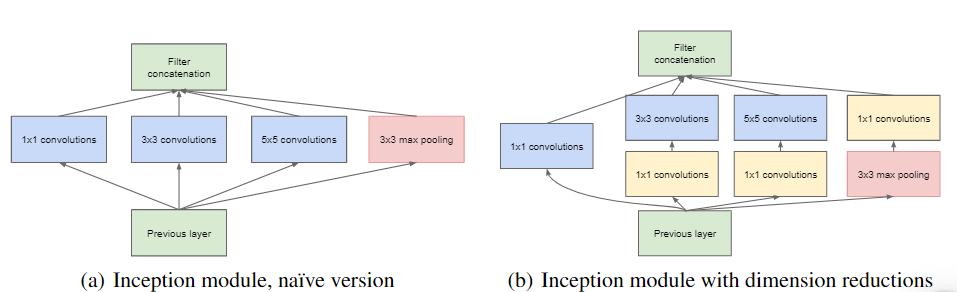
Google’s Inception Architecture based network was an important milestone in the development of CNN classifiers. Prior to its inception, most popular CNNs just stacked convolution layers of different kernel sizes deeper and deeper, hoping to get better performance. Using the Inception Architecture (defined int next section), Google created a deep Neural Network – GoogLeNet, which had far better performance than any CNNs available for Image Classification. This model was faster to train and had better performance than any available CNN architecture. This model was also able to go deeper than any other Network and thus can better extract features and classify Images. The InnoHAR model was inspired from the GoogLeNet Model Architecture. Like GoogLeNet, it tries to use Inception like architecture to achieve better performance in HAR problems.
The Inception-like module from section 3.3, are the building block of the InnoHAR model. Different layers are connected as follows in order to create the aforementioned model: • The Input layer is passed through three Inception-like modules. • After that we connect it with max-pooling layer to help the network better eliminate misjudgment caused by noise disturbance. • Then we pass it through another Inception module and a max pooling layer. • Finally, the output is passed through two GRU layers, so that the model can better extract the sequential temporal dependencies. • Then we’ll pass the output of GRU Layers through the SoftMax layer for classification.
This model basically works in two different parts: Spatial feature extraction and temporal feature extraction.
For Spatial feature extraction, the Inception-like module from previous section is used. In each Inception-like module, a 1x1 convolution kernel is used to directly activate the combination of multi-channel information and pass it to the next layer. Two convolution kernels of 1x3 and 1x5 are cascaded respectively by a 1x1 convolution kernel, and the feature information of different scales is extracted for the whole model. The output splicing with only 1x1 convolution, also produces a ResNet residual connection effect. At the same time, there is a 1x3 pooling layer followed by a 1x1 convolution kernel to provide feature enhancement and filtering. For temporal feature extraction, either LSTM (Long Short-term Memory) or GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) could have been used. Since GRU provides better time efficiency, GRU layers are used in this model. Two GRU layers are used to extract temporal data. Finally, a Dense layer with soft-max activation was added at last in order to classify the extracted features.
Note - I have just implemented this. I do not claim to have dveloped this architecture.