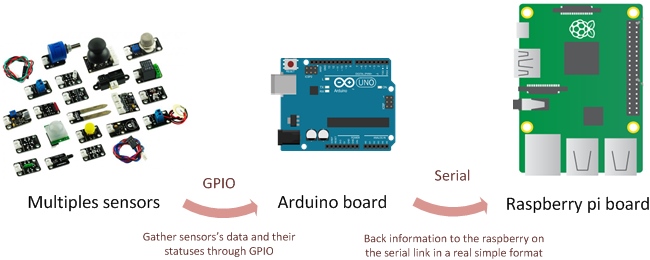
A very simple system of communication between Arduino and Raspberry using the serial to collect data from several sensors.
// Required library
#include <Arduilink.h>
// Unique identifier of the node
#define NODE_ID 0
// Create the link
Arduilink link = Arduilink(NODE_ID);
// Setup function
void setup()
{
// Declare several sensors
link.addSensor(1, S_INFO, "Temperature sensor (DHT)", "celcius degree");
link.addSensor(2, S_INFO, "Humidity sensor (DHT)", "percent");
// Start serial link
Serial.begin(9600);
link.init();
}
// Loop function
void loop()
{
link.setValue(1, mySensor.getTemperature());
link.setValue(2, mySensor.getHumidity());
sleep(5000);
}
// Serial events
void serialEvent()
{
lnk.handleInput();
}Once the Arduino is connected, the python service can be started . This server will connect permanently to the serial link, to be ready to read and write information to the Arduino. After starting the server, the client enables notably to gather the value of a sensor.
$ sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0
$ sudo ./arduilink_server.py --file /dev/ttyUSB0 --rate 9600 --port 900 &
Socket: listening on port 900 ...
Serial: connected on /dev/ttyUSB0 (9600)
Serial: device is ready
$ ./arduilink_client.py --port 900 --get 2
35.05The serial protocol used between the Gateway and the Controller is a simple semicolon separated list of values.
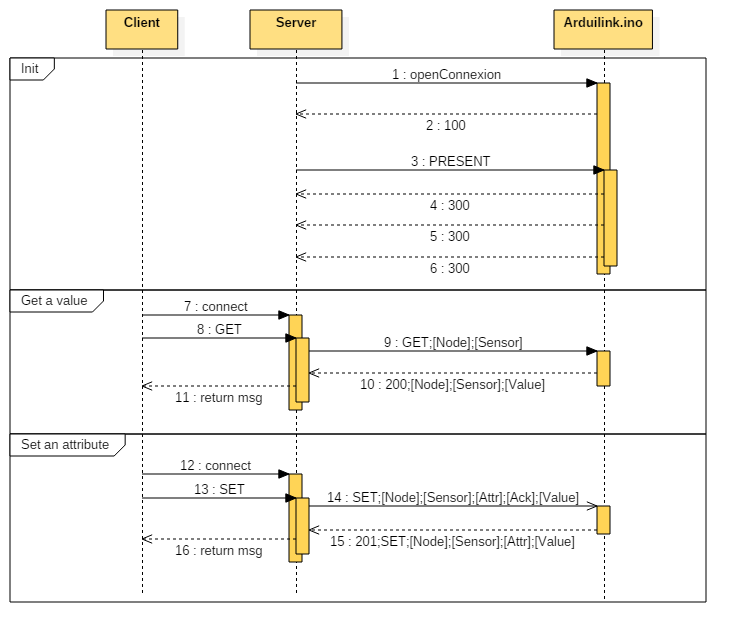
When you just get connected to serial link, the arduino will send a welcome message:
#####100;node-id;protocol-version\n
Then, the arduino can send a description of all connected sensors:
#####300;node-id;sensor-id;sensor-flags;sensor-unit;sensor-verbose-attribute;sensor-name\n
Each time a sensor has a new value, the following is sent:
#####200;node-id;sensor-id;data-value\n
Ask the arduino to present all his sensors:
#####PRESENT;node-id\n
Ask a description of a given sensor:
#####INFO;node-id;sensor-id\n
Gather the value of a given sensor:
#####GET;node-id;sensor-id\n
Change an attribute of a given sensor:
#####SET;node-id;sensor-id;attribute-name;ack;attribute-value\n
The arduino can answer with the following codes. If a SET command is succesfull the response will be:
#####201;node-id;sensor-id;attribute;new-attribute-value\n
If an error occures, the following response can be returned if the attribute is not recognized:
#####400;ATTR;invalid-attribute-name;\n
And the following if the attribute's value is not a valid option:
#####400;OPT;invalid-attribute-name;invalid-attribute-value\n
Finally, for each command, you can get 404 errors:
#####404;NODE;node-id\n
#####404;SENSOR;sensor-id\n
You have to create sensors in the embedded arduino code, in the setup function.
public void Arduilink::addSensor(uint id, uint flags, char* description, char* unit);The following flags are allowed:
| Flag | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| S_INFO | The sensor is able to return the current value (with GET action) | 1 |
| S_HIT | The sensor is able to send heartbeats each time a measure is recorded | 2 |
| S_ACTION | The sensor is able to receive custom actions like switching on/off | 4 |
| S_BATTERY | The sensor is able to gather his own battery level | 8 |
Unit value is an arbitrary string; you must specify a coherent unit according to the measured physical quantity.
| Type | Physical quantities | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Other | Digital value (State) | boolean, unitless |
| Other | Analogic value (Dimmer) | numeric value, unitless |
| Base | Length | meter (m) |
| Base | Mass | kilogram (kg) |
| Base | Time | second (s) |
| Base | Temperature | kelvin (K), degree celcius (C°) |
| Base | Amount of substance | mole (mol) |
| Derived | Luminous intensity | candela (cd) |
| Derived | Angle | radian (rad), degrees (°) |
| Derived | Frequency | hertz (Hz) |
| Derived | Force, weight | newton (N) |
| Derived | Pressure, stress | pascal (Pa) |
| Derived | Energy, work, heat | joule (J) |
| Base | Electric current | ampere (A) |
| Derived | Electric power | watt (W) |
| Derived | Electric charge | coulomb (C) |
| Derived | Electric potential difference | volt (V) |
| Derived | Electric capacitance | farad (F) |
| Derived | Electric resistance, impedance | ohm |
| Derived | Electric conductance | siemens (S) |
| Derived | Magnetic field | weber (Wb) |
| Derived | Luminous flux | lumen (lm) |
| Derived | Luminous intensity | lux (lx) |
| Derived | Area | length * length |
| Derived | Volume | length * length * length |
| Derived | Speed | length / time |
| Derived | Angular moment | mass / time / angle |
| ... | ... | ... |