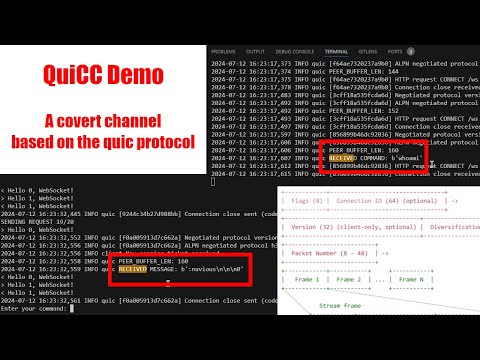
Covert channels are means of transmitting information in a clandestine way that are not observable by a passive warden and are resistant to intercept or disruption by an active warden.
This covert channel is implemented using the quic protocol defined by RFC 9000 and RFC 9369 by exploiting high entropy header fields. In this implementation the connection id field is specifically targeted with future work to utilize other high-entropy header fields.
NOTE: In the above demo the RSA bit strength is set to 1024. This was done only to speed up implementation and debugging execution during development of the project. The implementation at time of writing defaults to 4096 bit RSA.
First build the container:
sudo docker build -t quicc .Next create a network:
sudo docker network create quiccNext run the server:
sudo docker run --rm -it --name quicc --network quicc quicc \
python3 http3_cc_server.py \
--certificate aioquic/tests/ssl_cert.pem \
--private-key aioquic/tests/ssl_key.pemFinally run the client:
sudo docker run --rm -it --network quicc quicc \
python3 http3_cc_client.py \
--ca-certs aioquic/tests/pycacert.pem \
wss://quicc:4433/wsgit clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/nuvious/QuiCC.git
cd QuiCCFor the HTTP server and client examples provided by the aioquic library, the requirements are not included in the package dependencies so we have to install them manually.
sudo apt install build-essential libssl-dev python3-dev
pip3 install aioquic/ dnslib jinja2 starlette wsprotopython3 http3_cc_server.py \
--certificate aioquic/tests/ssl_cert.pem \
--private-key aioquic/tests/ssl_key.pempython3 http3_cc_client.py \
--ca-certs aioquic/tests/pycacert.pem \
wss://localhost:4433/wsNOTE: If running the client and server on separate hosts, replace localhost
with the DNS entry; in this example quicc.local.
On both the client and server you should be presented with this prompt:
Welcome to the QuiCC console.
Enter 'm:[MESSAGE]' to send a message.
Enter 'c:[COMMAND]' to send a remote command.
Enter 'f:[FILE]' to send a file.
Enter 'k' to send a keepalive message to recieve responses.
Enter 'q' to quit.
Enter your command:Typing a command m:hi should produce the following output on the server
logs:
2024-07-12 01:06:01,587 INFO quic RECEIVED MESSAGE: b'hi'Typing a command f:test_file.txt should result in the following output on the
server logs:
RECEIVED FILE SAVED TO: ::ffff:127.0.0.1-message-1.binThe ::ffff:127.0.0.1-message-1.bin should hold the contents of test_file.txt
Typing a command c:whoami should result in the following output on the
server logs:
2024-07-12 01:11:09,287 INFO quic RECEIVED COMMAND: b'whoami'At this point stdout and stderr will be queued to be sent back but we need
to send requests to get CIDs sto decrypt the output. To do this simply use
the command k and a keep-alive message will be sent and the result of
the command should appear in the client logs:
2024-07-12 01:12:44,387 INFO quic RECEIVED MESSAGE: b':nuvious\n\n\n0'If you're running the server on a separate machine, you'll need to change out
the example key and cert used by the server to ones that match your server
host domain. You'll need to add a entry to the dns record for the ip used; in this
case I used quicc.local.
On the server run the below in the root of the project:
openssl genrsa -out ca-key.pem 4096
openssl req -new -x509 -days 365 -key ca-key.pem -out aioquic/tests/pycacert.pem -subj '/CN=QuiCCA'
openssl genrsa -out aioquic/tests/ssl_key.pem 4096
openssl req -new -key aioquic/tests/ssl_key.pem -out csr.pem -subj '/CN=quicc.local' -nodes
openssl x509 -req -in csr.pem -out aioquic/tests/ssl_cert.pem \
-CA aioquic/tests/pycacert.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -days 3650 \
-extfile <(printf "subjectAltName=DNS:quicc.local\nkeyUsage=digitalSignature,keyEncipherment\nextendedKeyUsage=serverAuth,clientAuth\nbasicConstraints=CA:FALSE\nsubjectKeyIdentifier=hash\nauthorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer\nauthorityInfoAccess=caIssuers;URI:http://testca.pythontest.net/testca/pycacert.cer,OCSP;URI:http://testca.pythontest.net/testca/ocsp/\ncrlDistributionPoints=URI:http://testca.pythontest.net/testca/revocation.crl")You'll then need to copy over the pycacert.pem and replace the
aioquic/tests/pycacert.pem file with it on the client machine.
Known issues for this implementation of the covert channel are documented in the Github Issues section of this repository. If you find a vulnerability in this project related to intercept, disruption or denial of service that may be mitigated, feel free to open up an issue and/or contribute to the project.