We are a team of four seniors in the Houston Baptist University Class of 2022 from the College of Science and Engineering. Our team is comprised of two Electrical Engineering majors, one Computer Science major, and one Cyber Engineering major.
Delivery robots have been around for years and some college campuses and small towns utilize them for food and mail deliveries. However, most of these places are sponsored by the robotics company and do not actually purchase the robots themselves due to the high cost for even just a single unit.
We wanted to create a system that improved upon existing delivery robots on three ways:
-
COST: Competitors' (like Starship Industries) robots cost ~$5500, we wanted ours to stay below $1000
-
REPAIRABILITY: We wanted our robot to be easy to repair using off-the-shelf and inexpensive components
-
UPGRADEABLE: We wanted our robot to have code that can easily be upgraded to add new features or simply be modified to integrate in with existing food ordering services at the deployed location
Our complete PDF writeup of this project can be found here
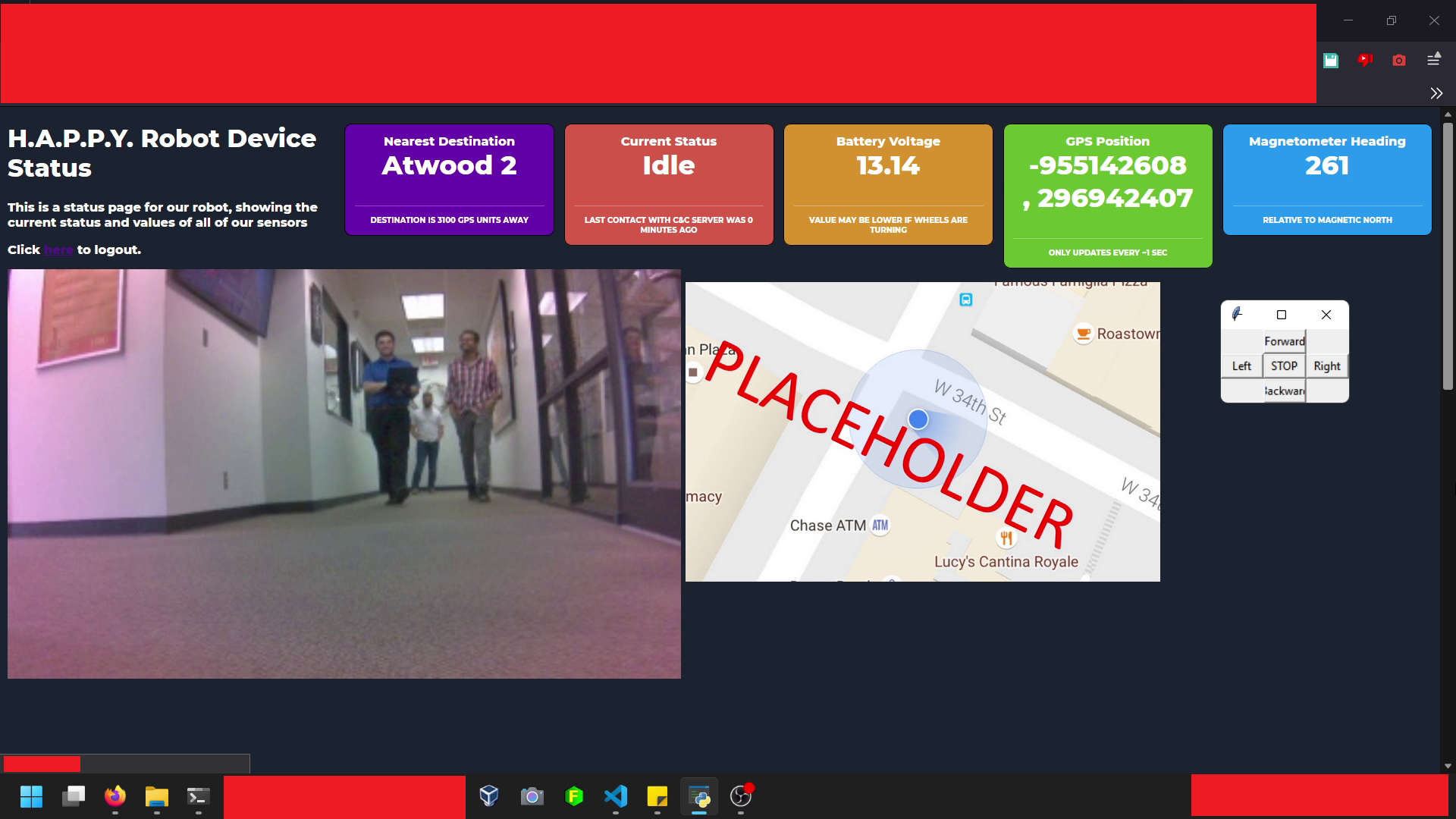
Below is a screenshot of the web UI that runs on the robot to show the current camera view and the status of all connected sensors
Below is referenced pertaining to our code
Computer Vision code based off samples found here: https://github.com/dusty-nv/jetson-inference/
I2C and PCA9685 code based off documentation here: https://www.jetsonhacks.com/2019/07/22/jetson-nano-using-i2c/
Magnetometer code working based off documentation here: https://tutorials-raspberrypi.com/build-your-own-raspberry-pi-compass-hmc5883l/
Full documentation on Wayback Machine: http://web.archive.org/web/20160503183933/http://think-bowl.com/raspberry-pi/i2c-python-library-3-axis-digital-compass-hmc5883l-with-the-raspberry-pi
Drive code is written in Python 3 and uses the adafruit_servokit library. Command to install the library is below:
pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-servokit
Serial communication utilizes pyserial which can be installed using the following command:
sudo apt-get install python3-serial
BEFORE RUNNING CODE, confirm persmissions for serial are set to all by running the following command:
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyACM0
You cannot simply run the code as root because the i2ctools Python library is not recognized if the script is run as root
I2C devices connected can be listed by address by running the following command:
i2cdetect -y -r 1
Web UI is python utilizing the Flask framework and turbo flask plugin, both of which can be installed by running the following command:
pip3 install flask turbo-flask
Camera streaming to web UI is performed using opencv. However, the OpenCV version available for download for python does not work, and you must compile from source (takes about 8 hours on the Jetson Nano) using the bash script included in the repository (deprecated folder)
Analog to Digital converter requires the Adafruit Circuitpython library to run, install via this command:
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-ads1x15
LED Status bar needs an adafruit library, install via this command:
pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-ht16k33
Currently, the web UI and RC code will not run in the same code, so you can run them separately by using the commands stored in "startupcommands.txt"
...and you can kill all python processes with the following command:
sudo pkill python
Unfortunately, we were unable to finish autonomous driving by the time our project was finished. However, we were able to successfully get our robot to navigate using remote control and detect people using the Nvidia Jetson Inference libraries.
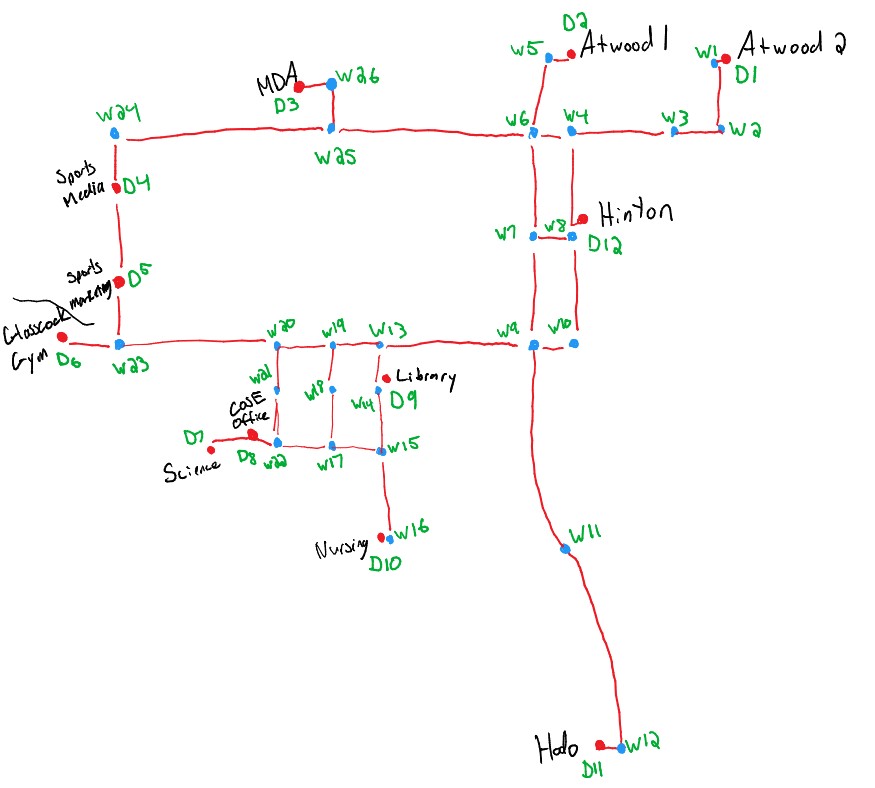
We were hoping to create the navigation algorithm by storing a list of waypoints and essentially use them as virtual "beacons" that the robot will drive between. Below is the map of paths on campus with waypoints (W##) and destinations (D##) labeled.
Hopefully the next generation of students at HBU will be able to pick up where we left off and improve this robot beyond our original goals!