- Category Chosen: Data Concierge https://2017.spaceappschallenge.org/challenges/ideate-and-create/data-concierge/details
- Goal: Facebook chatbot to automate earth data processing pipelines all the way from looking for datasets to visualising them with graphs
- End-Product: Apollo-bot is a smart AI Chatbot designed to lower the barrier of entry to NASA Earth data.
- Apollo-bot Facebook Messenger App UI https://www.facebook.com/Apollo-bot-1797571867226705/
- Go to "About". Click "Send Message"
- Apollo-bot Facebook Messenger Developer Admin https://developers.facebook.com/apps/154496488416785/messenger/
- Token (Page Access)
- Webhook
- Apollo-bot Facebook Chat Demo
- Apollo-bot Facebook Messenger App UI https://www.facebook.com/Apollo-bot-1797571867226705/
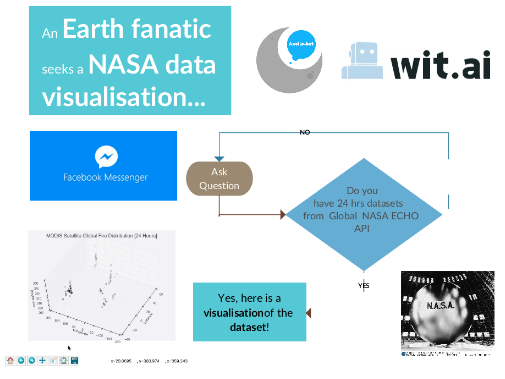
* Apollo-bot flow diagram of User-Bot conversation
* [Apollo-bot Presentation Slides](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ltfschoen/Apollo-bot/master/presentation/Apollo-bot_Presentation.pdf)
- Benefits and Judging Criteria:
- - Technical:
- - Cleverly addresses challenge in new way
- - GitHub file includes code
- - Level of project maturity and game-changing potential
- Ready to scale
- - Product Design for future plans on project page for the Best Mission Concept award
- - Storytelling:
- - Project page complete
- - Team explains story of solution in an attention grabbing, authentic, and passionate fashion
- - Story explained communicates why the team is special
- - Story explained provides context (not necessitating a reviewer to have to refer to documentation to understand)
- - Reflect the team's personality in the story
- - Galactic Impact:
- - Solution with most potential to improve life on Earth or in the universe.
- - Most Inspirational:
- - Solution that captures our hearts.
- - People’s Choice:
- - Solution voted for the most by Earthlings on social media.
- - Best use of data:
- - Solution that best makes space data accessible, or leverages it to a unique application
- - Best use of hardware: The solution that exemplifies the most innovative use of hardware.
- - Best mission concept: The solution with most plausible solution concept and design.
- - Impact (possible for this project)
- - Quality:
- Fast access to NASA data.
- Automated search and discovery of NASA data. Machine learning tool that trains and learns with usage to improve confidence in its accuracy with its design using Wit (built with NLU algorithms upon proven Facebook technologies including Facebook's AI and NLP platforms: DeepText and FBLearner Flow) that integrates with Facebook's Messenger API and GUI.
- Automated consolidation and visualisation of NASA data response using data science.
- Integrated social media sharing of NASA data response.
- - Quantity and Scalability:
- Immediate improvement in accessing NASA's Earth science datasets and resources
- Accessible to new consumers and enthusiasts on Facebook
- - Scalable
- Potential to bring change since scalable across other all NASA datasets and resources
- Potential to shift behaviour of consumers through accessibility and engagement
- Potential to address environmental issues through less time consuming and therefore energy consuming search and discovery of NASA data to expand audience and allow rapid mitigation.
- Potential for project to advance the state of AI and ML technology adoption
- - Quality:
- - Creativity
- Approach creative
- Engaging experience with intuition of user intent by using machine learning to help
- Delivers response using data science visualisations
- - Product
- - Usefulness of the tool and data and resources that it captures is determined based on recording the frequency that different branch pathways are used by consumers as a means of assessing user feedback and identify areas for improvement
- - Consider perspectives and user flows of various professionals, outdoor enthusiasts, and those with specific curiosities, and the types of information they would be interested in (i.e. datasets, images, articles)
- - Helps users with their searches with suggestions that identify which datasets and resources are useful to them and how to access them
- Fits the challenge needs by offering consumers and enthusiasts an engaging automated and accessible interface to NASA datasets and resources
- User-friendly technology integrated into Facebook to allow two-way voice interaction across all devices
- Complete solution ready to use and ready to scale
- - Sustainability
- - Organised using open source Scrum Project Management (issues track using backlog, ready, in progress, done status) using Waffle.io and linked with GitHub repository accessible to the team and other contributors
- - Users may create and customise their own custom Wit.ai Flow code and generate new server-side action functions
- - Landing page with .co domain name with hosting and email to register users prior to Facebook app approval
- - Presentation
- - Team communicates project story and its importance at Space Apps 2017
- Story - Lower the barrier of entry to discover NASA earth data
- Importance
- Improves accessibility to educational and resource data (communication between Earth science data enthusiasts and consumers with terabytes of NASA's Earth science datasets and resources obtained from 18 satellites and 3 instruments aboard the ISS)
- Connects and engages user interests and establish statistics on user interest across data sets
- - Added Team members to Google Spreadsheet
- - Team communicates project story and its importance at Space Apps 2017
- - Technical:
- Key Features:
- Wit.ai Natural Language Processing (NLP) Flow code
- Wit.ai server
- Facebook integration of Bot is automated and interactive
- Bot response text-to-speech conversion
- Bot response data visualisation
- "Humour percentage" adjustment maintains user engagement with random NASA jokes
- TODO
- - Review 30-second pitch guide https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B29cHowEF59OWmNhOU9pNGhsYjQ/view?pli=1
- - Tweet organisations and hashtags - @spaceappssydney @nasaspaceappssydney @dotCO @academyxi @NASAKennedy @BlueChilliGroup @CityConnectBC @coderfactory @UTSEngage @canva @awscloud #nasaapps #SpaceApps #SpaceAppsSydney
- - Update Team Project Page on Space Apps Sydney 2017 website
- - Upload work to GitHub repository
- - Submit project at to Space Apps Project Page
- Setup
-
Show Project dependencies. Install dependencies
pip freeze > requirements.txt pip install -r requirements.txt -
Editor IDE
- Recognise .py files on Mac
- Press
CMD + ,, go to Editor > File Types, Add *.py
- Press
- Fix any errors
- Go to File > Project Structure, Click "Problems", Click "Fix"
- Recognise .py files on Mac
-
Facebook Messenger Config
- Create Facebook Page for the Apollo-bot https://www.facebook.com/Apollo-bot-1797571867226705/
- Login to Apollo-bot app at https://developers.facebook.com/apps/154496488416785
- Go to Products > Messenger > Settings
- Go to "Token Generation", Select "Apollo-bot" from drop-down associated with its Facebook Page
- Copy the generated Page Access Token and check it matches with value in .env file for key FACEBOOK_MESSENGER_PAGE_TOKEN
- Go to "Webhooks"
- Click "Edit events", ensure "messaging", "message_deliveries", "messaging_optins" and "messaging_postbacks" is selected.
- Click drop-down to subscribethe Webhook to page events and select "Apollo-bot"
- Go to Products > Webhooks
- Click "Edit Page Subscription"
- Replace with Apollo-bot production server URL
- i.e. Jarryd's https://apollobot3.herokuapp.com/
- OR Lukes https://apollo-bot-server.herokuapp.com
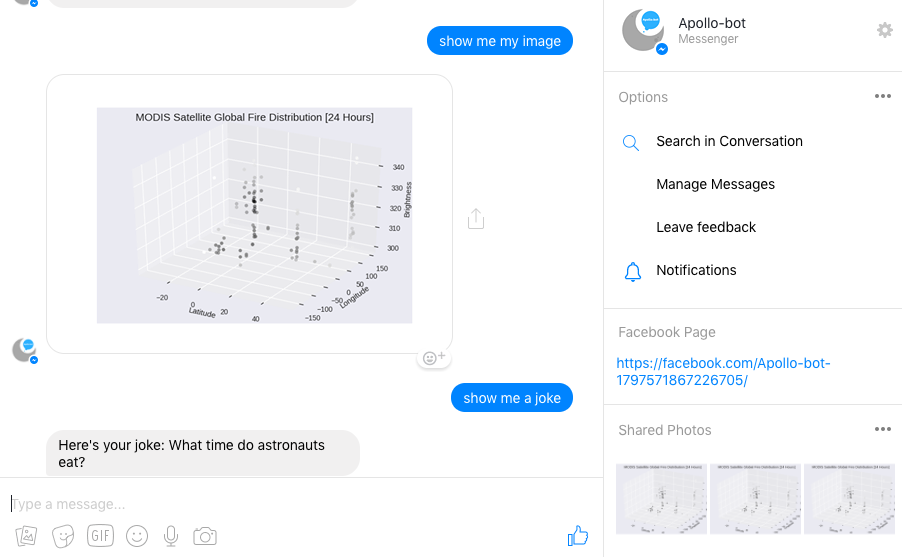
show me my imagereturns pre-made seaborn plot (image) in response to user message. It does this by returning the image when the server detects the text matchesshow me my image(not due to Wit.ai story)show me a jokereturns a joke (due to Wit.ai story)
- OR Ngrok address (see pre-deployment testing)
- Add Verify Token of "facebook_verify_token", and ensure this value matches in apollobot.py comparison of "hub.verify_token"
- Replace with Apollo-bot production server URL
- Click "Edit Page Subscription"
-
Pre-Deployment Testing
- Download https://ngrok.com/
- Run Flask app using local server at http://127.0.0.1:5000/
export FLASK_APP=apollobot.py flask run # python -m flask run
-
Deployment
heroku login # Create Heroku App at https://apollo-bot-server.herokuapp.com/ # Add Python Buildpack https://github.com/heroku/heroku-buildpack-python # Add Buildpack to allow a list of apt packages to be installed from Aptfile # Show list of installed Buildpacks # Note: Order of execution of the Buildpack is given by the index argument heroku apps:create apollo-bot-server --stack cedar --region us; \ heroku buildpacks:set --index 1 heroku/python; \ heroku buildpacks:set --index 2 https://github.com/heroku/heroku-buildpack-apt; \ heroku buildpacks; # Add .env keys and values to Heroku config vars heroku config:add ROOT_URL=https://apollo-bot-server.herokuapp.com; \ heroku config:set FACEBOOK_MESSENGER_PAGE_TOKEN=""; \ heroku config:set WIT_AI_APP_SERVER_ACCESS_TOKEN=""; \ heroku config:set FACEBOOK_MESSENGER_VERIFY_TOKEN=""; # Add and show Heroku App config heroku config --app apollo-bot-server --json # Show tracked remote repositories git remote -v # Push latest changes (from relevant branch) git push heroku master # Or for pushing specific local branch to Heroku master git push -f heroku yourbranch:master # Restart server if necessary heroku restart # Watch Heroku production server logs heroku logs --tail --app apollo-bot-server # Login to Heroku production server for debugging heroku run bash --app apollo-bot-server # Update the Callback URL and Verify Token in Webhooks on Facebook Developer (if not set yet) -
Other options (NOT WORKING)
-
Gunicorn local server
-
Go to File > Other Settings > Default Settings > Build, Execution, Deployment > Python Debugger
- Select the checkbox "gevent compatible debugging"
-
Go to "Edit Configurations", Create new Python config and call it "gunicorn".
- Add "Script" /Users//miniconda3/bin/gunicorn
- Add "Script Parameters" of "-b 127.0.0.1:5000 apollobot:app", where the host and port matches the server address defined in apollobot.py, and where "apollobot" refers to primary starting script apollobot.py, and where "app" is what to refer to it as. This will for gunicorn to bind to all IPs on your machine on port 5000
- Set the "Working Directory" to /Users//code/Apollo-bot instead of /Users/Ls/miniconda3/bin
-
-
Ngrok tunnel
- Ensure that Flask web server is running at 127.0.0.1:5000
- Exposing port to public internet with
./ngrok http 5000. The "Forwarding" address points to 127.0.0.1:5000. - Go to the "Forwarding" address (i.e. https://[generated_id].ngrok.com)
- Go to http://localhost:4040 to see detailed request logging for all traffic going through your ngrok url
- Note: Does not allow save when add to Webhooks in Facebook Messenger "Webhooks" setup along with Verify Token. Maybe due to Webhooks must have a valid SSL certificate signed by a certificate authority
-
-
TODO
- Remove
debug=Truefromapp.runwhen no more errors
- Remove
-