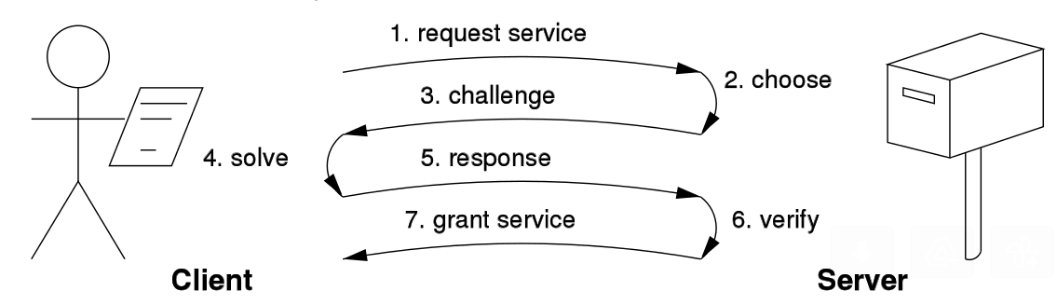
This project is a solution for the following problem statement.
Design and implement “Word of Wisdom” TCP server. TCP server should be protected from DDOS attacks with the Prof of Work (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proof_of_work), the challenge-response protocol should be used.
- The choice of the POW algorithm should be explained.
- After Prof of Work verification, server should send one of the quotes from “word of wisdom” book or any other collection of the quotes.
- Docker file should be provided both for the server and for the client that solves the POW challenge
- Go 1.20+ installed (to run tests, start server or client without Docker)
- Docker installed (to run docker-compose)
docker compose up
This command will fire up docker containers for server and client, perform compilation, run test, run the server and client services - inside the docker containers.
The server will be up ad running forever (until interrupted by OS). The client will send numnber of requests specified by client-config.yaml parameters and exit.
This solution uses TCP-based protocol. Message is encoded by gob and then encrypted by an asymmetric encryption algorithm - RSA. Message sent from client to server and back has universal format:
- header - integer number to indicate, which type of request was sent (analogue of URL in HTTP-protocol)
- payload - array of bytes to handle any kind of meaningful data (depends on type of request)
Solution supports 5 types of requests, switching by header:
- 0 - Step1ChallengeRequest // from client to server - request new challenge from server
- 1 - Step2TwoChallengeResponse // from server to client - message with challenge for client
- 2 - Step3QuoteRequest // from client to server - message with solved challenge
- 3 - Step4QuoteResponse // from server to client - message with a quote
There are additional types of messages, designed in the communication protocol but not implemented due to time limitation:
- 400 - Client side error - sent by server to client if server decides client made a message mistake.
- 500 - Server side error - sent by server to client if there is an internal server error.
Idea of Proof of Work for DDOS protection is that client, which wants to get some resource from server, should firstly solve some challenge from server. This challenge should require more computational work on the client side and verification of the challenge's solution - much less on the server side.
There are some different algorithms of Proof Work. I compared next three algorithms as more understandable and having most extensive documentation:
'd like to use Proof of Useful work because all other PoW algorithms use computer resources without significant outcome. The PoW may and should be used to useful calculations, for example to multiply matrixes for ML, to train AI models, etc. But to implement this approach one need to spend significant amount of time and perform reliable testing. At the moment of writing this, there are no good yet relatively simple implementations of Proof of Useful Work (please refer to References at the end of the page). So, I rejected the idea of using the Proof of Useful work approach.
After comparison, I chose Hashcash. Other algorithms have next disadvantages:
- In Merkle tree server should do too much work to validate client's solution. For tree consists of 4 leaves and 3 depth server will spend 3 hash calculations.
- In guided tour puzzle client should regularly request server about next parts of guide, that complicates logic of protocol.
Hashcash, instead has next advantages:
- simplicity of implementation
- lots of documentation and articles with description
- simplicity of validation on server side
- possibility to dynamically manage complexity for client by changing required leading zeros count
Of course Hashcash also has disadvantages like:
- Compute time depends on power of client's machine. For example, very weak clients possibly could not solve challenge, or too powerful computers could implement DDOS-attacks. But complexity of challenge could be dynamically solved by changing of required zeros could from server.
- Pre-computing challenges in advance before DDOS-attack. Some clients could parse protocol and compute many challenges to apply all of it in one moment. It could be solved by additional validation of hashcash's params on server. For example, on creating challenge server could save rand value to Redis cache and check it's existence on verify step (that is implemented in this solution).
But all of those disadvantages could be solved in real production environment.
- Proof of Useful work. Research paper. https://github.com/cfschilham/kophos/blob/master/proof_of_useful_work.pdf
- A Proof of Useful Work for Artificial Intelligence on the Blockchain https://arxiv.org/pdf/2001.09244.pdf
- Coin.AI: A Proof-of-Useful-Work Scheme for Blockchain-Based Distributed Deep Learning https://www.mdpi.com/1099-4300/21/8/723