(c) 2014-2024 by Jan W. Krieger jan@jkrieger.de
This is a lightweight C/C++ library, which is able to read and write basic TIFF files. It is significantly faster than libTIFF, especially in writing large multi-frame TIFFs.
This software is licensed under the term of the GNU Lesser General Public License 3.0 (LGPL 3.0).
- library docukentation: https://travis-ci.org/jkriege2/TinyTIFF
- API documentation: http://jkriege2.github.io/TinyTIFF/modules.html
- build instructions: http://jkriege2.github.io/TinyTIFF/page_buildinstructions.html
- usage instructions: http://jkriege2.github.io/TinyTIFF/page_useinstructions.html
The methods in this file allow to read TIFF files with limited capabilites, but very fast (comapred to libtiff) and also more frames from a multi-frame TIFF than libtiff (which is currently limited to 65535 frames due to internal data sizes!).
This library currently support TIFF files, which meet the following criteria:
- TIFF-only (no BigTIFF), i.e. max. 4GB
- uncompressed frames
- one, or more samples per frame
- data types: UINT, INT, FLOAT, 8-64bit
- planar and chunky data organization, for multi-sample data
- no suppoer for palleted images
- stripped TIFFs only, tiling is not supported
This example reads all frames from a TIFF file:
TinyTIFFReaderFile* tiffr=NULL;
tiffr=TinyTIFFReader_open(filename);
if (!tiffr) {
std::cout<<" ERROR reading (not existent, not accessible or no TIFF file)\n";
} else {
if (TinyTIFFReader_wasError(tiffr)) {
std::cout<<" ERROR:"<<TinyTIFFReader_getLastError(tiffr)<<"\n";
} else {
std::cout<<" ImageDescription:\n"<< TinyTIFFReader_getImageDescription(tiffr) <<"\n";
uint32_t frames=TinyTIFFReader_countFrames(tiffr);
std::cout<<" frames: "<<frames<<"\n";
uint32_t frame=0;
if (TinyTIFFReader_wasError(tiffr)) {
std::cout<<" ERROR:"<<TinyTIFFReader_getLastError(tiffr)<<"\n";
} else {
do {
const uint32_t width=TinyTIFFReader_getWidth(tiffr);
const uint32_t height=TinyTIFFReader_getHeight(tiffr);
const uint16_t samples=TinyTIFFReader_getSamplesPerPixel(tiff);
const uint16_t bitspersample=TinyTIFFReader_getBitsPerSample(tiff, 0);
bool ok=true;
std::cout<<" size of frame "<<frame<<": "<<width<<"x"<<height<<"\n";
std::cout<<" each pixel has "<<samples<<" samples with "<<bitspersample<<" bits each\n";
if (ok) {
frame++;
// allocate memory for 1 sample from the image
uint8_t* image=(uint8_t*)calloc(width*height, bitspersample/8);
for (uint16_t sample=0; sample<samples; sample++) {
// read the sample
TinyTIFFReader_getSampleData(tiffr, image, sample);
if (TinyTIFFReader_wasError(tiffr)) { ok=false; std::cout<<" ERROR:"<<TinyTIFFReader_getLastError(tiffr)<<"\n"; break; }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// HERE WE CAN DO SOMETHING WITH THE SAMPLE FROM THE IMAGE
// IN image (ROW-MAJOR!)
// Note: That you may have to typecast the array image to the
// datatype used in the TIFF-file. You can get the size of each
// sample in bits by calling TinyTIFFReader_getBitsPerSample() and
// the datatype by calling TinyTIFFReader_getSampleFormat().
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
}
free(image);
}
} while (TinyTIFFReader_readNext(tiffr)); // iterate over all frames
std::cout<<" read "<<frame<<" frames\n";
}
}
}
TinyTIFFReader_close(tiffr); This simplified example reads the first sample from the first frame in a TIFF file:
TinyTIFFReaderFile* tiffr=NULL;
tiffr=TinyTIFFReader_open(filename);
if (!tiffr) {
std::cout<<" ERROR reading (not existent, not accessible or no TIFF file)\n";
} else {
const uint32_t width=TinyTIFFReader_getWidth(tiffr);
const uint32_t height=TinyTIFFReader_getHeight(tiffr);
const uint16_t bitspersample=TinyTIFFReader_getBitsPerSample(tiff, 0);
uint8_t* image=(uint8_t*)calloc(width*height, bitspersample/8);
TinyTIFFReader_getSampleData(tiffr, image, 0);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// HERE WE CAN DO SOMETHING WITH THE SAMPLE FROM THE IMAGE
// IN image (ROW-MAJOR!)
// Note: That you may have to typecast the array image to the
// datatype used in the TIFF-file. You can get the size of each
// sample in bits by calling TinyTIFFReader_getBitsPerSample() and
// the datatype by calling TinyTIFFReader_getSampleFormat().
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
free(image);
}
TinyTIFFReader_close(tiffr); This library currently creates TIFF files, which meet the following criteria:
- TIFF-only (no BigTIFF), i.e. max. 4GB
- multiple frames per file (actually this is the scope of this lib, to write such multi-page files fast), but with the limitation that all frames have the same dimension, data-type and number of samples. The latter allows for the desired speed optimizations!
- uncompressed frames
- one sample per frame
- data types: UINT, INT, FLOAT, 8-64-bit
- photometric interpretations: Greyscale, RGB, including ALPHA information
- planar (R1R2R3...G1G2G3...B1B2B3...) or chunky (R1G1B1R2G2B2R3G3B3...) data organization for
- writes stripped TIFFs only, no tiled TIFFs
The methods in this file allow to write TIFF files with limited capabilites, but very fast. Usually writing TIFF files with a library like libTIFF is relatively slow, when multiple images are written into a single file. The methods in this files overcome this problem by implementing a tiny writer lib that allows to write a TIFF file where all images have the same properties (size, bit depth, ...). This is a situation thet occurs e.g. in cases where a camera acquires a video that should be saved as TIFF file. The library works like this (write 50 32x32 pixel 8-bit images:
TinyTIFFWriterFile* tif=TinyTIFFWriter_open("myfil.tif", 8, 1, 32, 32, TinyTIFFWriter_Greyscale);
if (tif) {
for (uint16_t frame=0; frame<50; frame++) {
const uint8_t* data=readImage();
TinyTIFFWriter_writeImage(tif, data);
}
TinyTIFFWriter_close(tif);
}The images are written in big- or little-endian according to your system. The TIFF header is set accordingly, so we do not need to shuffle around bytes when writing, but the created TIFF file may differ from hardware system to hardware system, although the same data is written (once in little-endian, once in big-endian). Currently this library saves all images as unsigned int, but with given bit-depth (8, 16, 32 or 64). Also this library explicitly writes a resolution of 1 in both directions.
You can also store multi-sample images. Their interpretation has to be specified in the call to TinyTIFFWriter_open(), e.g. for an RGB-image, use:
TinyTIFFWriterFile* tif=TinyTIFFWriter_open("myfil.tif", 8, 3, 32, 32, TinyTIFFWriter_RGB);
if (tif) {
for (uint16_t frame=0; frame<50; frame++) {
const uint8_t* data=readImage();
TinyTIFFWriter_writeImage(tif, data);
}
TinyTIFFWriter_close(tif);
}Note, that TinyTIFFWriter_writeImage() expects the image data in the given buff data is given in interleaved order, i.e. R1G1B1R2G2B2R3G3B3... and writes it out in the same order.
If you specify more or less samples, the same rules apply. You can use the extended method TinyTIFFWriter_writeImageMultiSample() if your data is not in chunky format, or you want
to write the data out in planar form, instead of chunky (e.g. to make the data readable by TinyTIFFReader.
Also it is possibly to specify that one of the extra channels ahall be used as ALPHA information. then you need to call TinyTIFFWriter_open(..., TinyTIFFWriter_RGBA) or TinyTIFFWriter_open(..., TinyTIFFWriter_GreyscaleAndAlpha). All samples additional to the ones covered by the interpretation flag are treated as extraSamples with unspecified type (see TIFF specification for details).
Internally this library works like this: TinyTIFFWriter_open() will basically only initialize the internal datastructures and write the TIFF header. It also determines the byte order used by the system and sets the TIFF header acordingly. As the image size is known, the size of every image in the file can be predetermined (we assume a maximum number of TIFF directory entries). The size will be:
MAX_HEADER_ENTRIES*12 + SOME_FREE_SPACE + WIDTH*HEIGHT*SAMPLES(BITS_PER_SAMPLES/8)
--------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
directory/image description data image data
The free space, indicated as SOME_FREE_SPACE is used to store contents of extended fields, like RATIONAL or ARRAY fields. Every image in the file will have this size and unused bytes are set to 0x00. TinyTIFFWriter_writeImage() then works like this: The image description data is first assembled in memory, then the complete image description data and the complete image data is written to the file all together. This reduces the number of file access operations and writes the data in two reltively large chunks which allows the operating system to properly optimize file access. Finally this method will save the position of the NEXT_IFD_OFFSET field in the image header. The NEXT_IFD_OFFSET field is filled with the adress of the next potential image. Finally the method TinyTIFFWriter_close() will write 0x00000000 into the NEXT_IFD_OFFSET of the last image (as saved above) which ends the list of images in the file. This ansatz for writing TIFF files is only about a factor of 2 slower than directly writing binary data into a file. In addition the time needed to write an image stays equal also when writing many images, which is NOT the case for libtiff.
The library was developed due to a problem with libTIFF, when a lot (>1000) frames are written into a TIFF-file. LibTIFF does not need constant time per frame (i.e. the time to write a multi-frame TIFF grows linearly with the number of frames), but the time to write a frame increases with the number of frames.
The following performance measurement shows this. It was acquired using tinytiffwriter_speedtest from this repository and shows the average time required to write one frame (64x64x pixels, 16-bit integer) out of a number (10, 100, 1000, ...) of frames. It compares the performance of libTIFF, TinyTIFFWriter and simply writing the dtaa using fwrite() ("RAW"). It was acquired on an Ryzen 5 3600+, Win10, 32-bit Release-build, writing onto a Harddisk (not a SSD)
| Ryzen 5 3600+, Win10, 32-bit Release-build, writing onto a Harddisk, libTiff 3.8.2 | Ryzen 7 5800H, Win11, 64-bit Release-build, writing onto an SSD, libTiff 4.6.0 |
|---|---|
 |
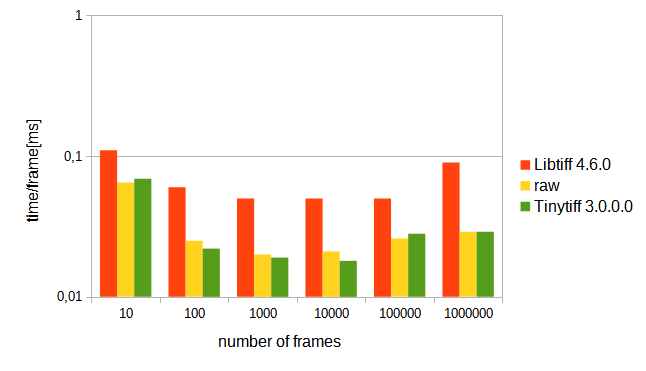 |
For a microscope developed during my PhD thesis, it was necessary to write 100000 frames and more with acceptable duration. Therefore libTIFF was unusable and TinyTIFFWriter was developed.
As can be seen in the graph above. The performance of TinyTIFFWriter and fwrite()/RAW is comparable, whereas the performance of LibTIFF falls off towards large files on harddisks. On SSDs the performance of libTIFF does not show an increase with number of images, but is still significantly (1.5-3x, note the logarithmic y-axis) faster than libTIFF.
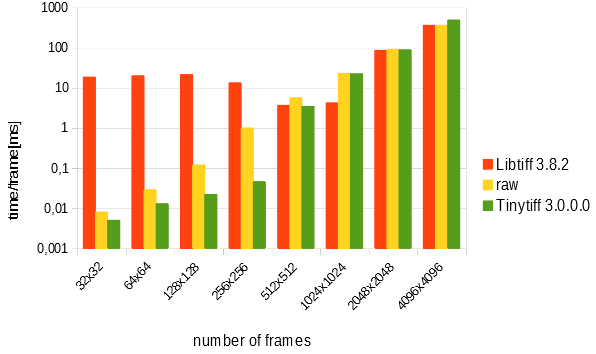
The following image shows another performance measurement, this time for different frame sizes (64x64-4096x4096, acquired on an Ryzen 5 3600+, Win10, 32-bit Release-build, writing onto a Harddisk (not a SSD)):
| Ryzen 5 3600+, Win10, 32-bit Release-build, writing onto a Harddisk, libTiff 3.8.2 | Ryzen 7 5800H, Win11, 64-bit Release-build, writing onto an SSD, libTiff 4.6.0 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
This suggests that for harddisks the performance of TinyTIFFWriter and fwrite() are comparable for all image sizes. For larger images, also the performance of libTIFF is in the same range, whereas for small images, libTIFF falls off somewhat. For SSDs, the libraries are closer together, but still TinyTIFFWriter is faster than libTIFF by a factor of 1.5-5x (again note the logarithmic scale on the y-axis!).








