-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 30
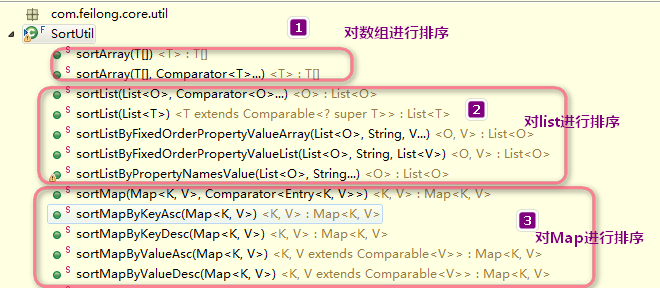
排序专家 SortUtil
JAVA开发排序少不了的,曾几何时以为排序就是数据库SQL order by,后来你会发现,你的数据可能源自于别人的API,也可能直接源自EXCEL...这时要排序,好吧 我去写自定义 Comparator,好累好累的说
我们来看看 排序专家 - SortUtil
主要由下面几个部分组成:
| 方法 | Description |
|---|---|
| sortArray(T[]) | 对 数组 arrays 进行排序. |
| sortArray(T[], Comparator...) | 对 数组 arrays使用 comparator 进行排序. |
对 数组 arrays 进行排序.
示例:
sortArray(toArray(5, 10, 3, 2) = [2,3,5,10]以前代码需要写成:
public static String toSalesPropertiesIdsJson(Long...itemPropertiesIdLongs){
Arrays.sort(itemPropertiesIdLongs);
return JsonUtil.format(itemPropertiesIdLongs, 0, 0);
}现在可以重构成:
public static String toSalesPropertiesIdsJson(Long...itemPropertiesIdLongs){
return JsonUtil.format(sortArray(itemPropertiesIdLongs), 0, 0);
}**再如: **
// 得到默认分类,目前是最小的
private Long getDefaultCategoryId(Long[] categoriesIds){
Arrays.sort(categoriesIds);
return categoriesIds[0];
}可以重构成:
// 得到默认分类,目前是最小的
private Long getDefaultCategoryId(Long[] categoriesIds){
return sortArray(categoriesIds)[0];
}对 数组 arrays 使用 comparator 进行排序.
示例: 场景: 对字符串数组先按照长度比较,如果长度相等,那么再按照字母比较
String[] arrays = { "almn", "fba", "cba" };
Comparator<String> comparator = new Comparator<String>(){
@Override
public int compare(String s1,String s2){
Integer length = s1.length();
Integer length2 = s2.length();
//先判断长度,长度比较
int compareTo = length.compareTo(length2);
//如果长度相等,那么比较自己本身的顺序
if (0 == compareTo){
compareTo = s1.compareTo(s2);
}
return compareTo;
}
};
sortArray(arrays, comparator);
assertArrayEquals(toArray("cba", "fba", "almn"), arrays);| 方法 | Description |
|---|---|
| sortList(List) | 对 集合 list 进行排序. |
| sortList(List, Comparator...) | 对集合 list,使用指定的 comparators 进行排序. |
| sortListByFixedOrderPropertyValueArray(List, String, V...) | 对 集合 list,属性 propertyName 按照固定顺序值 propertyValues 进行排序. |
| sortListByFixedOrderPropertyValueList(List, String, List) | 对 集合 list,属性 propertyName 按照固定顺序值 propertyValues 进行排序. |
| sortListByPropertyNamesValue(List, String...) | 对集合 list,按照指定属性的值(组合)进行排序. |
对 集合 list 进行排序.
说明:
-
Collections.sort底层就是调用的是Arrays.sort
示例:
sortList(toList(5, 10, 3, 2)) = [2,3,5,10]对集合 list,使用指定的 comparators 进行排序.
示例: 场景: 将 user list 按照 id进行排序
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User(12L, 18));
list.add(new User(2L, 36));
list.add(new User(5L, 22));
list.add(new User(1L, 8));
SortUtil.sortList(list, new PropertyComparator<User>("id"));
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(list));返回:
[
{"id": 1,"age": 8},
{"id": 2,"age": 36},
{"id": 5,"age": 22},
{"id": 12,"age": 18}
]当然对于上述示例,你可以直接调用:
SortUtil.sortListByPropertyNamesValue(list, "id");我们再来个复杂点的例子: 将 user list 按照 "刘备" 排在 "关羽" 前面 进行排序,如果名字相同再按照 age进行排序
User guanyu = new User("关羽", 30);
User liubei60 = new User("刘备", 60);
User liubei25 = new User("刘备", 25);
User liubei30 = new User("刘备", 30);
User liubei10 = new User("刘备", 10);
String[] names = { "刘备", "关羽" };
List<User> list = CollectionsUtil.select(toList(liubei60, liubei30, liubei10, guanyu, liubei25), "name", names);
sortList(
list, //
new PropertyComparator<User>("name", new FixedOrderComparator<>(names)),
new PropertyComparator<User>("age"));返回:
assertThat(list, contains(liubei10, liubei25, liubei30, liubei60, guanyu));对 集合 list,属性 propertyName 按照固定顺序值 propertyValues 进行排序.
示例: 场景: 将user list中 "刘备" 排在 "关羽"前面
User zhangfei = new User("张飞", 23);
User guanyu = new User("关羽", 30);
User liubei = new User("刘备", 25);
List<User> list = toList(zhangfei, guanyu, liubei);
List<User> resultList = CollectionsUtil.select(list, "name", "刘备", "关羽");
Collections.sort(resultList, new PropertyComparator<User>("name", new FixedOrderComparator<>("刘备", "关羽")));此时你可以直接调用:
List<User> resultList = CollectionsUtil.select(list, "name", "刘备", "关羽");
SortUtil.sortListByFixedOrderPropertyValueArray(resultList, "name", "刘备", "关羽"));返回:
assertThat(resultList, contains(liubei, guanyu));对 集合 list,属性 propertyName 按照固定顺序值 propertyValues 进行排序.
示例: 场景: 将user list中 "刘备" 排在 "关羽"前面
User zhangfei = new User("张飞", 23);
User guanyu = new User("关羽", 30);
User liubei = new User("刘备", 25);
List<User> list = toList(zhangfei, guanyu, liubei);
List<User> returnList = CollectionsUtil.select(list, "name", toList("刘备", "关羽"));
returnList = sortListByFixedOrderPropertyValueList(returnList, "name", toList("刘备", "关羽"));返回:
assertThat(returnList, contains(liubei, guanyu));对集合 list,按照指定属性的值(组合)进行排序.
示例: 场景: 将user list 先按照 id 再按照 age 进行排序
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User(12L, 18));
list.add(new User(2L, 36));
list.add(new User(2L, 2));
list.add(new User(2L, 30));
list.add(new User(1L, 8));
SortUtil.sortListByPropertyNamesValue(list, "id", "age");
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.formatWithIncludes(list, "id", "age"));返回:
[
{"id": 1,"age": 8},
{"id": 2,"age": 2},
{"id": 2,"age": 30},
{"id": 2,"age": 36},
{"id": 12,"age": 18}
]| 方法 | Description |
|---|---|
| sortMapByKeyAsc(Map<K, V>) | 按照key asc顺序排序. |
| sortMapByKeyDesc(Map<K, V>) | 按照key desc 倒序排序. |
| sortMapByValueAsc(Map<K, V>) | 根据value 来顺序排序(asc). |
| sortMapByValueDesc(Map<K, V>) | 根据value 来倒序排序(desc). |
| sortMap(Map<K, V>, Comparator<Entry<K, V>>) | 使用 基于 Entry 的 mapEntryComparator 来对 map进行排序. |
按照key asc顺序排序.
注意:
- 原 map 的顺序不变
- 该方法使用了 PropertyComparator,允许 null key,null key排在最前面
- 如果直接使用
java.util.TreeMap.TreeMap(Map),TreeMap不允许 key是null,如果有key是null,那么将会抛出NullPointerException
示例:
Map<String, Comparable> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 123);
map.put("c", 345);
map.put(null, 1345);
map.put("b", 8);
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(SortUtil.sortMapByKeyAsc(map)));返回:
{
null: 1345,
"a": 123,
"b": 8,
"c": 345
}按照key desc 倒序排序.
注意:
- 原 map 的顺序不变
- 该方法使用了
PropertyComparator,允许 null key,null key排在最后面
示例:
Map<String, Comparable> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 123);
map.put("c", 345);
map.put(null, 88);
map.put("b", 8);
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(SortUtil.sortMapByKeyDesc(map)));返回:
{
"c": 345,
"b": 8,
"a": 123,
null: 88
}根据value 来顺序排序(asc).
注意:
- 原 map 的顺序不变
示例:
Map<String, Comparable> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", 123);
map.put("c", 345);
map.put("b", 8);
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(SortUtil.sortMapByValueAsc(map)));返回:
{
"b": 8,
"a": 123,
"c": 345
}根据value 来倒序排序(desc).
注意:
- 原 map 的顺序不变
示例:
Map<String, Comparable> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("a", 123);
map.put("c", 345);
map.put("b", 8);
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(SortUtil.sortMapByValueDesc(map)));返回:
{
"c": 345,
"a": 123,
"b": 8
}使用 基于 Entry 的 mapEntryComparator 来对 map进行排序.
说明:
- 原 map 的顺序不变
- 由于是对Entry排序的, 既可以按照key来排序,也可以按照value来排序哦
示例: 比如有以下的map
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a13", 123);
map.put("a2", 345);
map.put("a8", 8);如果我们只是使用 :
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(SortUtil.sortByKeyAsc(map)));返回:
{
"a13": 123,
"a2": 345,
"a8": 8
}此时可以看出 a13是以字符串的形式进行比较的,我们可以使用以下的自定义的 Comparator,来达到排序的效果
PropertyComparator<Entry<String, Integer>> propertyComparator = new PropertyComparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(
"key",
new RegexGroupNumberComparator("a(\\d*)"));
LOGGER.debug(JsonUtil.format(SortUtil.sortMap(map, propertyComparator)));返回:
{
"a2": 345,
"a8": 8,
"a13": 123
}core