This repository will help you deploy a Docker based development full stack for Sugar, meeting all the platform requirements for a different set of platform combinations.
There are few stacks available, with in itself multiple platform combinations. You can read more about the specific stacks on the links below:
- Sugar 9 - This stack is also valid for 9.1, 9.2 and 9.3 for local development of Sugar Cloud only versions
- Sugar 8
You will find additional stacks within the stack directory of the project.
For most stacks, there are both the pre-built version (eg on Sugar 9: ./stacks/sugar9/php73.yml) and a locally built version (eg on Sugar 9: ./stacks/sugar9/php73-local-build.yml). The locally built version will be built run-time, and therefore those stacks will let you specify additional changes you might require to the docker images provided. Local builds will take much longer to deploy than pre-built ones.
There are mainly three types of stack:
- Single Apache web server - Initial development
- Single Apache web server with local run-time build - Initial development when you need to modify the stack to better suit specific needs
- An Apache load balancer with a cluster of two Apache web servers behind it - A more real-life environment to verify that everything works correctly
There are multiple stack components as docker containers, that perform different duties. Not all the stack components might be used on a specific stack setup. Some of the stack components are listed below:
- Apache load balancer - Load balances requests between the cluster of Apache PHP web servers, round robin
- Apache PHP web server - Web server(s)
- MySQL database - Database
- Elasticsearch - Sugar search engine
- Redis - Two purposes: Sugar object caching service and PHP Session storage/sharing service
- Cron - Sugar background scheduler processing. Note that this is enabled immediately and it will run
cron.phpas soon as the file is available, and it will attempt to do so every 60 seconds since its last run. This container is used for any other CLI execution required during development - Permission - Sets Sugar instance permissions correctly and then terminates
- The first step for everything to work smoothly, is to add on your computer's host file /etc/hosts the entry "docker.local" to point to your machine's ip (it might be 127.0.0.1 if running the stack locally or within the VM running Docker)
- Clone the repository with
git clone https://github.com/esimonetti/SugarDockerized.git sugardockerand enter sugardocker withcd sugardocker - Run the utility
./utilities/setownership.shto set the correct ownership of the data directory - Select the stack combination to run by choosing the correct yml file within the subdirectories inside stacks. See next step for more details and an example.
- Run
docker-compose -f <stack yml filename> up -dfor the selected . As an example if we selectedstacks/sugar8/php71.yml, you would rundocker-compose -f stacks/sugar8/php71.yml up -d. To facilitate the task of starting and stopping stacks and to switch between them, is available this utility script.
The main stacks work with Sugar version 9.0 and all its platform requirements. Additional stacks are aligned with the platform requirements of version 8.0, 7.9 and stacks for Sugar Cloud only versions for local development only.
- Run the stack with
docker-compose -f <stack yml filename> up -d - Stop the stack with
docker-compose -f <stack yml filename> down
Alternatively, leverage the utility script stack.sh that will help with automation.
- Apache load balancer: sugar-lb
- Apache PHP web server; On single stack: sugar-web1 On cluster stack: sugar-web1 and sugar-web2
- MySQL database: sugar-mysql
- Elasticsearch: sugar-elasticsearch
- Redis: sugar-redis
- Cron: sugar-cron
- Permission: sugar-permissions
To verify all components hostnames just run docker ps when the stack is up and running.
Please note that on this setup, only the web server or the load balancer (if in single web server or cluster stack) and the database can be accessed externally. Everything else is only allowed within the stack components.
- Linux
- Apache
- MySQL
- PHP
- Redis
- Elasticsearch
- Browser url: http://docker.local/sugar/ - Based on the host file entry defined above on the local machine
- MySQL hostname: sugar-mysql
- MySQL db name: sugar
- MySQL user: root
- MySQL password: root
- Elasticsearch hostname: sugar-elasticsearch
- Redis hostname: sugar-redis
Apache web servers have enabled:
- mod_headers
- mod_expires
- mod_deflate
- mod_rewrite
Apache web servers have PHP with enabled:
- Zend OPcache - Configured for Sugar with the assumption the files will be located within the correct path
- XHProf and Tideways profilers
- Xdebug is installed but it is not enabled by default (due to its performance impact). If there is the need to enable it, you would have to uncomment the configuration option on the PHP Dockerfile of choice, and leverage the stack configuration with local build.
-
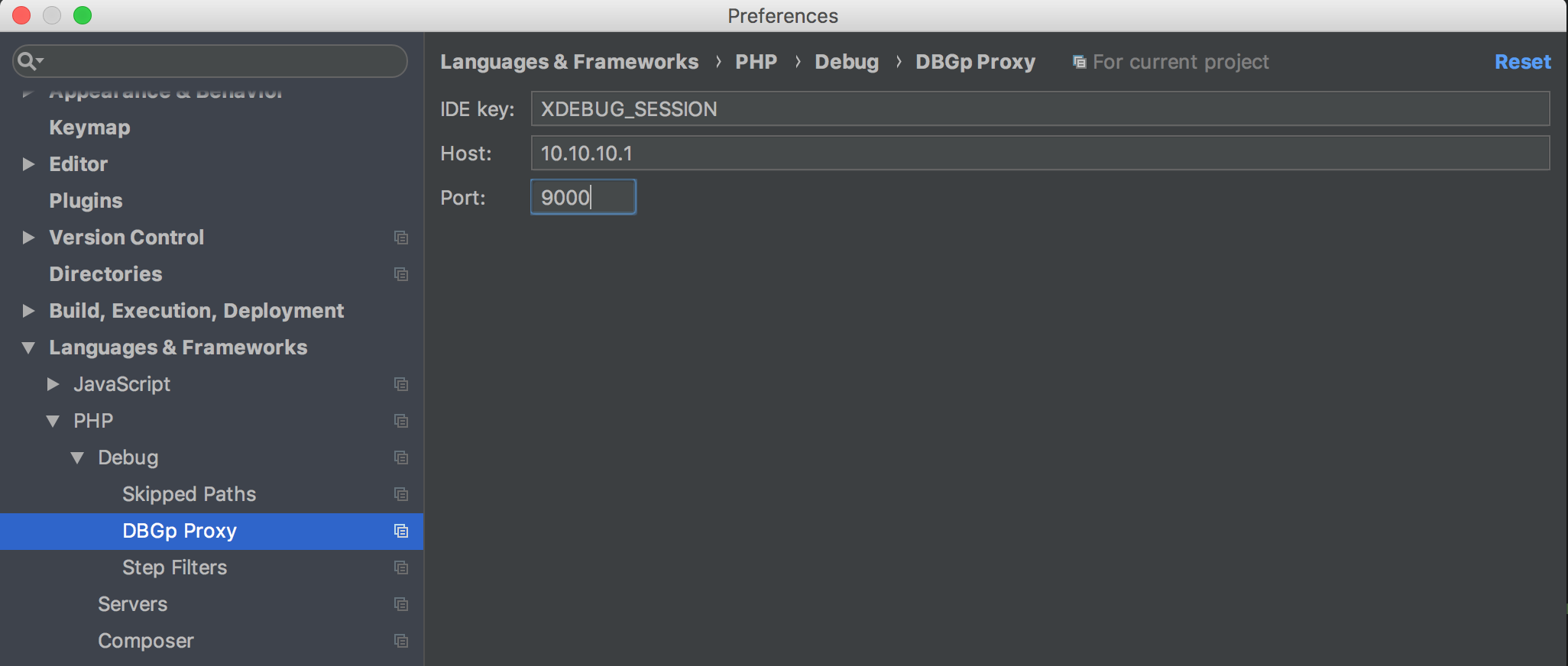
If you use an IDE such as PHPStorm, you can setup DBGp Proxy under the menus Preference -> Language & Framework -> PHP -> Debug -> DBGp Proxy. Example settings are available in the screenshot below:
-
Debug with Xdebug Helper
If you use Chrome as a browser, you can install the extension Xdebug helper. When ready to debug, click the debug button on the Xdebug helper, and click on "Start listening for PHP Debug Connections" within PHPStorm


-
Debug with Postman
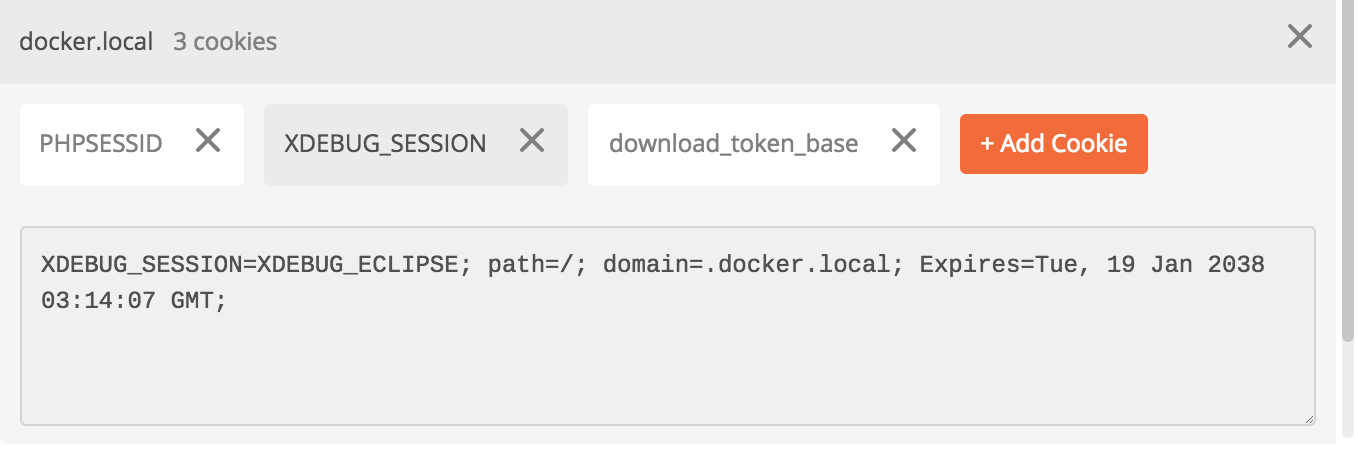
It is possible to debug a specific API endpoint through Postman leveraging a similar approach. In this example, we are going to debug the login authentication api endpoint rest/v11_1/oauth2/token. The first step is to add the cookie "XDEBUG_SESSION" in Postman. The same cookie is set through the Xdebug helper, and the keyword is referenced on the PHPstorm settings and on Xdebug PHP server side settings as well. See screenshots below:

-
-
Session storage is completed leveraging the Redis container.
If you notice that your Elasticsearch container is not running (check with docker ps), it might be required to tweak your Linux host settings.
To be able to run Elasticsearch version 5 and above, it is needed an increase of the maximum mapped memory a process can have. To complete this change permanently run:
echo "vm.max_map_count=262144" | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
Alternatively the limit can be increased runtime with:
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
images/php/XY/apache/- Image for Apache with PHP version X.Ximages/php/XY/cron/- Image for PHP version X.Y, for background jobs and any CLI needimages/mysql/XY/- Image for MySQL version X.Yimages/elasticsearch/XY/- Image for Elasticsearch X.Yimages/permissions/- Image for permissions fixing containerimages/loadbalancer/- Image for Apache load balancerimages/jmeter/- Image for Jmeterimages/sidecar-build/- Image for building Sidecar's javascriptimages/traefik/- Traefik image to expose Sugar within the local network when using a VMimages/ldap/- OpenLDAP image
Most images are currently leveraging Debian linux.
All persistent storage is located within the ./data directory tree within your local checkout of this git repository.
- The Sugar application files served from the web servers and leveraged by the cronjob server have to be located in
./data/app/sugar/. Within the web servers and the cronjob server the location is/var/www/html/sugar/. Everything within./data/app/can be accessed through the browser, but the Sugar instance files have to be within./data/app/sugar/ - MySQL files are located in
./data/mysql/XY/ - Elasticsearch files are located in
./data/elasticsearch/XY/ - Redis files are located in
./data/redis/ - LDAP files are located in
./data/ldap/
Do not change the permissions of the various data subdirectories, as it might cause the system to not work correctly.
This setup is designed to run only a single Sugar instance. It also requires the application files to be exactly on the right place for the following three reasons:
- File system permissions settings
- PHP OPcache settings (eg: blacklisting of files that should not be cached)
- Cronjob background process running
For the above reasons the single instance Sugar's files have to be located inside ./data/app/sugar/ (without subdirectories), for the stack setup to be working as expected.
If you do need multiple instances, as long as they are not running at the same time, you can leverage the provided tools to replicate and swap the data directories.
To help with development, there are a set of tools provided within the utilities directory of this repository. Some of the scripts are mentioned below.
./utilities/setownership.sh
All directories and files within "data" are now owned by uid:gid 1000:1000
It sets the correct ownership of the data directories
./utilities/stack.sh 80 down
./utilities/stack.sh 80 down
stacks/sugar8/php71.yml down
Stopping sugar-cron ... done
Stopping sugar-web1 ... done
Stopping sugar-redis ... done
Stopping sugar-mysql ... done
Stopping sugar-elasticsearch ... done
Removing sugar-cron ... done
Removing sugar-web1 ... done
Removing sugar-redis ... done
Removing sugar-mysql ... done
Removing sugar-permissions ... done
Removing sugar-elasticsearch ... done
Removing network sugar8_default
No stopped containers
It helps to take the default stack for the sugar version passed as a parameter, up or down. It expects two parameters: version number (eg: 80, 90 etc) and up/down.
Have a look at the configuration file ./utilities/stacks.conf, to know all the available stack combinations for the script. For some of the main stacks is available the "local" version of the stack, that allows local modification of settings and local docker image building.
./utilities/runcli.sh "php ./bin/sugarcrm password:weak"
It helps to execute a command within the CLI container. It requires the stack to be on
./utilities/backup.sh 802_2018_11_21
Backing up sugar to "backups/backup_802_2018_11_21"
[sudo] password for docker:
Application files backed up on backups/backup_802_2018_11_21/sugar
Database backed up on backups/backup_802_2018_11_21/sugar.sql
It takes a snapshot of sugar files on backups/backup_802_2018_11_21/sugar and a MySQL database dump on backups/backup_802_2018_11_21/sugar.sql.
The script assumes that the database name is sugar and the web directory is sugar as well. The script does not take backups of Elasticsearch and/or Redis.
./utilities/restore.sh 802_2018_11_21
Restoring sugar from "backups/backup_802_2018_11_21"
sugar-permissions
Application files restored
Database "sugar" dropped
Database restored
Debug: Entering directory .
Repairing...
Repair completed in 9 seconds.
System repaired
It restores a previous snapshot of sugar files from backups/backup_802_2018_11_21/sugar and of MySQL from backups/backup_802_2018_11_21/sugar.sql
The script assumes that the database name is sugar and the web directory is sugar as well. The script does not restore Elasticsearch and/or Redis.
To be able to achieve this consistently, it is recommended to leverage the single web server stack.
By running the command docker logs -f sugar-web1 it is then possible to tail the output from the access and error log of Apache and/or PHP
You would just need to run again the permissions docker container with docker start sugar-permissions. The container will fix the permissions and ownership of files for you and then terminate its execution.
Apache and Cron run as the sugar user. Se the following options on config_override.php
$sugar_config['default_permissions']['user'] = 'sugar';
$sugar_config['default_permissions']['group'] = 'sugar';
The application contains few scripts built to facilitate the system's repair from command line. The scripts will wipe the various caches (including OPcache and Redis if used). It will also warm-up as much as possible the application, to improve the browser experience on first load. The cron container from which the repair runs, has also been optimised to speed up the repairing processing. To run the repair from the docker host, assuming that the repository has been checked out on sugardocker execute:
cd sugardocker
./repair
Add on config_override.php the following options:
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled'] = false;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_redis'] = false;
$sugar_config['external_cache']['redis']['host'] = 'sugar-redis';
Make sure there are no other caching mechanism enabled on your config/config_override.php combination, otherwise set them as disabled = true.
To run a PHP script execute something like the following sample commands:
docker@docker:~/sugardocker$ ./utilities/runcli.sh "php ../repair.php --instance ."
Debug: Entering directory .
Repairing...
Completed in 8 seconds
docker@docker:~/sugardocker$ ./utilities/runcli.sh "whoami"
sugar
docker@docker:~/sugardocker$ ./utilities/runcli.sh "pwd"
/var/www/html/sugar
If needed, sudo is available as well without the need of entering a password. Just make sure the permissions and ownership (user sugar) is respected.
Both XHProf extension and Tideways extensions are configured in most stacks.
To enable profiling:
- If you choose to use Tideways, add this custom code to your Sugar installation and repair the system.
- Configure
config_override.phpspecific settings (see below based on the stack extension)
XHProf Sugar config_override.php configuration:
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['enable'] = true;
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['log_to'] = '../profiling';
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['sample_rate'] = 1;
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['flags'] = 0;
Tideways Sugar config_override.php configuration:
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['enable'] = true;
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['manager'] = 'SugarTidewaysProf';
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['log_to'] = '../profiling';
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['sample_rate'] = 1;
$sugar_config['xhprof_config']['flags'] = 0;
Make sure new files are created on ./data/app/profiling/ when navigating Sugar. If not, ensure that the directory permissions are set correctly so that the sugar user can write on the directory.
Please note that profiling degrades user performance, as the system is constantly writing to disk profiling information and tracking application stats. Use profiling only on replica of the production environment.
- Download XHProf viewer zip file
- Unzip its files content within
./data/app/performance/ - Make sure the
config_override.phpsettings available on./data/app/performance/are kept as is (<?php $config['profile_files_dir'] = '../profiling';) - Access the viewer on http://docker.local/performance/ and verify that the collected data is viewable
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled'] = false;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_redis'] = false;
$sugar_config['external_cache_force_backend'] = 'redis';
$sugar_config['external_cache']['redis']['host'] = 'sugar-redis';
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_wincache'] = true;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_db'] = true;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_smash'] = true;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_apc'] = true;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_zend'] = true;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_memcache'] = true;
$sugar_config['external_cache_disabled_memcached'] = true;
$sugar_config['cache_expire_timeout'] = 600; // default: 5 minutes, increased to 10 minutes
$sugar_config['disable_vcr'] = true; // bwc module only
$sugar_config['disable_count_query'] = true; // bwc module only
$sugar_config['save_query'] = 'populate_only'; // bwc module only
$sugar_config['collapse_subpanels'] = true; // 7.6.0.0+
$sugar_config['hide_subpanels'] = true; // bwc module only
$sugar_config['hide_subpanels_on_login'] = true; // bwc module only
$sugar_config['logger']['level'] = 'fatal';
$sugar_config['logger']['file']['maxSize'] = '10MB';
$sugar_config['developerMode'] = false;
$sugar_config['dump_slow_queries'] = false;
$sugar_config['import_max_records_total_limit'] = '2000';
$sugar_config['verify_client_ip'] = false;
Tweak the above settings based on your specific needs.
These stacks have been built on a Mac platform, that is known to not perform well with Docker mounted volumes.
Personally I run Docker on a Debian based minimal VirtualBox VM with fixed IP, running a NFS server. I either mount NFS on my Mac when needed or SSH directly into the VM. The Debian Docker VirtualBox VM for Mac is available here with its latest downloadable version here.
Alternatively, (...if you are brave enough to run Docker locally on a Mac) you can attempt to use mounted volumes for the data storage (Redis, MySQL and Elasticsearch) and the delegated option. An example of this setup working, can be found here stacks/sugar9/php73-mac.yml and it can be initiated with ./utilities/stack.sh 90-mac up.
