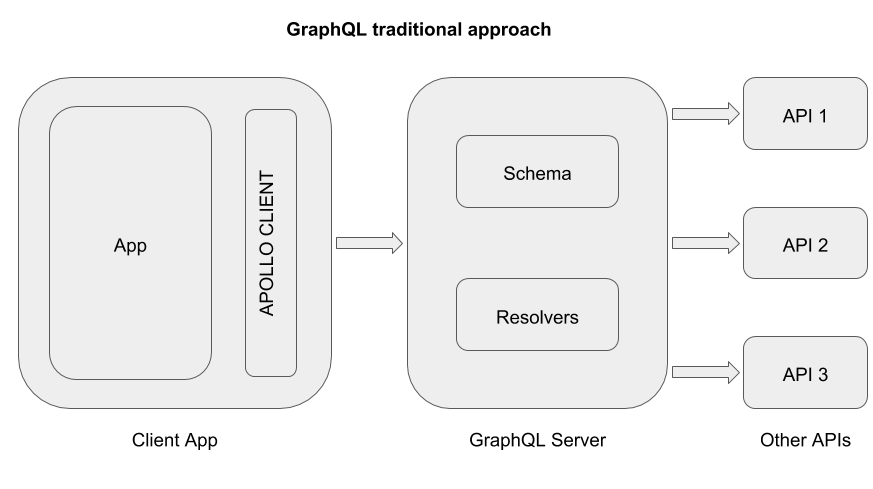
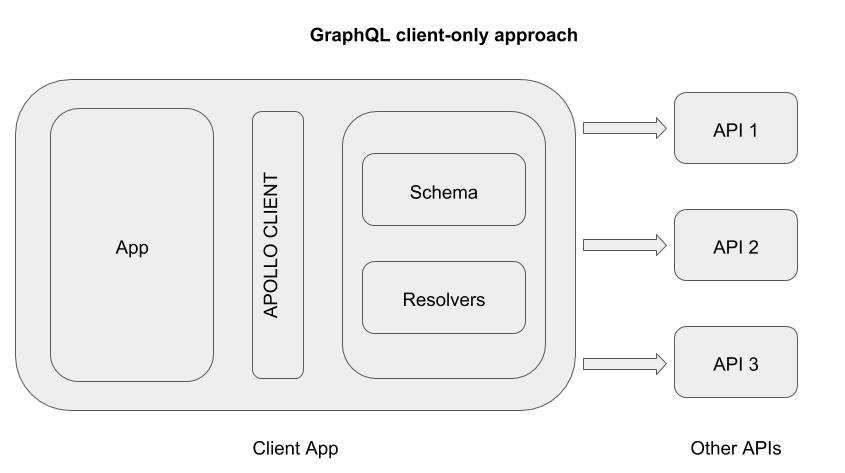
- You do not need a GraphQL server to use the GraphQL APIs on the client. (Example)
- You do not need a separate GraphQL server to stitch the schemas of two existing GraphQL APIs. (Example)
GraphQL is essentially a syntax that describes how to ask for data. A GraphQL API is something that accepts queries in GraphQL syntax and resolves them to whatever is asked by a query. Traditionally, this are written on a server and exposed on a single endpoint. However, since the growth of Apollo Client, and the tools around it, this GraphQL wrapper can be written on the client as well.
This example makes a simple hello-world GraphQL schema.
import { makeExecutableSchema } from 'graphql-tools';
import { SchemaLink } from 'apollo-link-schema';
import { InMemoryCache } from 'apollo-cache-inmemory';
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-client';
const typeDefs = `
type Hello {
message: String
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
message: (root, args, context, info) => "hello-world"
}
};
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({
typeDefs,
resolvers
});
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: new SchemaLink({ schema }),
cache: new InMemoryCache()
})
// You can use this client in your app and it will work like any other GraphQL serverCheck out this example where we have written a GraphQL wrapper over the Meta weather REST API.
This is an example of stitching two remote GraphQL schemas.
import { makeRemoteExecutableSchema, introspectSchema, mergeSchemas } from 'graphql-tools';
import { SchemaLink } from 'apollo-link-schema';
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-client';
const uri1 = 'https://server1.com/graphql';
const uri2 = 'https://server2.com/graphql';
const getRemoteExecutableSchema = async (uri) => {
const httpLink = new HttpLink({ uri });
const remoteSchema = await introspectSchema(httpLink);
return makeRemoteExecutableSchema({ schema: remoteSchema, link: httpLink });
}
const executableSchema1 = await getRemoteExecutableSchema(uri1);
const executableSchema2 = await getRemoteExecutableSchema(uri2);
const newSchema = mergeSchemas({
schemas: [
executableSchema1,
executableSchema2
]
});
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: new SchemaLink({ schema: newSchema }),
cache: new InMemoryCache()
});
// You can use this client in your app and it will work like any other GraphQL serverYou can also have custom resolvers if you want to link your schemas in some way. You just have to add them to the resolvers field in the mergeSchemas function.
const resolvers = {
Query: {
...
},
Mutation: {
...
}
}
const newSchema = mergeSchemas({
schemas: [
executableSchema1,
executableSchema2
],
resolvers: resolvers
});Check out this example where we stitch a remote GraphQL schema with a local GraphQL schema.