Machine Learning is helping the retail industry in many different ways. We can imagine that from forecasting the performance of sales to identifying the buyers, there are many applications of machine learning (artificial intelligence) in the retail industry. “Market Basket Analysis” is one of the best applications of machine learning in the retail industry. By analyzing the past purchase behavior of customers, we can find out which products are frequently bought together by the customers.
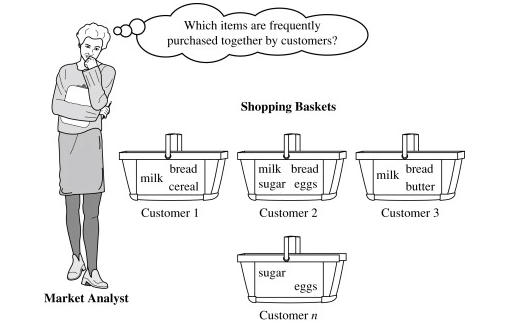
A popular example of frequent itemset mining is Market Basket Analysis. This process identifies customer buying habits by finding associations between the different items that customers place in their “shopping baskets,” as you can see in the following figure. The discovery of this kind of association will be helpful for retailers or marketers to develop marketing strategies by gaining insight into which items are frequently bought together by customers, whether from a grocery store or online retail.
For example, if customers are buying milk, how probably are they to also buy bread (and which kind of bread) on the same trip to the supermarket? This information may lead to an increase in sales by helping retailers to do selective marketing based on predictions, cross-selling, and planning their ledge space for optimal product placement.
Let I = {I1, I2,…, Im} be an itemset. These itemsets are called antecedents. Let D, the data, be a set of database transactions where each transaction T is a nonempty itemset such that T ⊆ I. Each transaction is associated with an identifier called a TID(or Tid). Let A be a set of items(itemset). T is the Transaction that is said to contain A if A ⊆ T. An Association Rule is an implication of form A ⇒ B, where A ⊂ I, B ⊂ I, and A ∩B = φ.
The rule A ⇒ B holds in the data set(transactions) D with supports, where ‘s’ is the percentage of transactions in D that contain A ∪ B (i.e., the union of set A and set B, or both A and B). This is taken as the probability, P(A ∪ B). Rule A ⇒ B has confidence c in the transaction set D, where c is the percentage of transactions in D containing A that also contains B. This is taken to be the conditional probability, like P(B|A). That is,
support(A⇒ B) =P(A ∪ B) confidence(A⇒ B) =P(B|A)
Apriori Algorithm is a widely-used and well-known Association Rule algorithm and is a popular algorithm used in market basket analysis. It is also considered accurate and overtop AIS and SETM algorithms. It helps to find frequent itemsets in transactions and identifies association rules between these items. The limitation of the Apriori Algorithm is frequent itemset generation. It needs to scan the database many times, leading to increased time and reduced performance as a computationally costly step because of a large dataset. It uses the concepts of Confidence and Support.