Code and documents:
- Poster_HadrienBontemps.pptx : a summary of the studied method in the form of a research poster
- RapportEcrit_HadrienBontemps.pdf: an academic report elaborating on an implementation of the method in Pytorch
- AttentionDETECT.ipynb: a Jupyter Notebook with the main code
Datasets:
- MiniSAR_Selection: 7 images selected for training, 2 for test
- MiniSAR_SubImages: 588 training sub-images, 183 test sub-images
The following folders were preliminary steps towards the creation of the final datasets and can be ignored:
- MiniSAR_GFF: original SAR dataset downloaded from https://www.sandia.gov/radar/pathfinder-radar-isr-and-synthetic-aperture-radar-sar-systems/complex-data/
- Matlab_GFF_Reader: use the file "gffquickview.m" to open GFF images, and "main.m" to convert and store them to JPG
- MiniSAR_JPG: converted GFF MiniSAR images through the "main.m" file of the Matlab_GFF_Reader folder
Before running AttentionDETECT.ipynb, please install the dependencies listed in the "requirements.txt" file:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Existing CNN-based methods for target detection in SAR images can achieve good performance but most of them rely on fully-supervised learning which require a large number of target-level labeled training samples.
→ Semi-supervised learning only require a small number of target-level labeled training samples (targets of interest + their positions) and a large number of image-level labeled training samples (simple marks whether the image contains the target of interest or not).
- SAR images with complex scenes contain significant amounts of clutter, and some man-made clutter is very similar to the targets of interest.
→ The attention mechanism is one of the most effective methods to solve this problem. The idea of the attention mechanism is to automatically focus on important regions.
-
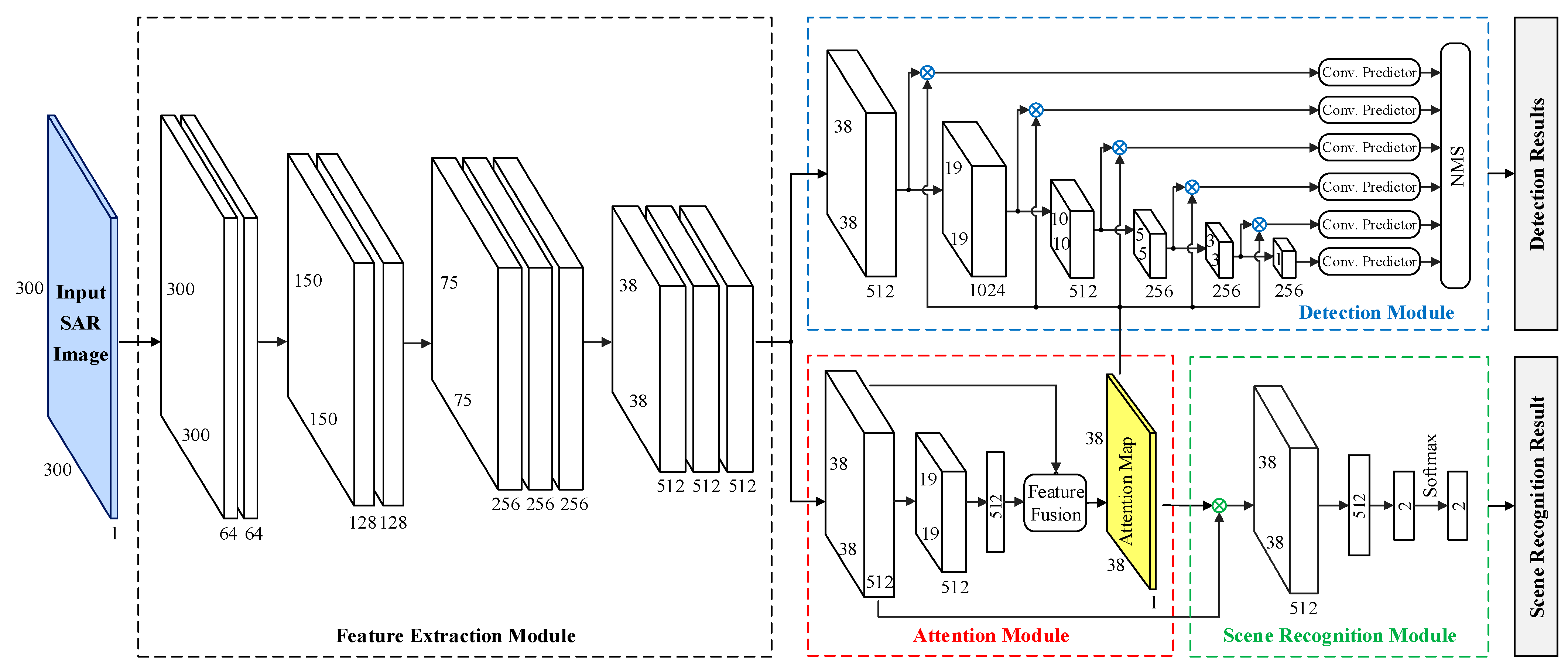
The proposed semi-supervised learning method takes SSD (Single-Shot Detector) as the detection branch and constructs an auxiliary scene recognition branch, where these two branches share a feature extraction module and an attention module.
-
In the feature extraction module, the deep features of the input SAR image will be extracted. In the attention module, the network can generate the attention map automatically, and then the feature maps and attention map are multiplied to focus on the target area and suppress the background clutter area.
-
The detection branch can output the bounding boxes of the targets in the SAR image, and the scene recognition branch outputs the binary classification result indicating whether the input SAR image contains targets.
-
During the training stage, the target-level labeled training samples will pass through the detection branch, and the image-level labeled training samples will pass through the scene recognition branch.
-
During the test stage, a novel coarse-to-fine detection procedure is used to reduce the false alarms. Considering the help of global scene information in SAR images, we first apply the coarse scene recognition branch to the input SAR image, and the scene recognition results of the coarse scene recognition branch are binary classification results indicating if the input SAR images contain the targets or not.
-
According to the scene recognition results, the fine target detection branch is performed on the input SAR images which may contain the targets, and the final detection results of the fine target detection branch are the predicted specific locations of the targets. In this way, the proposed method can reduce the number of false alarms.
-
Given an input SAR image Xinput (300×300×1), the feature extraction module is first employed to extract the deep features L (38×38×512) of Xinput by the deep convolutional network.
-
Then the attention module takes L as input. By fusing the deep features and the global descriptor and applying the softmax activation function, the attention module can obtain the attention map A (38×38×1).
-
In the scene recognition module, the inputs are the deep features L and the attention map A. They are multiplied to obtain the global feature g (R^512), then a fully connected layer and softmax function are used to get the output of the scene recognition module outSR (R^2), it denotes whether the input SAR image Xinput contains targets or not.
-
In the detection module, the inputs are also the deep features L and the attention map A. By performing a series of convolution operations and pooling operations on L, the multi-scale feature maps L (38×38×512), L2 (19×19×1024), L3 (10×10×512), L4 (5×5×256), L5 (3×3×256), are obtained, then these multi-scale feature maps are multiplied by attention map A.
-
Finally, the convolution predictors composed of some convolution layers are used to predict the targets. After the non-maximum suppression (NMS), the outputs of the detection module can be obtained, which are the predicted specific locations of the targets.
-
Similar to SSD, the feature extraction module is a modified VGGNet.
-
Our feature extraction module is designed to contain four convolution stages. There are two convolutional layers in the first two convolutional stages, and three convolutional layers in the last two convolutional stages.
-
The size of the convolutional kernels of the convolutional layers in the feature extraction module is all 3 × 3, and each convolutional stage is composed of multiple cascaded convolutional layers.
-
In the proposed method, each convolutional layer is followed by a ReLU activation function layer.
-
At the end of each convolutional stage is the pooling layer.
-
The input of the attention module is the deep features L (M×M×Nc) obtained by the feature extraction module, where M and Nc are the spatial size and the channel dimension of L.
-
First, the deep features L are fed into a convolutional layer, and then we use a max pooling layer with a pixel window of 2 × 2 and a stride of 2 to down-sample the feature maps. Finally, a fully connected layer is adopted after the max pooling layer to obtain the global descriptor f (R^Nc), which can be regarded as a global representation of the input SAR image.
-
In the fusion module, the local feature and the global descriptor f are fused by a compatibility measure. Specifically, each local feature is added to the global descriptor f, and then multiplied by the learnable weight W (R^Nc) to obtain the compatibility score Si,j ∈ R: Si,j = W.T(l(i,j) + f)
-
Finally, the M compatibility scores are normalized by softmax operation to acquire the attention map A (MxM).
-
The scene recognition module is used to classify the input SAR image. The input of the scene recognition module is the deep features and attention map of the SAR image, and the output is the scene classification result of the SAR image.
-
First, the attention map and the deep features are dot-multiplied according to the spatial position, and then the vector corresponding to each spatial position of the feature maps are added to obtain the global feature. In other words, the global feature g is obtained by the weighted summation of all local features, where the weight is attention map.
-
Then, the global feature g is used to obtain scene classification results by fully connected layers and softmax classifiers. The loss function of the scene recognition module is the cross-entropy loss function
-
The task of the detection module is to predict the bounding boxes of targets. In the detection module, the deep features are passed through multiple convolution layers to extract multi-scale feature maps.
-
In our method, the multi-scale feature maps are first multiplied by the attention map and then fed into the convolution predictors.
-
Since the sizes of multi-scale feature maps are different, they cannot be directly multiplied by a fixed-size attention map. Therefore, we down-sample the attention map many times to generate multiple attention maps with different sizes, which are matched with the sizes of multi-scale feature maps respectively.
-
Then, the multi-scale feature maps after multiplication are fed into convolutional predictors to predict targets and their bounding boxes.
-
Finally, the NMS algorithm is employed to remove redundant targets to obtain the final detection results.