Analyzing system login activities for security audits and compliance.
LastLog Audit offers a comprehensive and customizable solution for analyzing login activities on Linux/Unix systems. Designed for system administrators and security professionals, it facilitates security audits, compliance checks, and forensic investigations with ease.
📘 Explore the full documentation · 🐞 Report Bug · 🛠️ Request Feature
Click to collapse/expand
LastLog Audit: Security Login Activity Analyzer Enhance your security audits and compliance checks.
LastLog-Audit offers a comprehensive solution for analyzing system login activities, designed to assist in security audits, compliance checks, and forensic investigations on Linux/Unix systems. This tool parses /var/log/lastlog to provide detailed and customizable reports on user login activities, making it an indispensable asset for system administrators and security professionals.
Discover the potential of LastLog-Audit in streamlining your security processes. Whether it's for enhancing security protocols, ensuring compliance, or conducting detailed forensic analyses, LastLog-Audit brings robustness and ease to the management of login activity data. Dive into a new level of audit efficiency and control with LastLog-Audit. Begin your journey towards more secure and compliant systems today.
Setting up LastLog-Audit is streamlined for ease of use. Please follow the guidelines below to ensure you meet the necessary prerequisites before installation.
LastLog-Audit is developed for Linux/Unix environments, focusing on delivering a robust login activity analysis tool. Here's what you need to know about its compatibility:
Ensure Python 3.11.2 or newer is installed on your system. You can check your current Python version by running python3 --version in your terminal. If you need to upgrade or install Python, use your distribution's package manager or visit the official Python website for more detailed instructions.
⚠️ Note:LastLog-Audithas been rigorously tested on Ubuntu 23.10 x64. This testing was conducted using Python 3.11.2. WhileLastLog-Auditis expected to function on other Unix-like systems and versions of Python above 3.6, Ubuntu 23.10 x64 with Python 3.11.2 is the recommended setup for the most reliable experience.
To get started with LastLog Audit, you can choose from downloading it directly, cloning the repo, or using a command to pull the latest version. Here's how:
Option 1: Using wget or curl For a quick setup, you can download the main script using wget or curl:
# Using wget
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/franckferman/LastLog-Audit/stable/LastLog-Audit.py
# Or using curl
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/franckferman/LastLog-Audit/stable/LastLog-Audit.pyOption 2: Clone with Git First, ensure you have Git installed on your system. Open your favorite terminal and run the following command to clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/franckferman/LastLog-Audit.gitThis method clones the entire project to your local machine.
Option 3: Direct Download from GitHub If you prefer not using Git, you can download the project directly:
Visit the project's page at https://github.com/franckferman/LastLog-Audit.
Click on the <> Code button, then select Download ZIP.
After downloading, extract the ZIP file to your preferred location.
Whichever method you choose, ensure Python 3 is installed on your system to run LastLog Audit successfully.
Using LastLog Audit is straightforward, enabling you to analyze system login activities efficiently. Here's how to get started:
To run LastLog Audit, execute the following command in your terminal, adjusting the script name as necessary:
python3 LastLog-Audit.pyLastLog Audit comes with a variety of options to customize its output and functionality. Here’s a quick overview:
- --file FILE: Specifies the path to the lastlog file. The default is /var/log/lastlog.
- --display {table,line}: Chooses between tabular (table) and line-by-line (line) output formats. The default is table.
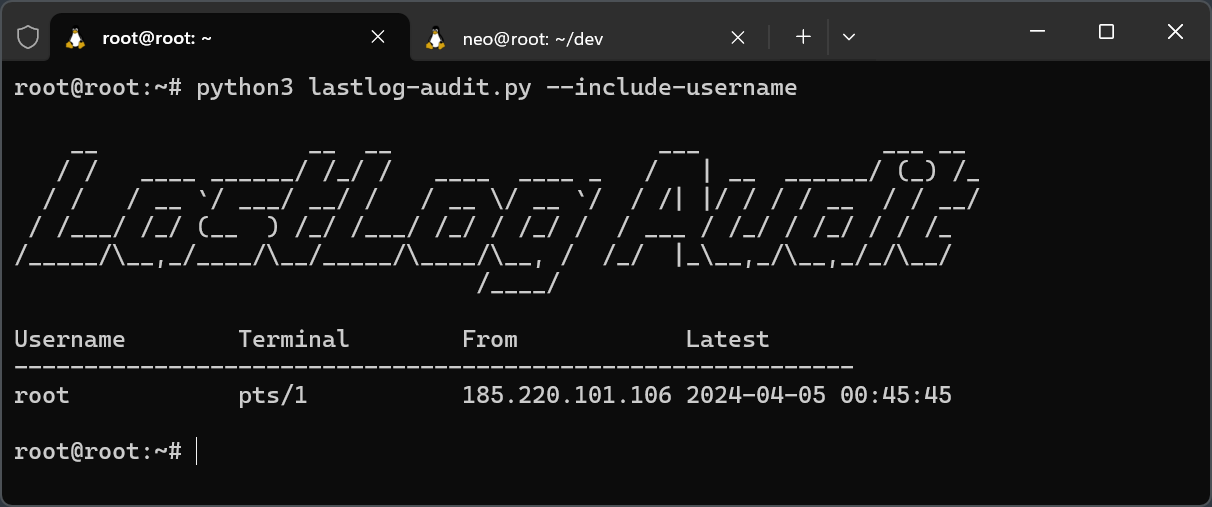
- --include-username: Includes usernames in the output. Note: This is accurate only when run on the target system due to UID mapping.
- --export EXPORT: Specifies the path for exporting the data. If left unspecified, the output is displayed in the console.
- --export-format {txt,csv}: Determines the format for exported data (txt or csv). This option requires --export to be set.
Here are a few examples to illustrate common LastLog Audit usage scenarios:
Analyze and display last login activities in a table format (default behavior):
python3 LastLog-Audit.pyExport last login activities to a CSV file:
python3 LastLog-Audit.py --export ~/output.csv --export-format csvInclude usernames and display output in line-by-line format:
python3 LastLog-Audit.py --include-username --display lineFor more details on all available options, run python3 LastLog-Audit.py -h.
Encountering issues? Don't worry. If you come across any problems or have questions, please don't hesitate to submit a ticket for assistance: Submit an issue on GitHub
We truly appreciate and welcome community involvement. Your contributions, feedback, and suggestions play a crucial role in improving the project for everyone. If you're interested in contributing or have ideas for enhancements, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request on our GitHub repository. Every contribution, no matter how big or small, is highly valued and greatly appreciated!
Explore the star history of this project and see how it has evolved over time:
Your support is greatly appreciated. We're grateful for every star! Your backing fuels our passion. ✨
This project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, Version 3.0. For more details, please refer to the LICENSE file in the repository: Read the license on GitHub