CatSmoothing smooths Shapely
geometries, LineString and (Multi)Polygon, using the Catmull-Rom spline algorithm and can compute tangent angles at each vertex of a list of lines.
The implementation is based on the
Splines
library, but offers performance improvements and additional features.
You can try CatSmoothing directly in your browser by clicking the Binder badge above.
- Written in Rust for performance and runs in parallel using Rayon
- Creating splines from 2D/3D vertices of a line that allows computing n-th derivatives
- Smoothing geometries with Centripetal Catmull-Rom splines with uniform spacing (spacing is determined iteratively based on the arc length of the input geometry)
- Computing tangent vectors at each vertex of a line
- Optional Gaussian filtering to reduce noise in input geometries before smoothing
Install CatSmoothing via pip or micromamba:
Using pip:
pip install catsmoothingUsing micromamba (or conda/mamba):
micromamba install -c conda-forge catsmoothingCatSmoothing provide one class called CatmullRom that is general purpose,
Catmull-Rom spline interpolation class. You can tweak the alpha parameter of
the class to interpolate with different versions of the Catmull-Rom spline
from 2D/3D vertices of a line and compute n-th derivatives.
For smoothing geometries, CatSmoothing uses the centripetal Catmull-Rom spline
algorithm, i.e., alpha=0.5. There are two functions that can be used
for smoothing geometries: smooth_linestrings and smooth_polygon. There is also
a function for computing tangent angles (in radians) at each vertex of a line.
For fitting a Catmull-Rom spline to a line, we can use the following code:
from catsmoothing import CatmullRom
verts = [(0, 0), (0, 0.5), (1.5, 1.5), (1.6, 1.5), (3, 0.2), (3, 0)]
n_pts = 15
smoothed = {}
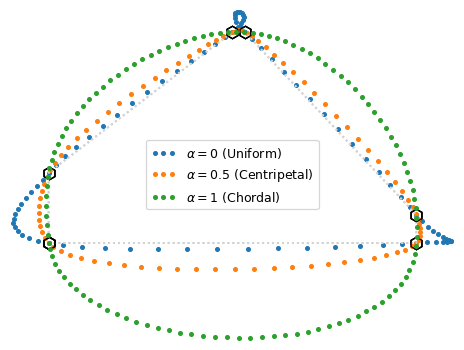
for alpha in (0, 0.5, 1):
s = CatmullRom(verts, alpha=alpha, bc_type="closed")
dots = int((s.grid[-1] - s.grid[0]) * n_pts) + 1
distances = s.grid[0] + np.arange(dots) / n_pts
smoothed[alpha] = s.evaluate(distances)For smoothing a geometry, we can use the following code:
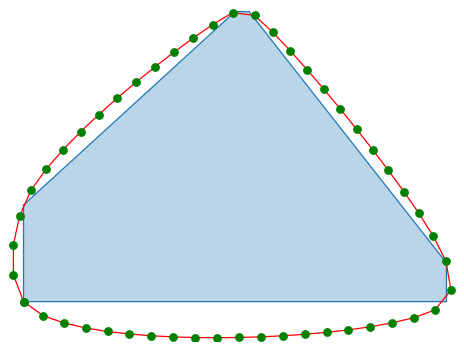
from shapely import Polygon
import catsmoothing as cs
poly = Polygon(verts)
ploy_smoothed = cs.smooth_polygon(poly, n_pts=50)For smoothing a noisy line, we can use the following code:
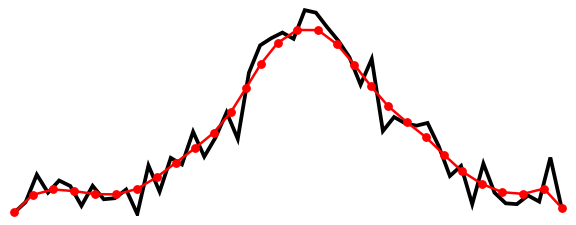
import numpy as np
from shapely import LineString
import catsmoothing as cs
rng = np.random.default_rng(123)
x = np.linspace(-3, 2.5, 50)
y = np.exp(-(x**2)) + 0.1 * rng.standard_normal(50)
line = LineString(np.c_[x, y])
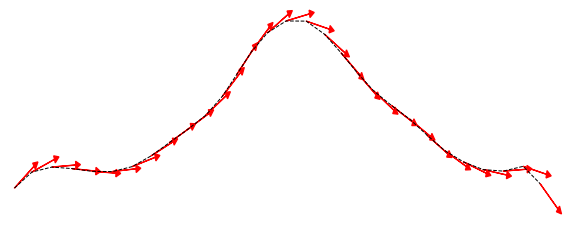
line_smoothed = cs.smooth_linestrings(line, n_pts=30, gaussian_sigmas=2)We can then compute the tangent angles in radians at each vertex of the smoothed line:
tangents = cs.linestrings_tangent_angles(line_smoothed)For more examples, visit the documentation.
We welcome contributions! For guidelines, please refer to the CONTRIBUTING.md and CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md.
CatSmoothing is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.