English | 简体中文
A collection of ready-to-run Jupyter* notebooks for learning and experimenting with the OpenVINO™ Toolkit. The notebooks provide an introduction to OpenVINO basics and teach developers how to leverage our API for optimized deep learning inference.
Notebooks with a button can be run without installing anything. Binder is a free online service with limited resources. For the best performance, please follow the Installation Guide and run the notebooks locally.
Brief tutorials that demonstrate how to use OpenVINO's Python API for inference.
| Notebook | Description | Preview |
|---|---|---|
| 001-hello-world |
Classify an image with OpenVINO |  |
| 002-openvino-api |
Learn the OpenVINO Python API |  |
| 003-hello-segmentation |
Semantic segmentation with OpenVINO |  |
| 004-hello-detection |
Text detection with OpenVINO |  |
Tutorials that explain how to optimize and quantize models with OpenVINO tools.
| Notebook | Description | Preview |
|---|---|---|
| 101-tensorflow-to-openvino |
Convert TensorFlow models to OpenVINO IR |  |
| 102-pytorch-onnx-to-openvino |
Convert PyTorch models to OpenVINO IR |  |
| 103-paddle-onnx-to-openvino |
Convert PaddlePaddle models to OpenVINO IR |  |
| 104-model-tools |
Download, convert and benchmark models from Open Model Zoo | |
| 105-language-quantize-bert | Optimize and quantize a pre-trained BERT model |
Demos that demonstrate inference on a particular model.
| Notebook | Description | Preview |
|---|---|---|
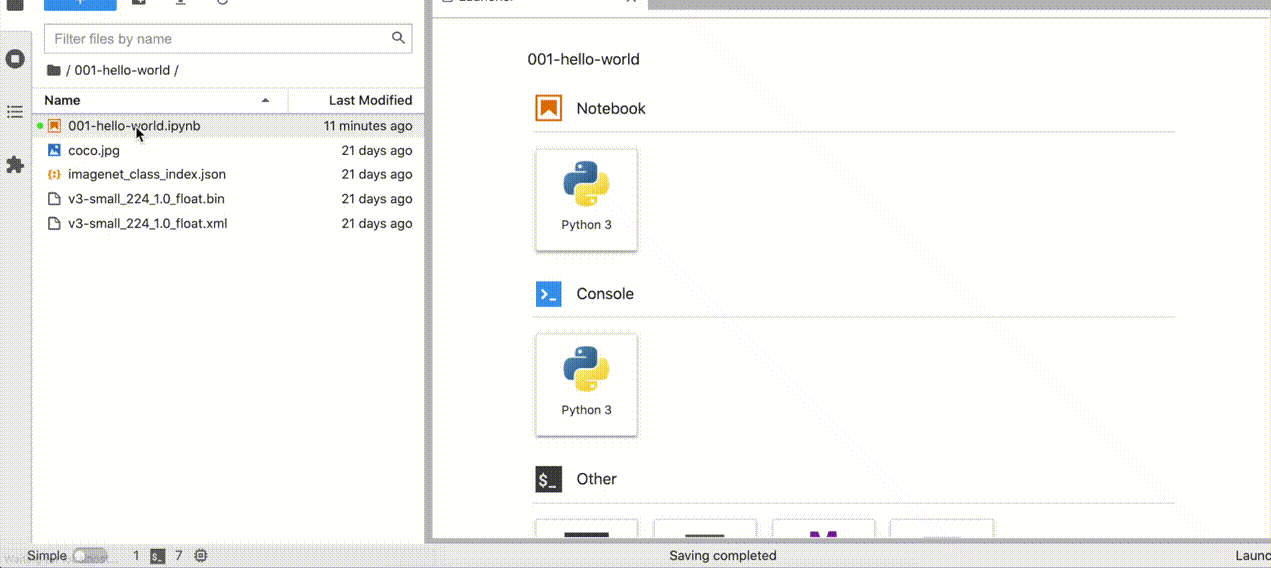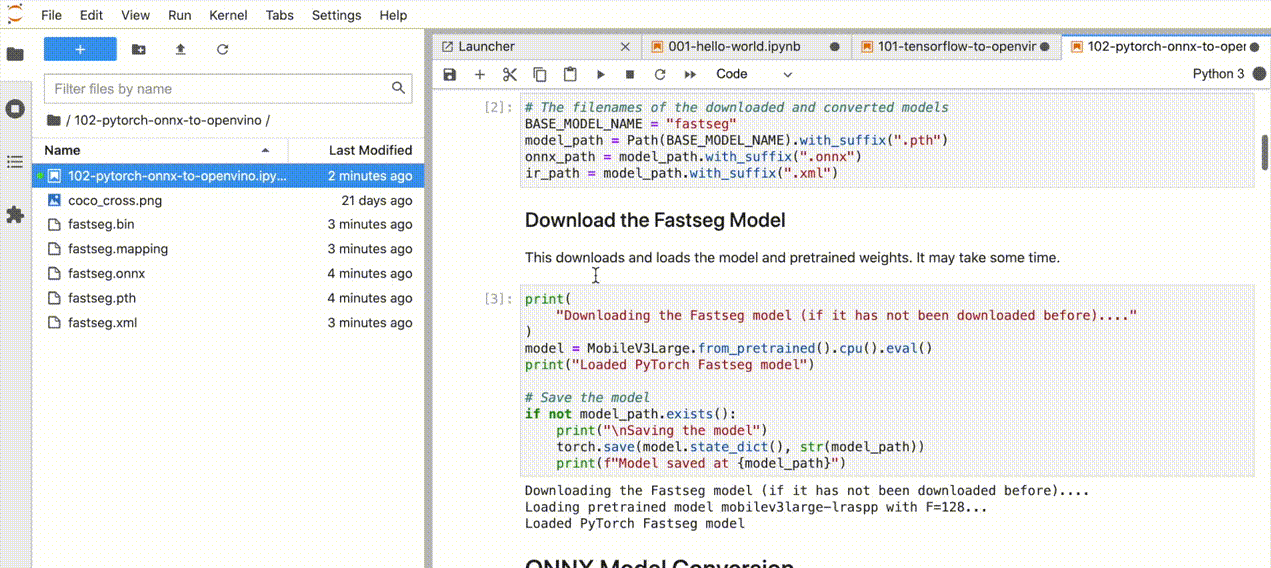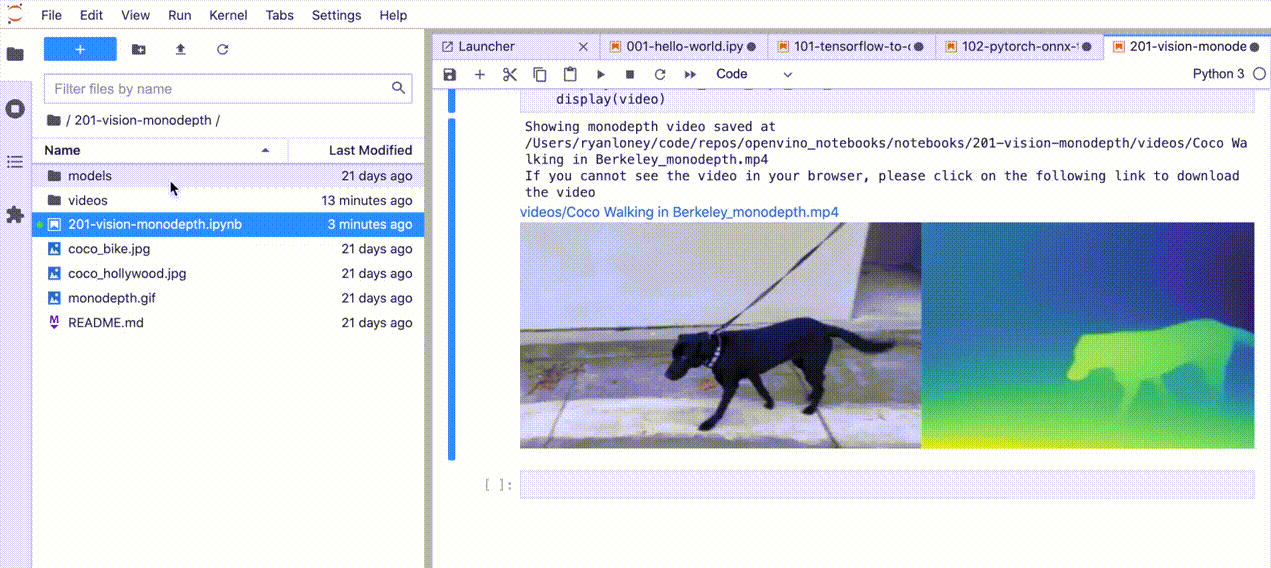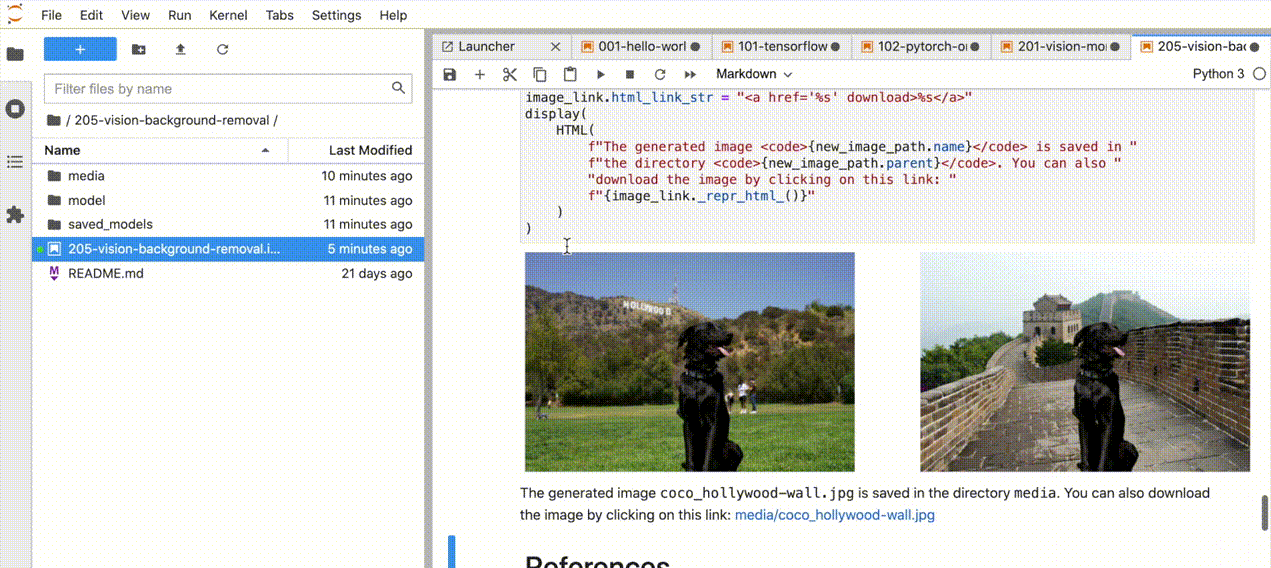
| 201-vision-monodepth |
Monocular depth estimation with images and video |  |
| 202-vision-superresolution-image |
Upscale raw images with a super resolution model |  → → |
| 202-vision-superresolution-video |
Turn 360p into 1080p video using a super resolution model |  → → |
| 205-vision-background-removal |
Remove and replace the background in an image using salient object detection |  |
| 206-vision-paddlegan-anime |
Turn an image into anime using a GAN |  → → |
| 207-vision-paddlegan-superresolution |
Upscale small images with superresolution using a PaddleGAN model |
Tutorials that include code to train neural networks.
| Notebook | Description | Preview |
|---|---|---|
| 301-tensorflow-training-openvino | Train a flower classification model from TensorFlow, then convert to OpenVINO IR |  |
| 301-tensorflow-training-openvino-pot | Use Post-training Optimization Tool (POT) to quantize the flowers model |
The notebooks run almost anywhere — your laptop, a cloud VM, or even a Docker container. The table below lists the supported operating systems and Python versions. Note: Python 3.9 is not supported yet, but it will be soon.
| Supported Operating System | Python Version (64-bit) |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu* 18.04 LTS, 64-bit | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 |
| Ubuntu* 20.04 LTS, 64-bit | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 |
| Red Hat* Enterprise Linux* 8, 64-bit | 3.6, 3.8 |
| CentOS* 7, 64-bit | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 |
| macOS* 10.15.x versions | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 |
| Windows 10*, 64-bit Pro, Enterprise or Education editions | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 |
| Windows Server* 2016 or higher | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8 |
OpenVINO Notebooks require Python and Git. For Python 3.8, C++ is also required. Select a guide for your operating system or environment:
| Windows 10 | Ubuntu | macOS | Red Hat | CentOS | Azure ML | Docker |
|---|
Or, if you have already installed Python, Git and C++, please follow the steps below.
python3 -m venv openvino_env
source openvino_env/bin/activatepython -m venv openvino_env
openvino_env\Scripts\activategit clone https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks.git
cd openvino_notebooksUpgrade pip to the latest version. Use pip's legacy dependency resolver to avoid dependency conflicts
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
python -m ipykernel install --user --name openvino_envIf you wish to launch only one notebook, like the Monodepth notebook, run the command below.
jupyter notebook notebooks/201-vision-monodepth/201-vision-monodepth.ipynbjupyter lab notebooksIn your browser, select a notebook from the file browser in Jupyter Lab using the left sidebar. Each tutorial is located in a subdirectory within the notebooks directory.
To end your Jupyter session, press Ctrl-c. This will prompt you to Shutdown this Jupyter server (y/[n])? enter y and hit Enter.
To deactivate your virtualenv, simply run deactivate from the terminal window where you activated openvino_env. This will deactivate your environment.
To reactivate your environment, run source openvino_env/bin/activate on Linux or openvino_env\Scripts\activate on Windows, then type jupyter lab or jupyter notebook to launch the notebooks again.
To remove your virtual environment, simply delete the openvino_env directory:
rm -rf openvino_envrmdir /s openvino_envjupyter kernelspec remove openvino_envIf these tips do not solve your problem, please open a discussion topic or create an issue!
- To check some common installation problems, run
python check_install.py. This script is located in the openvino_notebooks directory. Please run it after activating theopenvino_envvirtual environment. - If you get an
ImportError, doublecheck that you installed the Jupyter kernel. If necessary, choose the openvinoenv kernel from the _Kernel->Change Kernel menu) in Jupyter Lab or Jupyter Notebook - If OpenVINO is installed globally, do not run installation commands in a terminal where setupvars.bat or setupvars.sh are sourced.
- For Windows installation, we recommend using Command Prompt (cmd.exe), not PowerShell.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.