You can use this file as a template for your writeup if you want to submit it as a markdown file, but feel free to use some other method and submit a pdf if you prefer.
Behavioral Cloning Project
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Use the simulator to collect data of good driving behavior
- Build, a convolution neural network in Keras that predicts steering angles from images
- Train and validate the model with a training and validation set
- Test that the model successfully drives around track one without leaving the road
- Summarize the results with a written report
Here I will consider the rubric points individually and describe how I addressed each point in my implementation.
My project includes the following files:
- model.py containing the script to create and train the model
- drive.py for driving the car in autonomous mode
- model.h5 containing a trained convolution neural network
- writeup_report.md or writeup_report.pdf summarizing the results
Using the Udacity provided simulator and my drive.py file, the car can be driven autonomously around the track by executing
python drive.py model.h5The model.py file contains the code for training and saving the convolution neural network. The file shows the pipeline I used for training and validating the model, and it contains comments to explain how the code works.
My model consists of a convolution neural network with 3x3 filter sizes and depths between 32 and 128 (model.py lines 130-144)
The model includes ELU layers to introduce nonlinearity (code line 20), and the data is normalized in the model using a Keras lambda layer (code line 131). The layers also have l2 Regularizer.
The model contains dropout layers in order to reduce overfitting (model.py lines 138).
The model was trained and validated on different data sets to ensure that the model was not overfitting (code line 151-153). The model was tested by running it through the simulator and ensuring that the vehicle could stay on the track.
The model used an adam optimizer, the learning rate was tuned manually to 1e-4 (model.py line 152).
Training data was chosen to keep the vehicle driving on the road. I used a combination of center lane driving, recovering from the left and right sides of the road ...
For details about how I created the training data, see the next section.
The overall strategy for deriving a model architecture was to train faster and better model to overcome few difficulties faced by the car in extreme turns.
My first step was to use a convolution neural network model similar to the Nvidia Self driving car model. I thought this model might be appropriate because it has better performing history.
In order to gauge how well the model was working, I split my image and steering angle data into a training and validation set. I found that my first model had a low mean squared error on the training set but a high mean squared error on the validation set. This implied that the model was overfitting.
To combat the overfitting, I modified the model so that instead of RELU i used ELU. This showed significant improvement.
Then I ...
The final step was to run the simulator to see how well the car was driving around track one. There were a few spots where the vehicle fell off the track. I increased the epochs to improve the driving behavior in these cases.
At the end of the process, the vehicle is able to drive autonomously around the track without leaving the road.
The final model architecture (model.py lines 109-138) consisted of a convolution neural network with the following layers and layer sizes ...
Here is a visualization of the architecture (note: visualizing the architecture is optional according to the project rubric)
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
lambda_2 (Lambda) (None, 160, 320, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
cropping2d_2 (Cropping2D) (None, 62, 320, 3) 0
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_6 (Conv2D) (None, 29, 158, 24) 1824
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_7 (Conv2D) (None, 13, 77, 36) 21636
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_8 (Conv2D) (None, 5, 37, 48) 43248
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_9 (Conv2D) (None, 3, 35, 64) 27712
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_10 (Conv2D) (None, 1, 33, 64) 36928
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 1, 33, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten_2 (Flatten) (None, 2112) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 100) 211300
_________________________________________________________________
dense_6 (Dense) (None, 50) 5050
_________________________________________________________________
dense_7 (Dense) (None, 10) 510
_________________________________________________________________
dense_8 (Dense) (None, 1) 11
=================================================================
Total params: 348,219
Trainable params: 348,219
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
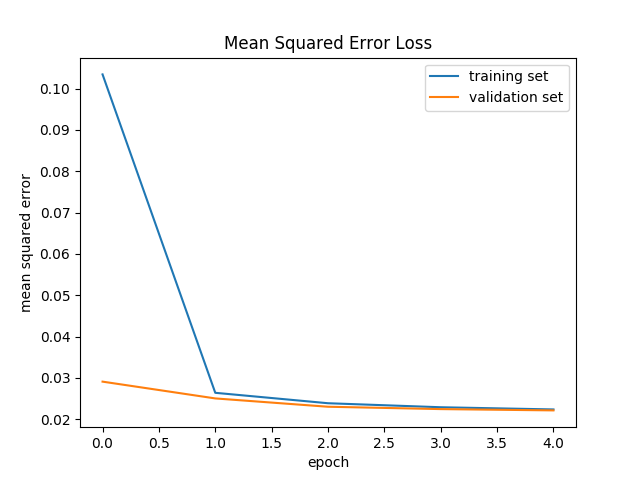
After training the following plot was observed:
To capture good driving behavior, I first recorded two laps on track one using center lane driving. Here is an example image of center lane driving:
I then recorded the vehicle recovering from the left side and right sides of the road back to center so that the vehicle would learn to about extreme turns. These images show what a recovery looks like starting from :
Then I repeated this process on track two in order to get more data points.
To augment the data sat, I also flipped images and angles thinking that this would make an unbiased model as the previous model contained left bias. For example, here is an image that has then been flipped:
After the collection process, I had X number of data points. I then preprocessed this data by cropping image in the keras model itself.
I finally randomly shuffled the data set and put 20% of the data into a validation set.
I used this training data for training the model. The validation set helped determine if the model was over or under fitting.
The final video is as follows