-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 8.4k
Nacos Config En
Nacos is an easy-to-use dynamic service discovery, configuration and service management platform for building cloud native applications.
Use Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config to quickly access Nacos configuration management capabilities based on Spring Cloud’s programming model.
please use the starter with the group ID as com.alibaba.cloud and the artifact ID as spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
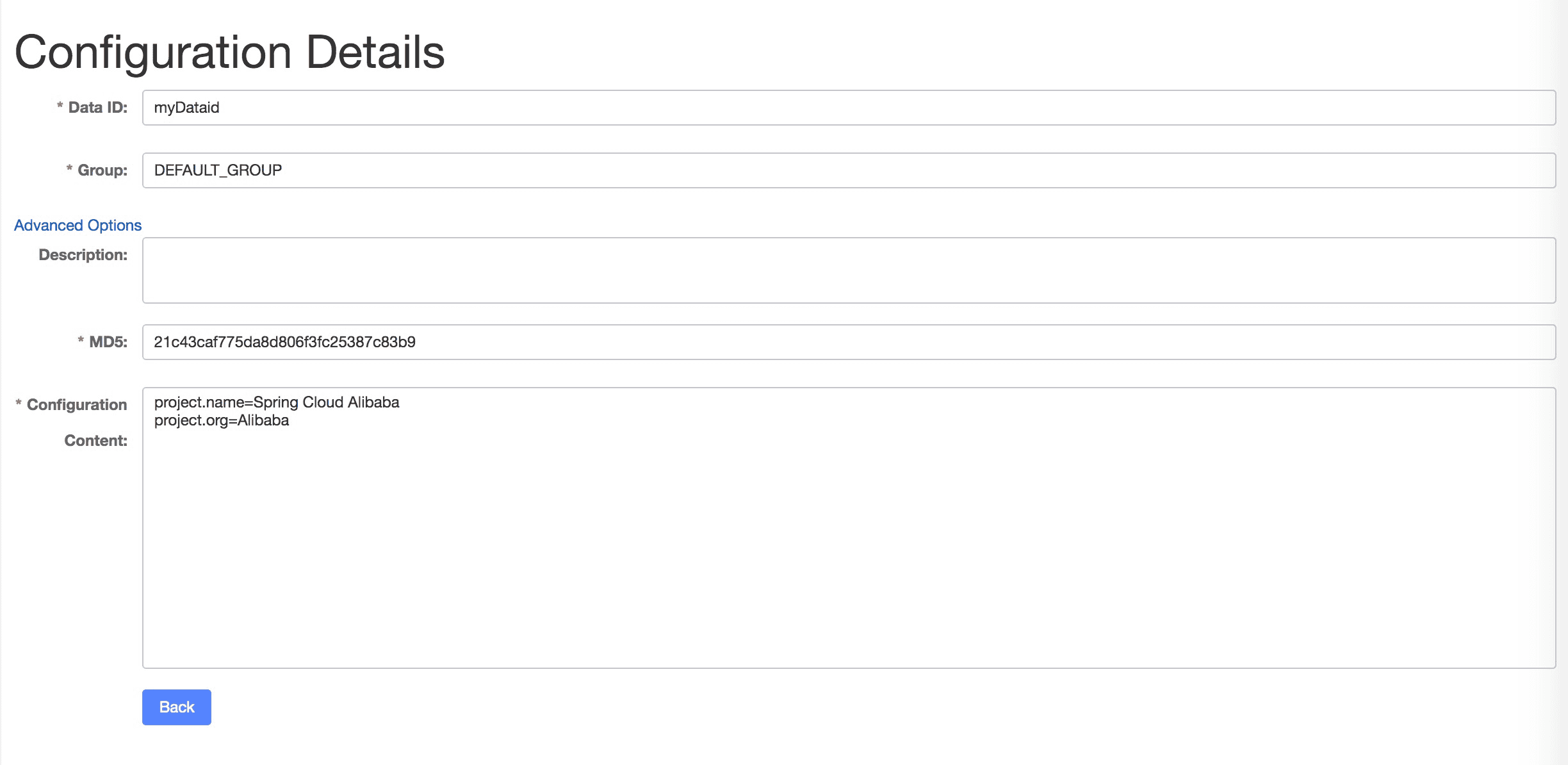
</dependency>Nacos Config uses DataId and GROUP to determine a configuration.
The following figure shows that the DataId uses myDataid, GROUP uses DEFAULT_GROUP, and configures a configuration item of the format Properties:
For specific startup methods, refer to the "Nacos Server Startup" section of the Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Discovery section.
After the Nacos Server is started, add how to configure it:
Data ID: nacos-config.properties
Group : DEFAULT_GROUP
Configuration format: Properties
Configuration content: user.name=nacos-config-properties
user.age=90|
Note
|
The default file extension of DataId is properties. |
If you want to use Nacos to manage externalized configurations for your applications, please use the starter with the group ID as com.alibaba.cloud and the artifact ID as spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>Now we can create a standard Spring Boot application.
@SpringBootApplication
public class NacosConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(NacosConfigApplication.class, args);
String userName = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("user.name");
String userAge = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("user.age");
System.err.println("user name :" +userName+"; age: "+userAge);
}
}Before running this example, we need to configure the address of the Nacos server in bootstrap.properties. For example:
# DataId By default, the `spring.application.name` configuration is combined with the file extension (the configuration format uses properties by default), and the GROUP is not configured to use DEFAULT_GROUP by default. Therefore, the Nacos Config configuration corresponding to the configuration file has a DataId of nacos-config.properties and a GROUP of DEFAULT_GROUP
spring.application.name=nacos-config
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848|
Note
|
If you use domain name to access Nacos, the format of spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr should be Domain name:port.
For example, if the Nacos domain name is abc.com.nacos, and the listerner port is 80, then the configuration should be spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=abc.com.nacos:80.
Port 80 cannot be omitted.
|
Run this example and you can see the following output:
2018-11-02 14:24:51.638 INFO 32700 --- [main] c.a.demo.provider.NacosConfigApplication : Started NacosConfigApplication in 14.645 seconds (JVM running for 15.139)
user name :nacos-config-properties; age: 90
2018-11-02 14:24:51.688 INFO 32700 --- [-127.0.0.1:8848] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@a8c5e74: startup date [Fri Nov 02 14:24:51 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchyNacos Config supports yaml format as well. You only need to complete the following 2 steps.
-
In the bootstrap.properties file, add the following line to claim that the format of DataId is yaml. As follows:
spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension=yaml-
Add a configuration with the DataId in yaml format on the Nacos console, as shown below:
Data ID: nacos-config.yaml
Group : DEFAULT_GROUP
Configuration format: YAML
Configuration content: user.name: nacos-config-yaml
user.age: 68After completing the preivous two steps, restart the testing program and you will see the following result.
2018-11-02 14:59:00.484 INFO 32928 --- [main] c.a.demo.provider.NacosConfigApplication:Started NacosConfigApplication in 14.183 seconds (JVM running for 14.671)
user name :nacos-config-yaml; age: 68
2018-11-02 14:59:00.529 INFO 32928 --- [-127.0.0.1:8848] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@265a478e: startup date [Fri Nov 02 14:59:00 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchyNacos Config also supports dynamic configuration updates. The code for starting Spring Boot application testing is as follows:
@SpringBootApplication
public class NacosConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(NacosConfigApplication.class, args);
while(true) {
//When configurations are refreshed dynamically, they will be updated in the Enviroment, therefore here we retrieve configurations from Environment every other second.
String userName = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("user.name");
String userAge = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("user.age");
System.err.println("user name :" + userName + "; age: " + userAge);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
}
}When user.name is changed, the latest value can be retrieved from the application, as shown below:
user name :nacos-config-yaml; age: 68
user name :nacos-config-yaml; age: 68
user name :nacos-config-yaml; age: 68
2018-11-02 15:04:25.069 INFO 32957 --- [-127.0.0.1:8848] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Started application in 0.144 seconds (JVM running for 71.752)
2018-11-02 15:04:25.070 INFO 32957 --- [-127.0.0.1:8848] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@10c89124: startup date [Fri Nov 02 15:04:25 CST 2018]; parent: org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@6520af7
2018-11-02 15:04:25.071 INFO 32957 --- [-127.0.0.1:8848] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@6520af7: startup date [Fri Nov 02 15:04:24 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
//Read the updated value from Enviroment
user name :nacos-config-yaml-update; age: 68
user name :nacos-config-yaml-update; age: 68|
Note
|
You can disable automatic refresh with this setting`spring.cloud.nacos.config.refresh.enabled=false`. |
When configurations are loaded by Nacos Config, basic configurations with DataId of ${spring.application.name}. ${file-extension:properties} , and DataId of ${spring.application.name}-${profile}. ${file-extension:properties} are also loaded. If you need to use different configurations from different environments, you can use the ${spring.profiles.active} configuration provided by Spring.
spring.profiles.active=develop|
Note
|
When specified in configuration files, ${spring.profiles.active} must be placed in bootstrap.properties. |
Add a basic configuration in Nacos, with a DataId of nacos-config-develop.yaml, as shown below:
Data ID: nacos-config-develop.yaml
Group : DEFAULT_GROUP
Configuration format: YAML
Configuration content: current.env: develop-envRun the following Spring Boot application testing code:
@SpringBootApplication
public class NacosConfigApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(NacosConfigApplication.class, args);
while(true) {
String userName = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("user.name");
String userAge = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("user.age");
//Get the current deployment environment
String currentEnv = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("current.env");
System.err.println("in "+currentEnv+" enviroment; "+"user name :" + userName + "; age: " + userAge);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
}
}After started, you can see the output as follows in the console:
in develop-env enviroment; user name :nacos-config-yaml-update; age: 68
2018-11-02 15:34:25.013 INFO 33014 --- [ Thread-11] ConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@6f1c29b7: startup date [Fri Nov 02 15:33:57 CST 2018]; parent: org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@63355449To switch to the production environment, you only need to change the parameter of ${spring.profiles.active}. As show below:
spring.profiles.active=productAt the same time, add the basic configuration with the DataId in the Nacos of your production environment. For example, you can add the configuration with the DataId of nacos-config-product.yaml in Nacos of your production environment:
Data ID: nacos-config-product.yaml
Group : DEFAULT_GROUP
Configuration format: YAML
Configuration content: current.env: product-envStart the testing program and you will see the following result:
in product-env enviroment; user name :nacos-config-yaml-update; age: 68
2018-11-02 15:42:14.628 INFO 33024 --- [Thread-11] ConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@6aa8e115: startup date [Fri Nov 02 15:42:03 CST 2018]; parent: org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@19bb07ed|
Note
|
In this example, we coded the configuration in the configuration file by using the spring.profiles.active=<profilename> method. In real scenarios, this variable needs to be different in different environment. You can use the -Dspring.profiles.active=<profile> parameter to specify the configuration so that you can switch between different environments easily.
|
For details about namespaces in Nacos, refer to Nacos Concepts
Namespaces are used to isolate configurations for different tenants. Groups and Data IDs can be the same across different namespaces. Typical scenarios of namespaces is the isolation of configurations for different environments, for example, isolation between development/testing environments and production environments(configurations and services and so on).
The “Public” namespace of Nacos is used if no namespace is specified in ${spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace}. You can also specify a custom namespace in the following way:
spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=b3404bc0-d7dc-4855-b519-570ed34b62d7|
Note
|
This configuration must be in the bootstrap.properties file. The value of spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace is the id of the namespace, and the value of id can be retrieved from the Nacos console. Do not select other namespaces when adding configurations. Otherwise configurations cannot be retrieved properly.
|
DEFAULT_GROUP is used by default when no {spring.cloud.nacos.config.group} configuration is defined. If you need to define your own group, you can define it in the following property:
spring.cloud.nacos.config.group=DEVELOP_GROUP|
Note
|
This configuration must be in the bootstrap.properties file, and the value of Group must be the same with the value of spring.cloud.nacos.config.group.
|
As of Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config, data id can be self-defined. For detailed design of this part, refer to Github issue. The following is a complete sample:
spring.application.name=opensource-service-provider
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848
# config external configuration
# 1. Data Id is in the default group of DEFAULT_GROUP, and dynamic refresh of configurations is not supported.
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[0].data-id=ext-config-common01.properties
# 2. Data Id is not in the default group, and dynamic refresh of configurations is not supported.
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[1].data-id=ext-config-common02.properties
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[1].group=GLOBALE_GROUP
# 3. Data Id is not in the default group and dynamic referesh of configurations is supported.
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[2].data-id=ext-config-common03.properties
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[2].group=REFRESH_GROUP
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[2].refresh=trueWe can see that:
-
Support multiple data ids by configuring
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[n].data-id. -
Customize the group of data id by configuring
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[n].group. If not specified, DEFAULT_GROUP is used. -
Control whether this data id supports dynamic refresh of configurations is supported when configurations are changed by configuring
spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[n].refresh. It’s not supported by default.
|
Note
|
When multiple Data Ids are configured at the same time, the priority is defined by the value of “n” in spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[n].data-id. The bigger the value, the higher the priority.
|
|
Note
|
The value of spring.cloud.nacos.config.ext-config[n].data-id must have a file extension, and it could be properties or yaml/yml.
The setting in spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension does not have any impact on the custom Data Id file extension.
|
The configuration of custom Data Id allows the sharing of configurations among multiple applications, and also enables support of multiple configurations for one application.
To share the data id among multiple applications in a clearer manner, you can also use the following method:
spring.cloud.nacos.config.shared-dataids=bootstrap-common.properties,all-common.properties
spring.cloud.nacos.config.refreshable-dataids=bootstrap-common.propertiesWe can see that:
-
Multiple shared data ids can be configured using
spring.cloud.nacos.config.shared-dataids, and the data ids are separted by commas. -
spring.cloud.nacos.config.refreshable-dataidsis used to control which data ids will be refreshed dynamically when configurations are updated, and that the latest configuration values can be retrieved by applications. Data ids are separated with commas. If not specified, all shared data ids will not be dynamically refreshed.
|
Note
|
When using spring.cloud.nacos.config.shared-dataids to configure multiple shared data ids,
we agree on the following priority between the shared configurations: Priorities are decided based on the order in which the configurations appear. The one that occurs later is higher in priority than the one that appears first.
|
|
Note
|
When using spring.cloud.nacos.config.shared-dataids, the data Id must have a file extension, and it could be properties or yaml/yml.
And the configuration in spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension does not have any impact on the customized Data Id file extension.
|
|
Note
|
When spring.cloud.nacos.config.refreshable-dataids specifies the data ids that support dynamic refresh, the corresponding values of the data ids should also specify file extensions.
|
Nacos Config provides an Endpoint internally with a corresponding endpoint id of nacos-config.
Endpoint exposed json contains three properties:
-
Sources: Current application configuration data information
-
RefreshHistory: Configuration refresh history
-
NacosConfigProperties: Shows the current basic Nacos configurations of the current service
The followings shows how a service instance accesses the Endpoint:
{
"NacosConfigProperties": {
"serverAddr": "127.0.0.1:8848",
"encode": null,
"group": "DEFAULT_GROUP",
"prefix": null,
"fileExtension": "properties",
"timeout": 3000,
"endpoint": null,
"namespace": null,
"accessKey": null,
"secretKey": null,
"contextPath": null,
"clusterName": null,
"name": null,
"sharedDataids": "base-common.properties,common.properties",
"refreshableDataids": "common.properties",
"extConfig": null
},
"RefreshHistory": [{
"timestamp": "2019-07-29 11:20:04",
"dataId": "nacos-config-example.properties",
"md5": "7d5d7f1051ff6571e2ec9f90887d9d91"
}],
"Sources": [{
"lastSynced": "2019-07-29 11:19:04",
"dataId": "common.properties"
}, {
"lastSynced": "2019-07-29 11:19:04",
"dataId": "base-common.properties"
}, {
"lastSynced": "2019-07-29 11:19:04",
"dataId": "nacos-config-example.properties"
}]
}set spring.cloud.nacos.config.enabled = false to disable Spring Cloud Nacos Config AutoConfiguration.
The following shows the other configurations of the starter of Nacos Config:
| Configuration | Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Server address |
|
IP and port of the Nacos Server listener |
|
Dataid from nacos config |
|
First take the prefix, then go to the name, and finally take spring.application.name |
|
Dataid from nacos config |
|
First take the prefix, then go to the name, and finally take spring.application.name |
|
Encode for nacos config content |
|
Encode for nacos config content |
|
GROUP for nacos config |
|
|
GROUP for nacos config |
The suffix of nacos config dataId, also the file extension of config content. |
|
|
The suffix of nacos config dataId, also the file extension of config content(now support properties or yaml(yml)) |
Timeout for get config from nacos |
|
|
Timeout for get config from nacos |
Endpoint |
|
Endpoint |
|
Namespace |
|
Namespace |
|
AccessKey |
|
Alibaba Cloud account accesskey |
|
SecretKey |
|
Alibaba Cloud account secretkey |
|
The context path of Nacos Server |
|
The context path of Nacos Server |
|
Cluster name |
|
Cluster name |
|
Dataid for Shared Configuration |
|
Dataid for Shared Configuration, split by "," |
|
Dynamic refresh dataid for Shared Configuration |
|
Dynamic refresh dataid for Shared Configuration, split by "," |
|
custom dataid |
|
It’s a List,build up by |
- 文档
- Documents
- Open Source components
- Commercial components
- Example
- awesome spring cloud alibaba