Python versions supported:
- Alberto Chimenti (University of Padova)
- Clara Eminente (University of Padova)
- Matteo Guida (University of Padova)
This work is based on some of the results obtained in [1]
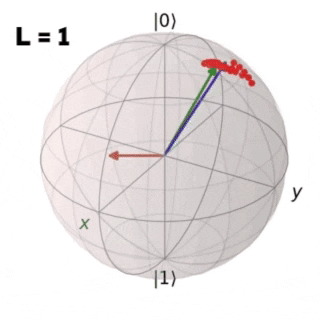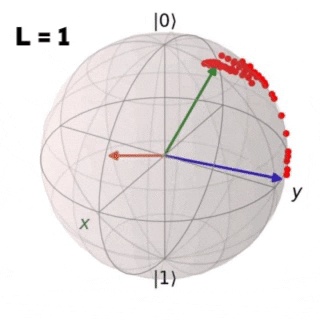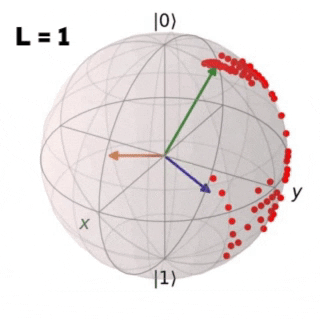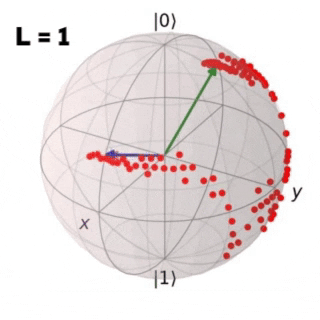
Controlling non-integrable many-body quantum systems of interacting qubits is crucial in many areas of physics and in particular in quantum information science. In the following work a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm is implemented in order to find an optimal protocol that drives a quantum system from an initial to a target state in two study cases: a single isolated qubit and a closed chain of L coupled qubits. For both cases the obtained results are compared with the ones achieved through Stochastic Descent (SD).
A complete explanation of the results and the code development can be found in Report.pdf.
In order to run the training just run:
python RL_training.py
To run SD:
python script_SD.py
In both the program use flag -h or --help to print a brief description of the script and useful informations about init parameters.
[1] Bukov, A. G. R. Day, D. Sels, P. Weinberg, A. Polkovnikov, and P. Mehta, Reinforcement learning in different phases of quantum control, Phys. Rev. X8, 031086 (2018).
[2] S. Montangero, Introduction to Tensor Network Methods: Numerical simulations of low-dimensional many body quantum systems (Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2018).