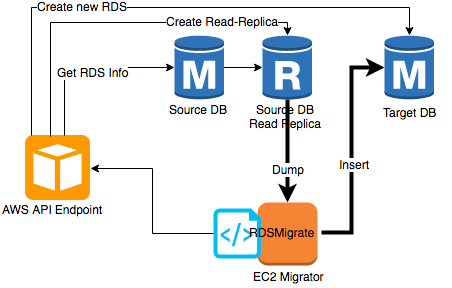
A fully automated RDS migration (to encrypted) script.
Create a usable copy of an existing MySQL RDS with encryption enabled (KMS).
In detail, the following are the operations that will be performed:
- Perform flight check
- Get information about the source RDS
- Create a temporary read replica for the source RDS. This will be used to get a consistent copy of the source RDS
- Create the KMS key for encrypting the target RDS
- Create the target encrypted RDS
- Stop replication between the source RDS and the temporary read replica
- Dump and export the data from the temporary read replica to the target RDS
- Copy RDS tags from the source RDS to the target RDS
- Copy application users from the temporary read replica to the target RDS
- Create replication user in the source RDS
- Let the target RDS catch up with the source RDS
- Rename the source RDS to a temporary name
- Rename the target RDS to the original name of the source RDS (so app doesn't need to be changed)
- Stop replication between the source RDS and target RDS
- Delete the temporary source RDS read replica
You need the following to run the script.
-
An EC2 instance (t2.micro would suffice). This instance must be able to connect to both the source and target RDS.
a. IAM Role. Create an IAM role for the EC2 instance with the following inline policies and permissions.
Role Name: EC2RoleDBReplication
Role Inline Policy Name:
AccessToKMS AccessToRDS AccessToIAM- AccessToKMS
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "Stmt1498031627000", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "kms:ListAliases", "kms:ListKeys", "kms:CreateKey", "kms:CreateAlias", "kms:Describe*" ], "Resource": [ "*" ] } ] }- AccessToRDS
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "Stmt1498038607000", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "rds:DescribeDBClusters", "rds:DescribeDBInstances" ], "Resource": [ "*" ] }, { "Sid": "Stmt1498038692000", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "rds:CreateDBInstanceReadReplica", "rds:Describe*", "rds:CreateDBInstance", "rds:ModifyDBInstance", "rds:DeleteDBInstance", "rds:AddTagsToResource", "rds:ListTagsForResource" ], "Resource": [ "*" ] } ] }- AccessToIAM
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "Stmt1499865345000", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "iam:ListPolicies", "iam:ListRoles", "iam:ListRolePolicies", "iam:GetRolePolicy" ], "Resource": [ "*" ] } ] }b. Security Group. Modify the security group of the source and target RDS instance to allow port 3306 from the EC2 replication instance. Also, make sure that the target RDS can connect to port 3306 of the source RDS.
c. Launch instance. In creating an instance for replication, attach the IAM role and security group created.
-
AWS CLI installed in the EC2 instance
-
MySQL client package
sudo yum install -y mysql
- pv tool which monitor the progress of data through a pipe
sudo yum install -y pv
- Clone (or download) the repository
cd /home/ec2-user/
git clone https://github.com/VoyagerInnovations/RDSMigration.git
- Run the script
Usage: ./migrate_database.sh [-i <iam_user_name>] [-n <db_instance_identifier>] [-u <db_admin_user>] [-p <db_admin_passwd>] [-m <yes/no> ] [-d <db_name>] [-a <account_number>] [-z <region_name>]
Options:
-i <iam_user_name> = IAM user who will administer the KMS key to be used in encrypting the database
-n <db_instance_identifier> = (Source) RDS Instance Identifier
-u <db_admin_user> = (Source) RDS DB Admin User
-p <db_admin_passwd> = (Source) RDS DB Admin Password
-m <yes/no> = Indicate if the RDS instance contains multiple databases
-d <db_name> = Specify the database name. This option can be excluded/skipped if the value of '-m' is yes
-a <account_number> = Specify the AWS account number where the resources resides
-z <region_name> = Specify the AWS Region where the resources resides
Example:
- For RDS with single database:
./migrate_database.sh -i test_user -n TestDB -u admin -p admin1234 -m no -d testdb -a 123456789012 -z ap-southeast-1- For RDS with multiple databases:
./migrate_database.sh -i test_user -n TestDB -u admin -p admin1234 -m yes -a 123456789012 -z ap-southeast-1- This script only works for AWS MySQL RDS
- Check the target DB data
- Stop the old RDS instance
- Check application user experience
- Delete the old RDS instance
- Terminate the EC2 migration instance (if no longer necessary)
- For RDS instances with existing read replica before migration, re-create the read replica to be able to catch up to the master.