2 ~ 6 Sets Venn Diagram For Python
Checkout this repository first:
git clone https://github.com/tctianchi/pyvenn.git
cd pyvennUse magic function in an ipython notebook:
%matplotlib inline
import vennOr use a non-interactive backend:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
import vennFetch labels for each subset of the venn diagram. The input argument is an array of iterable data(list, set, etc.). You will get a mapping table, where "10" indicates the number of elements in set 1 but not in set 2, "01" indicates the number of elements in set 2 but not in set 1, and so on.
In [5]: labels = venn.get_labels([
range(10),
range(5, 15)
], fill=['number', 'logic'])
In [6]: print labels
Out [6]: {'01': '01: 5', '10': '10: 5', '11': '11: 5'}Plot functions are based on the labels:
fig, ax = venn.venn2(labels, names=['list 1', 'list 2'])
fig.show()More examples:
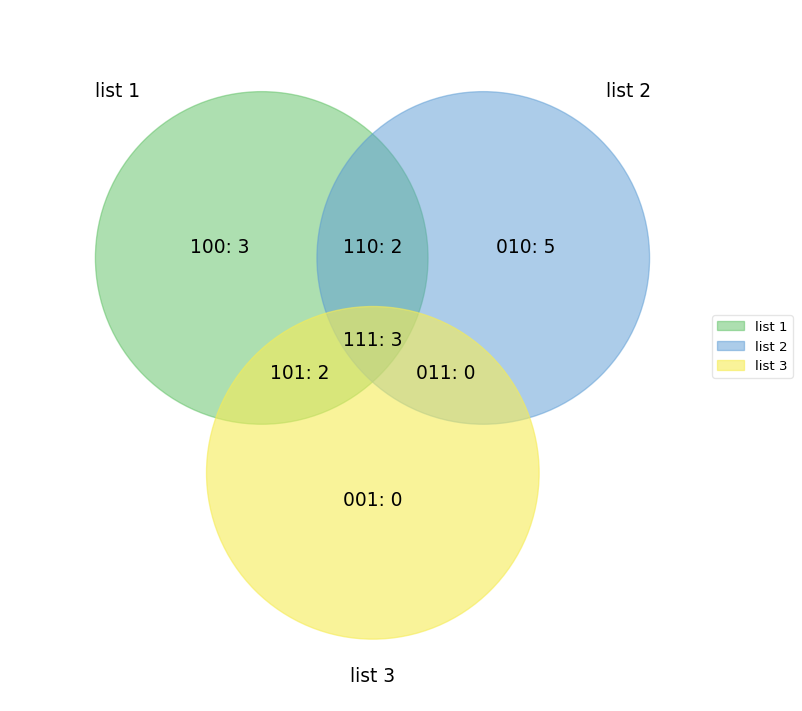
labels = venn.get_labels([range(10), range(5, 15), range(3, 8)], fill=['number', 'logic'])
fig, ax = venn.venn3(labels, names=['list 1', 'list 2', 'list 3'])
fig.show()labels = venn.get_labels([range(10), range(5, 15), range(3, 8), range(8, 17)], fill=['number', 'logic'])
fig, ax = venn.venn4(labels, names=['list 1', 'list 2', 'list 3', 'list 4'])
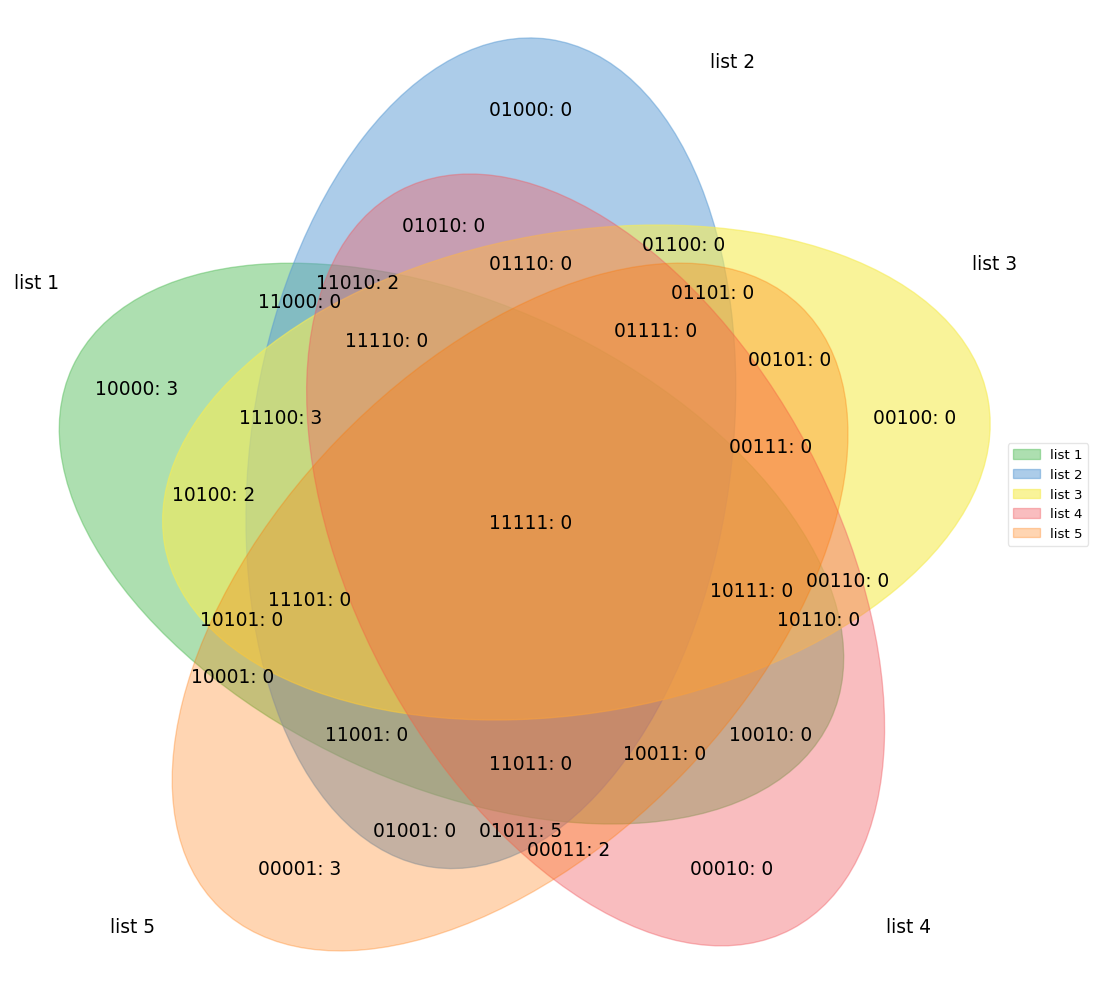
fig.show()labels = venn.get_labels([range(10), range(5, 15), range(3, 8), range(8, 17), range(10, 20)], fill=['number', 'logic'])
fig, ax = venn.venn5(labels, names=['list 1', 'list 2', 'list 3', 'list 4', 'list 5'])
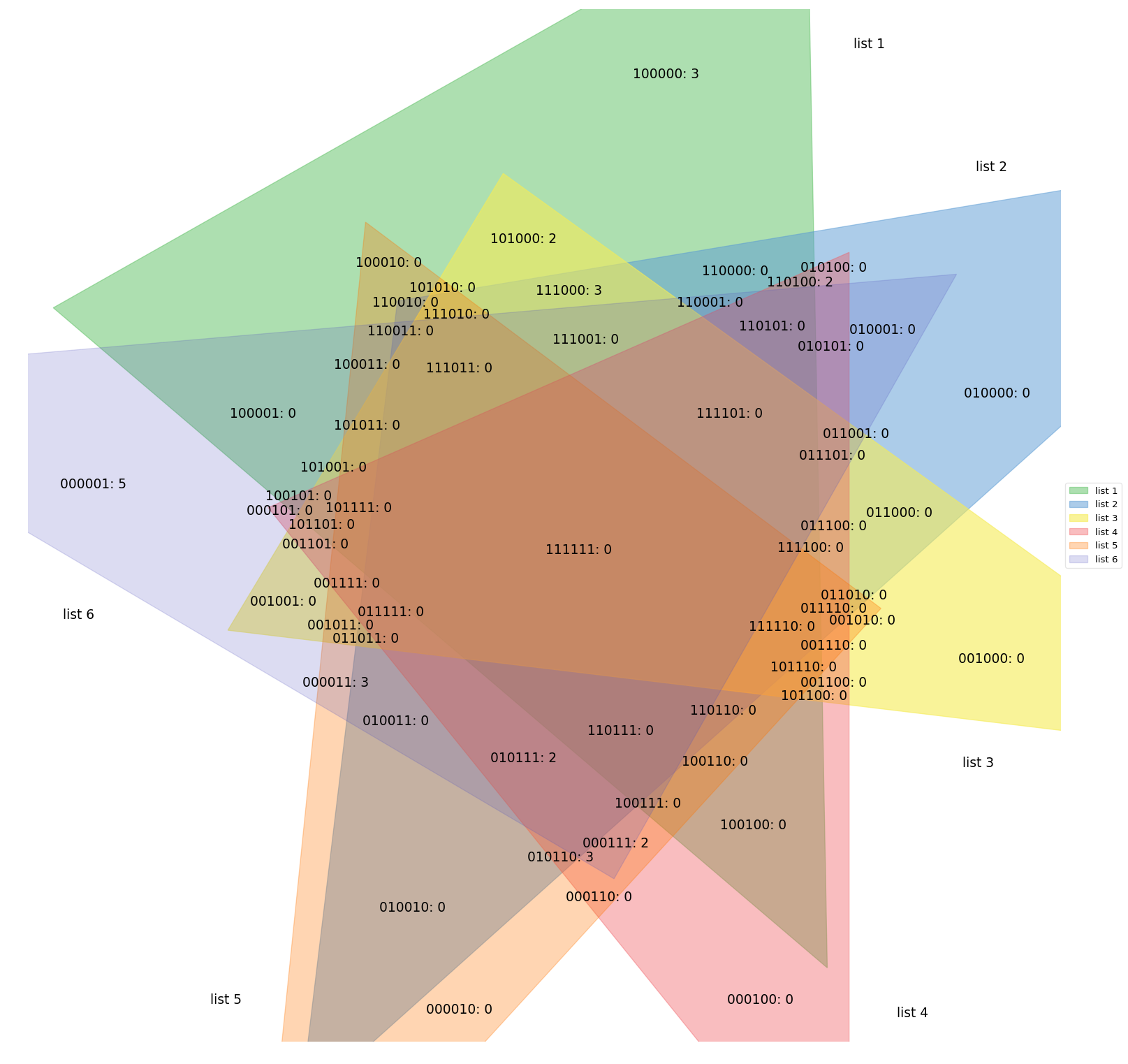
fig.show()labels = venn.get_labels([range(10), range(5, 15), range(3, 8), range(8, 17), range(10, 20), range(13, 25)], fill=['number', 'logic'])
fig, ax = venn.venn6(labels, names=['list 1', 'list 2', 'list 3', 'list 4', 'list 5', 'list 6'])
fig.show()