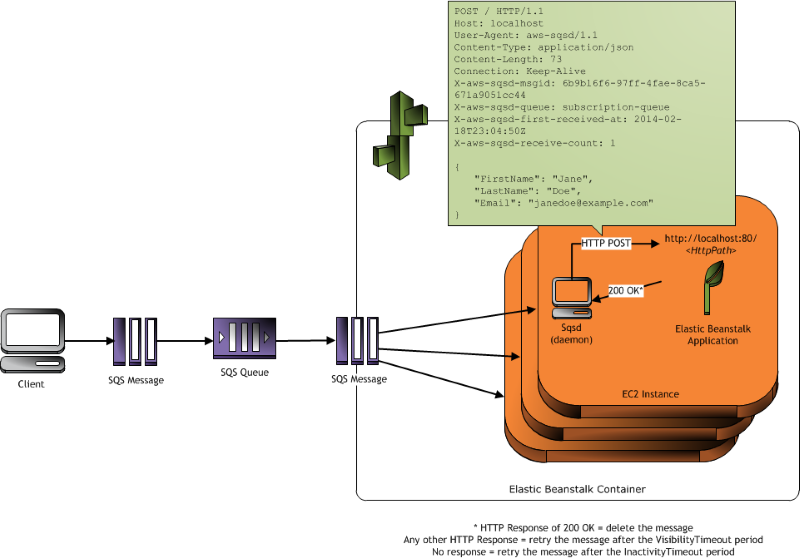
AWS Elastic Beanstalk SQS Daemon simulator.
This program simulates the SQS deamon which sends the queue messages to a HTTP endpoint as described in https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/using-features-managing-env-tiers.html
Setup your AWS credentials and region using environment variables. See https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-environment.html
Required flags are sqs-url or sqs-create-queue, but both can also be set using evironment variables SQS_URL or SQS_CREATE_QUEUE
Usage of aws_beanstalk_sqs_daemon.exe:
-connections uint
The maximum number of concurrent connections that the daemon can make to the HTTP endpoint. (default 50)
-sqs-create-queue string
Creates a queue with this name (use '[hostname]' as replacer for the local host name), subscribes it to the SNS topics listed in subscribe-to-sns-arns and then uses this queue to receive messages. Use this or sqs-url.
-http-timeout uint
Timeout in seconds to wait for HTTP requests. (default 30)
-http-url string
The URL to the application that will receive the data from the Amazon SQS queue. The data is inserted into the message body of an HTTP POST message. (default "http://localhost:9900/sqs")
-mime-type string
Indicate the MIME type that the HTTP POST message uses. (default "application/json")
-sqs-url string
The URL of the Amazon SQS queue from which messages are received. Use this or create-queue.
-subscribe-to-sns-arns string
Comma separated list of SNS topic ARNs to subscribe the created queue to (for existing queues no new subscriptions will be added).
-v Log all the things.
-visibility-timeout uint
Indicate the amount of time, in seconds, an incoming message from the Amazon SQS queue is locked for processing. After the configured amount of time has passed, the message is again made visible in the queue for another daemon to read. (default 60)