TIMECOP is a RESTful webservice engine that evaluates univariate and multivariate timeseries. It considerates that the time series has 3 stages: the current state of the time series as the last five points, the past state as all the previous points before the current state and the future state as the forecast of the next 5 points.
The aim of TIMECOP is to get insight on the behavior of the time series. To achieve this, the engine compares several time series forecasting algorithms and select the best one according to the MAE (mean absolute error) metric. The 3 different algorithms that compounds the engine are: Holt-Winters, ARIMA, and Recurrent Neural Networks using LSTM cells.
In the end we will obtain:
-
The best of the thre evaluated algos regarding the MSE metric.
-
Past anomalies. The past state points of the time series that have been considerated as anomalous.
-
Current anomalies. The engine returns a flag that tells you whether there are anomalies in the last 5 points or not and the current anomalous points if there were.
-
Future time series forecast of the next five points.
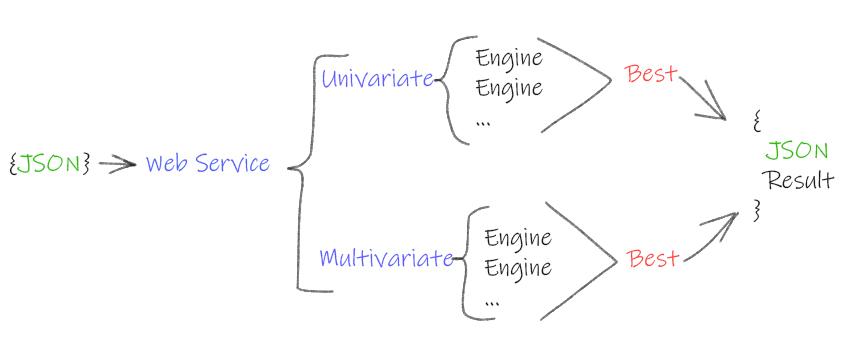
To use TIMECOP engine you will need to send a univariate or multivariate time series data points in a json format to the webservice. The only HTTP method created is POST. The service will then return you a json with the result of the analysis. The basic process is shown in the next figure:
The way to invoke the webservice is to POST the data points in a json format providing the webservice URL.
In the case of univariate time series we will need to send a json with a key value pair in the following format:
Key name: "data".
Values of data: array representing the time series points.
In the case of multivariate time series we want to analyze and predict one time series with respect to the rest of time series. For example if we have 3 time series, we will need to specify the time series that we want to predict whit respect to the 2 others. The json has to meet the following format:
Key name: "timeseries".
Values of data: several key value pairs representing the time series that will help us to predict the target time series:
Key name: "data".
Values of data: array representing the time series points.
....
Key name: "main".
Values of data: array representing the target time series points that we want to analyze and predict.
Here it is shown two examples invoking the webservice with a univariate time series and a multivariate one:
curl -i -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '
{
"data":[ 22125, 25817, 28779, 20960, 22254, 27392, 29945,16933, 17892,20533, 23569, 22417, 22084, 26580, 27454, 24081, 23451, 28991, 31386, 16896, 20045, 23471, 21747, 25621, 23859, 25500, 30998, 24475, 23145, 29701, 34365, 17556, 22077, 5702,22214,26886, 23191, 27831, 35406, 23195, 25110, 30009, 36242, 18450, 21845, 26488, 22394, 28057, 25451, 24872, 33424, 24052, 28449, 33533, 37351, 19969, 21701, 26249, 24493, 24603,26485, 30723, 34569, 26689, 26157, 32064, 38870, 21337, 19419, 23166, 28286, 24570, 24001, 33151, 24878, 26804, 28967, 33311, 40226, 20504, 23060, 23562, 27562, 23940, 24584,34303, 25517, 23494, 29095, 32903, 34379, 16991, 21109, 23740, 25552, 21752, 20294, 29009, 25500, 24166, 26960, 31222, 38641, 14672, 17543, 25453, 32683, 22449, 22316]
}
' http://127.0.0.1:5000/univariate/get
curl -i -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '
{
"timeseries":[
{
"data": [0.9500000476837158, 1.0, 1.0, 0.06666667014360428, 0.42222222685813904, 0.0833333358168602, 0.09444444626569748, 0.23333333432674408, 0.0833333358168602, 0.9833333492279053, 0.04444444552063942, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.08888889104127884, 1.0, 0.9277778267860413, 0.5166666507720947, 0.9666666984558105, 0.6666666865348816, 0.3333333432674408, 0.9055556058883667, 0.8277778029441833, 0.5777778029441833, 1.0, 1.0, 0.08888889104127884, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.05000000074505806, 0.5166666507720947, 1.0, 0.03888889029622078, 0.03888889029622078, 0.4166666865348816, 0.03888889029622078, 0.03888889029622078, 0.06666667014360428, 0.5777778029441833, 0.3055555522441864, 1.0] },
{
"data": [0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.375, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0]
}],
"main": [0.8571429252624512, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5714285969734192, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.4285714626312256, 0.5714285969734192, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.8571429252624512, 1.0, 0.0, 0.1428571492433548, 0.2857142984867096, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 1.0, 1.0, 0.8571429252624512, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.8571429252624512, 0.4285714626312256, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1428571492433548, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.1428571492433548, 0.1428571492433548, 1.0]
}
' http://127.0.0.1:5000/multivariate/get
The response of the webservice will provide the info of the behaviour of the time series in a json format as explained previously.
An example response will be:
{
"engine": "Holtwinters",
"future": {
"126": 15136.0, "127": 16733.0, "128": 20016.0, "129": 17708.0, "130": 18019.0, "131": 19227.0, "132": 22893.0, "133": 23739.0, "134": 21133.0, "135": 22591.0 },
"mae": 5994.289473684211,
"mse": 50689736.39473684,
"rmse": 7119.672492097992,
"past": [ {
"anomaly_score": 0.0,
"expected value": 20016.0,
"mae": 5994.289473684211,
"mse": 50689736.39473684,
"real_value": 33151.0,
"rmse": 7119.672492097992,
"step": 90.0 },
{
"anomaly_score": 1.0,
"expected value": 23739.0,
"mae": 5994.289473684211,
"mse": 50689736.39473684,
"real_value": 40226.0,
"rmse": 7119.672492097992,
"step": 95.0 },
{
"anomaly_score": 0.3460620525059665,
"expected value": 20008.0,
"mae": 5994.289473684211,
"mse": 50689736.39473684,
"real_value": 34303.0,
"rmse": 7119.672492097992, "step": 102.0
} ],
"present_alerts": [],
"present_status": "FALSE"
}
Here it is explained each element of the response:
WINNER ENGINE : The best engine regarding the MSE metric
"engine": "Holtwinters",
FORECAST : The forecast of the time series next 5 points
"future": {
"126": 15136.0, "127": 16733.0, "128": 20016.0, "129": 17708.0, "130": 18019.0, "131": 19227.0, "132": 22893.0, "133": 23739.0, "134": 21133.0, "135": 22591.0 },
METRICS : Basic metrics of the winner engine
"mae": 5994.289473684211, "mse": 50689736.39473684, "rmse": 7119.672492097992,
ANOMALIES IN THE PAST : Previous anomalies and its metrics
"past": [ { "anomaly_score": 0.0, "expected value": 20016.0, "mae": 5994.289473684211, "mse": 50689736.39473684, "real_value": 33151.0, "rmse": 7119.672492097992, "step": 90.0 }, { "anomaly_score": 1.0, "expected value": 23739.0, "mae": 5994.289473684211, "mse": 50689736.39473684, "real_value": 40226.0, "rmse": 7119.672492097992, "step": 95.0 }, { "anomaly_score": 0.3460620525059665, "expected value": 20008.0, "mae": 5994.289473684211, "mse": 50689736.39473684, "real_value": 34303.0, "rmse": 7119.672492097992, "step": 102.0 } ],
PRESENT STATUS : Currently alert points and alert flag
"present_alerts": [], "present_status": "FALSE" }