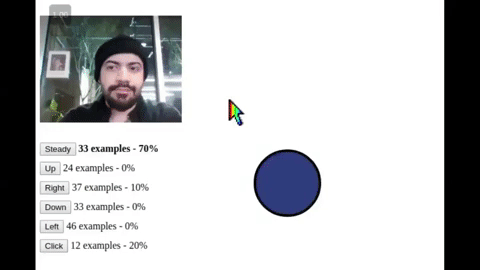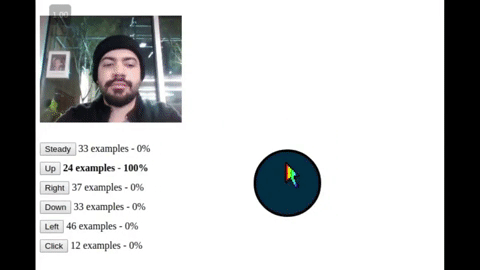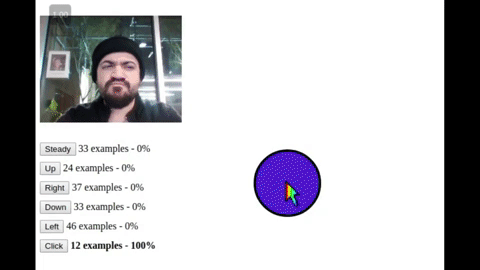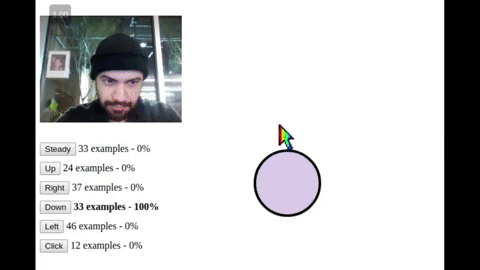
A platform for creating handsfree user interfaces, tools, games, and experiences for the web and IoT 🤯
Run the following from projects root directory:
# Install dependencies
npm install
# Start a server with hot-reload at localhost:3000
npm run serve
# Test the library (not the documentation site)
npm run test
# Build for production
npm run build
# Build and deploy (see /deploy.js to configure for your own server)
npm run deployFor detailed explanation on how things work, check out the Vuetify.js and CLI Plugin documentation.
Install with an HTML <script> tag anywhere after the open <body> tag...
<body>
<!-- Latest with bug fixes (Recommended for production) -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/handsfree@<3.1/dist/handsfree.js"></script>
<!-- Latest with bug fixes and new features (Recommended for development) -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/handsfree@<4/dist/handsfree.js"></script>
<!-- Latest with potential backwards incompatability (Recommended for testers) -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/handsfree/dist/handsfree.js"></script>
</body>...or with Node.
// Fromt the terminal in the project root
npm i handsfree
// Then in your script
const Handsfree = require('handsfree')Then in both cases add the following to your scripts:
handsfree = new Handsfree()
handsfree.start()That will inject handsfree into the page, including the required components (video and canvas elements), initialize models, and start tracking a single face. This setup includes the minimal plugins necessary to operate a web page, including:
- Scrolling
- Clicking
- Virtual Keyboard
See: /lib/plugins/SimpleKeyboard.js
See: /sandbox/demos/paper.js
The following is our directory sturcture. [In brackets] are
/- public -| Files available to both the library and documentation site
/- starters -| [DEVELOPERS] Standalone projects to get you started
/- lib -| [CORE DEVELOPERS] The main handsfree.js library
/-- components -| Cursor
/-- models -| Machine learning models
/-- plugins -| Core plugins
/- docs -| [DOC MAINTAINERS] The documentation site
/-- assets
/-- components
/-- demo
/-- plugins
/-- store
You can instantiate Handsfree with the following config (defaults are shown):
const handsfree = new Handsfree({
// Whether to show (true) the debugger (face mask over video) or not (false)
debug: false
})// Starts tracking faces and shows the webcam stream if debug is on
handsfree.start()
// Stops the webcam
handsfree.stop()
// Toggles the debugger on (true), off (false), or flips the state (null)
handsfree.toggleDebugger(true|false|null)The debugger is loaded into the first element in the DOM with the .handsfree-debug-wrap. If one doesn't exist, then it's added as the last root element of body. You should rarely need to debug visually, and it's preferred that you don't draw into this canvas at all.
Handsfree is built around a plugin architecture, which allows us to easily add and share functionality. We can even disable them!
To add a plugin, use the handsfree.use({}) method with the following form:
handsfree.use({
// Must be unique. Spaces and special characters are fine
// Plugins are called alphabetically - to make a plugin load before another prefix it with a number
name: '',
// Called once when the use method is called and after the plugin is added to the instance
onUse: () => {},
// Called once per frame, after calculations, along with the detected face object
// To overwrite/modify the properties of faces for use within other plugins, return the faces object
onFrame: (faces, handsfree) => {},
// Called any time Handsfree.start() is called
onStart: (handsfree) => {},
// Called any time Handsfree.stop() is called
onStop: (handsfree) => {}
})The onFrame recieves a faces array, which contains an object for each tracked face. The key properties of the a face object include:
{
cursor: {
// Where the main cursor is drawn (also the point the user is facing)
x: 0,
y: 0,
// The HTML element currently under the mouse
$target: 0,
// "Mouse" states for this face
state: {
// True during the first frame of a click, false after (even if still held)
mouseDown: false,
// True after the first frame of a click and every frame after until release
mouseDrag: false,
// True on the last frame of a click, immediately after the click is released
mouseUp: false
}
},
// A list of all 64 landmarks
points: [{x, y}, ...],
// The head's pitch (facing up/down)
rotationX: 0,
// The head's yaw (facing left/right)
rotationY: 0,
// The head's roll (think of an airplane doing a barrel roll)
rotationZ: 0,
// Not really sure...the heads overall size within the camera?
scale: 0,
// Where the head is relative to the left edge of the video feed
translationX: 0,
// Where the head is relative to the top edge of the video feed
translationY: 0
}There are 64 landmark points, reflected in the following image:

27 is where the cursor's screen vectors are estimated from.
An alternative to plugins is to use listen in on the window handsfree-trackFaces event:
/**
* Bind to the handsfree-trackFaces event
* @param {Handsfree} ev.detail.scope The handsfree instance
* @param {Object} ev.detail.faces An array of face objects
*/
window.addEventListener('handsfree-trackFaces', (ev) => {
// Do code with the handsfree instance: ev.detail.scope
// or with the faces ev.detail.faces.forEach(face => {})
})The handsfree-injectDebugger event is fired after the debugger is injected, but before handsfree is started. Use this event to draw into the canvas without the camera being turned on.
/**
* Bind to the handsfree-injectDebugger event
* @param {Handsfree} ev.detail.scope The handsfree instance
* @param {Canvas2DContent} ev.detail.canvasContext The 2D debug canvas context
*/
window.addEventListener('handsfree-injectDebugger', (ev) => {
// Do code with the handsfree instance: ev.detail.scope
// or draw into the canvas with ev.detail.canvasContext
})The document body contains .handsfree-stopped when handsfree is stopped (this includes when it's been initialized but not started), and .handsfree-started when it's on. This lets you style any page on the page!
This is the most fun and rewarding thing I have ever had making something, and it wouldn't have been possible without the many people. Some of these people include:
@Todo reach out to everyone and ask where they would like to be linked (use Twitter as fallback if OK)
If you like where we're headed, check out our Patreon:

March 4th 2018: https://twitter.com/LabOfOz/status/970556829125165056