This project analyses data to find sub-communities/clusters within the data based on the connections in data. A detailed description of community structure can be found on this Wikipedia page
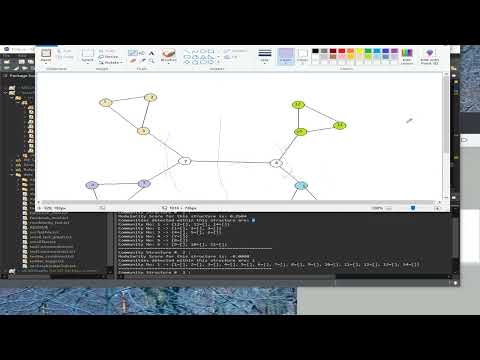
The picture below shows two sub-communities within the data, pointed out by blue and purple colours. In picture 2, a more complex structure of sub-communities is shown.
Picture 1
Picture 2
This program detects sub-communities/clusters within a community using the Girvan-Newman algorithm.
Girvan-Newman Algorithm is implemented in two ways.
- without using external libraries(from scratch)
- using external library i-e JUNG library (GirvanNewmanJung class implements this)
(Opens in Youtube)
The main Data Structure used is Graph using the adjacency list.
However, the adjacency matrix is also implemented only to calculate Modularity Matrix used to calculate Modularity
- The primary algorithm used is Girvan-Newman Edge Betweenness Algorithm for community finding.
- Brande’s edge betweenness algorithm is used to find the edge betweenness.
- Girvan-Newman method is used to find the modularity of the graph.
Modularity is a number representing how well the division of community is into sub-communities.
The total running time of the algorithm is O(n2m2), where n is the number of vertices and m is the total number of edges. This time complexity is calculated from the getCommunities() method.
In the getCommunities() method, I have a while loop which loops until no edges are left i-e O(m). within this loop, methods called are as follows with their complexities
brandes() -> O(n2 * m)
removeEdges() -> O(m)
getSCCs()-> O(n * m)
getModularity() -> O(n * m)
combining all the above complexities gives us the following
O(m) { O(n2 m) + O(m) + O(nm) + O(nm)} -> ignoring the smaller terms
= O(m) {O(n2m)}
= O(m) * O(n2m)
= O(n2m2)
The design is simple and focused towards readability.
GirvanNewman class is used to implement the Girvan Newman Algorithm without any libraries.
GirvanNewmanJung class implements the algorithm using the JUNG library.
GirvanNewman class has a significant chunk of code. It extends the CapGraph class to make it compatible with the provided Graph Interface and re-uses the CapGraph class code.
GirvanNewman class has two inner classes to represent the vertex and edge in the graph. Method brandes() calculates the edge-betweenness using Brande’s algorithm, based on which the edges with the highest betweenness are removed. Method getModularity() calculates the modularity of the community structure found by eliminating the edges.
Method getCommunities() performs all the work in a single call, finds edge-betweenness, removes edges, calculates modularity for every community structure found until no more edges are left, records communities with the top three modularity scores and returns them.
This class extends CapGraph class to make it compatible with the provided code. This is the main class to find communities in a graph using the Girvan-Newman Edge Betweenness algorithm. This class performs all the functions to find the communities in the given data. It has two inner classes, one each for Vertex and Edge, in the graph.
This is an inner class of the GirvanNewman class and serves as the vertex for the graph.
This is an inner class of GirvanNewman class and serves as the edge for the graph.
This class does not have much code and uses the JUNG library to find communities in the graph. This class depends on JungGraphLoader class to load the graph for GirvanNewmanJung class to work on.
Purpose and description of class: The only goal of this class is to load the graph for GiranNewmanJung class. It has only one static method, which loads the graph.