In this article, a predictive analysis is presented regarding the potential resignation of employees. The main objective is to develop three prediction models using machine learning techniques to identify employees who may be considering leaving the company in the near future. This analysis aims to assist companies in taking proactive measures to retain their key talent and improve job satisfaction.
This article analyzes the average cost per hire in the year 2024 and the factors influencing this cost.
-
2019: $4,129
-
2023: $4,700 (14% increase)
- Company Size: Larger companies can spread operational costs among a greater number of hires.
- Industry: Certain industries, such as cybersecurity, engineering, or nursing, experience talent shortages, increasing hiring costs.
- Location: Hiring costs vary by geographic location.
- Recruitment: Job postings, recruitment agency fees, candidate tracking software.
- Selection: Tests, interviews, candidate travel.
- Onboarding: Training, materials, existing employee time.
- Employee Time: Time employees spend on the hiring process, such as reviewing resumes and conducting interviews.
- Productivity Loss: Productivity loss incurred when a position is vacant.
- Turnover Costs: Costs associated with hiring a new employee to replace a departing one.
This analysis provides a deeper understanding of the cost of hiring an employee in 2024 and the different factors influencing this cost. Understanding these aspects is crucial for strategic decision-making in human resource management and financial planning for companies.
Source: https://toggl.com/blog/cost-of-hiring-an-employee
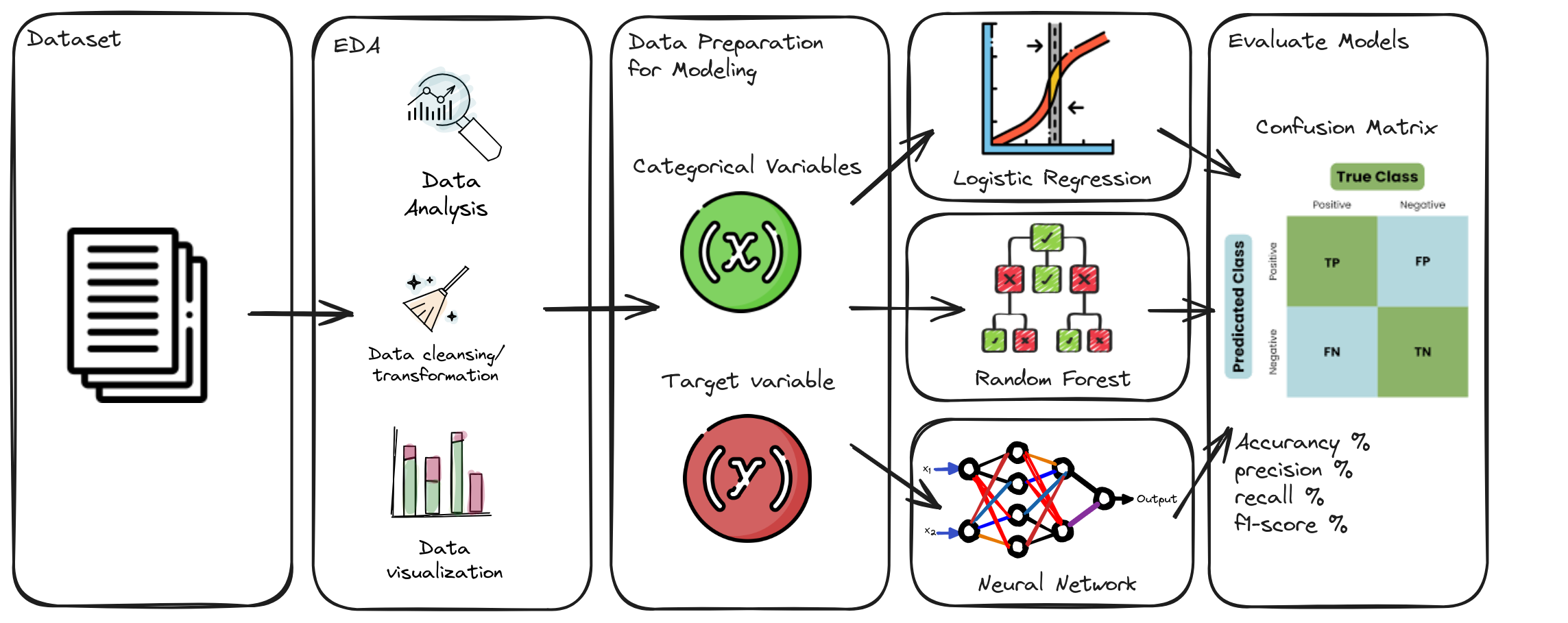
The data used in this analysis were obtained from https://www.kaggle.com/pavansubhasht/ibm-hr-analytics-attrition-dataset, containing relevant employee information, including demographic characteristics, employment history, performance evaluations, among others.
Before training predictive models, an exhaustive data preprocessing process was performed, including data cleaning, handling categorical variables, managing missing values, and feature scaling.
The most relevant categorical variables for predicting employee resignations were carefully selected. Various machine learning methodologies were explored and evaluated, including Random Forest, Logistic Regression, and Deep Learning. Each of these techniques was applied with the aim of capturing the complexity and diversity of the data, thus providing a comprehensive approach to building three robust and accurate predictive models.
Several machine learning models, including Logistic Regression, Random Forests, and Deep Learning, were trained using the training dataset.
The models were evaluated using metrics such as accuracy, recall, and F1-score. A detailed analysis of the confusion matrix was conducted to assess the model's performance in predicting employee resignations.