A QIIME 2 plugin providing pysyndna calculations of microbial cell counts and microbial ORF copy counts.
q2-pysyndna provides access to the functionality of the
pySynDNA package from
within QIIME 2. pySynDNA implements the Zaramela et al
method, using it to calculate absolute cell counts of each microbial species per gram
of sample using metagenomic shotgun sequencing data containing synDNA spike-ins.
Additionally, pySynDNA provides an approach for calculating the number of copies of
each microbial ORF per gram of sample via metatranscriptomic shotgun sequencing.
The method of Zaramela et al allows the calculation of microbial cell counts from metagenomics shotgun sequencing data when synthetic DNAs of known sequence and concentration have been included in the library. The calculation is performed in two parts: first, the known spiked-in mass of pooled synDNAs and the known concentrations of each synDNA within the pool are used to calculate the mass of each synDNA in the sample. These mass values are paired with the counts of each synDNA in the sample and a regression model is fitted to predict mass from counts within that sample. The counts for each microbial genome in the sample are then translated into masses via the regression model, and the masses are converted to genome counts using genome lengths and Avogadro's number (see Zaramela et al equation 2). Assuming approximately one genome per cell, the calculated genome counts are treated as approximate cell counts. Using the known starting mass of each sample, pySynDNA then calculates the cell counts of each microbe per gram of sample.
The microbial cell count per gram of sample calculations thus require four inputs:
- Per-sample metadata, including data on synDNAs added to each sample
- The concentrations of each individual synDNA within the pool
- The counts of each individual synDNA in each sample
- The counts of each microbial genome in each sample
- The lengths of each microbial genome
The synDNA counts and microbial genome counts inputs are themselves the
outputs of sequence processing performed by the
woltka meta-omics classifier. Woltka
functionality is available in QIIME 2 directly using the
q2-woltka plugin.
The microbial genome lengths file can also be copied directly from the
"genome ID to genome length (bp) mapping file" used by woltka.
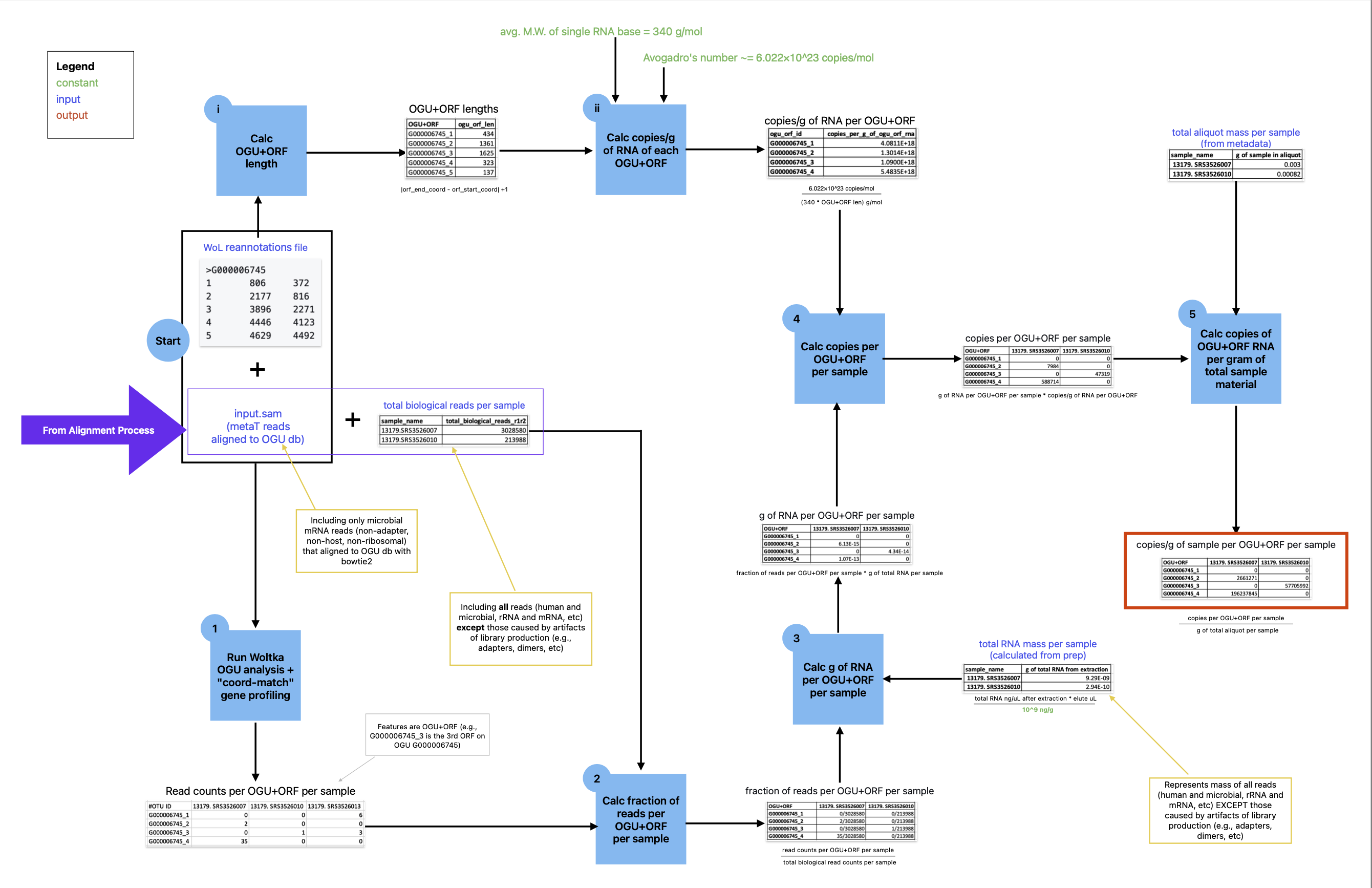
Microbial ORF counts from metatranscriptomics data can be used to calculate ORF copy counts by transforming them into fractions of the total observed expression and multiplying these fractions by the total mass to get the mass of each ORF in the sample. Multiplying by the number of copies per gram of each ORF, transforms the mass into the number of each ORF's copies in the sample. Finally, as in the metagenomics cell count calculation, pySynDNA divides by the known starting mass of each sample, thus calculating the copy counts of each ORF on each microbial genome, per gram of sample. The calculations are outlined in the figure below.
It is important to note that ORF counts are genome-specific: they are the copy counts of a particular ORF from a particular microbial genome, and are not summed across ORFs that are present in multiple genomes.
The ORF counts per gram of sample calculations require three inputs:
- Per-sample metadata
- The counts of each microbial ORF in each sample
- The coordinates of each microbial ORF on its genome
The microbial ORF counts inputs are themselves an
output of sequence processing performed by the
woltka meta-omics classifier. Woltka
functionality is available in QIIME 2 directly using the
q2-woltka plugin.
The microbial ORF coordinates file can also be copied directly from the
Web of Life reannotations file used by woltka.
q2-pysyndna requires an existing QIIME 2 environment (see documentation at
https://docs.qiime2.org for QIIME 2 installation instructions) that also includes an installation of the pysyndna
package. Following the pysyndna installation guide,
clone the pysyndna repository. Instead of creating a new conda
environment, update the activated QIIME 2 environment with the additional pysyndna
requirements:
conda env update --file pysyndna/environment.yml --prune
Then return to the pysyndna directions to install the library itself.
Finally, in the activated the QIIME 2 environment, install the
q2-pysyndna plugin repository from github:
pip install git+https://github.com/AmandaBirmingham/q2-pysyndna.git
After this, it is necessary to refresh the QIIME 2 plugin cache:
qiime dev refresh-cache
The q2-pysyndna plugin should now be in the list of installed plugins produced
by running qiime --help
q2-pysyndna offers two main functions: calculation of microbial cell
counts from metagenomic data that includes synDNA spike-ins, and calculation of microbial ORF copy counts from
metatranscriptomic data.
- Run woltka or q2-woltka to quantify synDNA counts and microbial genome counts
- If using woltka, the resulting count files will be in the
.biomformat - If using q2-woltka, they will be in the
.qzaQIIME artifact format
- If using woltka, the resulting count files will be in the
- Collect the genome-id-to-genome-length file used by woltka/q2-woltka.
- If using the Web of Life data release, this will be the file named
length.map.
- If using the Web of Life data release, this will be the file named
- Create a tab-separated per-sample metadata file including:
- A column named
sample_nameholding the per-sample identifier used in the count files. - A column named
syndna_pool_numbercontaining the identifier of the synDNA pool added to the sample. This must correspond to a synDNA identifier in the config file (see #2). - A column named
mass_syndna_input_ngcontaining the total mass, in nanograms, of the synDNA pool that was added to the sample. - A column named
raw_reads_r1r2containing the total number of reads (including both forward and reverse) sequenced for the sample. - A column named
calc_mass_sample_aliquot_input_gcontaining the mass, in grams, of the sample in the aliquot that went into the extraction. - A column named
vol_extracted_elution_ulcontaining the volume, in uL, of elute produced by the extraction. - A column name
extracted_gdna_concentration_ng_ulcontaining the concentration of gDNA (in ng/uL) extracted from each sample. - A column named
sequenced_sample_gdna_mass_ngcontaining the mass, in ng, of the portion of the sample gDNA that was sequenced.
- A column named
- Create comma-separated file specifying the concentrations of each individual synDNA within the pool.
- An example of the file format is shown below; note that the
syndna_idandsyndna_indiv_ng_ulheaders are required
- An example of the file format is shown below; note that the
syndna_id,syndna_indiv_ng_ul
p126,1
p136,0.1
p146,0.01
p156,0.001
p166,0.0001
p226,0.0001
p236,0.001
p246,0.01
p256,0.1
p266,1
- Activate the QIIME 2 environment installed above
- Import the necessary inputs
Option 1: from the command line
# Import a synDNA concentration file named "syndna_concs.csv"
qiime tools import \
--input-path syndna_concs.csv \
--output-path syndna_concs.qza \
--type SyndnaPoolConcentrationTable
# If the synDNA count table and microbial genome count table
# are NOT already in .qza format, import them.
# Start by importing a synDNA count table named "syndna_counts.biom"
qiime tools import \
--input-path syndna_counts.biom \
--output-path syndna_counts.qza \
--type 'FeatureTable[Frequency]'
# Next, import a microbial genome count table named "genome_counts.biom"
qiime tools import \
--input-path genome_counts.biom \
--output-path genome_counts.qza \
--type 'FeatureTable[Frequency]'
# Import a genome lengths file named "length.map"
qiime tools import \
--input-path length.map \
--output-path genome_lengths.qza \
--type 'FeatureData[Length]'
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
# Import necessary libraries
from qiime2 import Artifact, Metadata
from q2_types.feature_table import FeatureTable, Frequency
from q2_types.feature_data import FeatureData
from q2_pysyndna import SyndnaPoolConcentrationTable
from q2_pysyndna import Length
# Import a per-sample metadata file named "dna_metadata.tsv"
dna_metadata = Metadata.load("dna_metadata.tsv")
# Import a synDNA concentration file named "syndna_concs.csv"
syndna_concs = Artifact.import_data(
SyndnaPoolConcentrationTable, "syndna_concs.csv")
syndna_concs.save("syndna_concs.qza")
# If the synDNA count table and microbial genome count table
# are NOT already in .qza format, import them
# (note that if they *are* already in .qza file, one must
# instead "load" them, using Artifact.load())
# Start by importing a synDNA count table named "syndna_counts.biom"
syndna_counts = Artifact.import_data(
FeatureTable[Frequency], 'syndna_counts.biom')
syndna_counts.save("syndna_counts.qza")
# Next, import a microbial genome count table named "genome_counts.biom"
genome_counts = Artifact.import_data(
FeatureTable[Frequency], 'genome_counts.biom')
genome_counts.save("genome_counts.qza")
# Import a genome lengths file named "length.map"
genome_lengths = Artifact.import_data(
FeatureData[Length], 'length.map')
genome_lengths.save("genome_lengths.qza")
- Fit the per-sample regression models
- Optionally, specify the minimum integer number of counts per sample (across all microbial genomes) that are required for a sample to be included in the fit process. The smallest allowable value, and the default, is 1, which excludes any samples with zero total counts.
Option 1: from the command line
# Fit per-sample models, excluding any samples with zero counts
qiime pysyndna fit \
--i-syndna-concs syndna_concs.qza \
--i-syndna-counts syndna_counts.qza \
--m-metadata-file dna_metadata.tsv \
--p-min-sample-count 1 \
--o-regression-models regression_models.qza
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
import qiime2.sdk as sdk
# Get the q2-pysyndna plugin
pm = sdk.PluginManager()
a_plugin = pm.get_plugin(id="pysyndna")
# Fit per-sample models, excluding any samples with zero counts
fit_action = a_plugin.actions["fit"]
# NB: the minimum sample count is not specified as the default is 1
fit_obj, _ = fit_action(syndna_concs, syndna_counts, dna_metadata)
fit_obj.save("regression_models.qza")
- Generate visualizations of the fit log and the regression models
Option 1: from the command line
# Create a visualization of the regression models fit to the syndna counts
qiime pysyndna view-fit \
-i-linear-regressions regression_models.qza \
--o-visualization regression_models.qzv
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
# Create a visualization of the regression models fit to the syndna counts
fit_visualizer = a_plugin.visualizers["view_fit"]
fit_visualization = fit_visualizer(fit_obj)
fit_visualization.visualization.save("regression_models.qzv")
- View the fit log and regression model visualizations (e.g, with qiime2view)
- Examine the log to determine how many samples (if any) were excluded from the fit process
- Examine the regression models to examine their goodness of fit
- Calculate microbial cell counts per gram of sample
- Optionally, specify the length of the reads from the sequencing run (must be an integer >= 1). This value is usually 50-300 basepairs for Illumina sequencing; default is 150.
- Optionally, specify the minimum percent coverage of a microbial genome (in a specific sample) required to calculate cell counts for this genome. Must be a floating point number >= 1; default is 1.
- Optionally, specify the minimum allowable r-squared value for the linear regression model for a sample required to include that sample to calculate cell counts for this sample. Must be a floating point number between 0 and 1; default is 0.8.
- It is also possibly to specify an alternate output metric, but this option is not recommended except for power users.
Option 1: from the command line
# Calculate microbial cell counts per gram of sample
qiime pysyndna count-cells \
--i-regression-models regression_models.qza \
--i-genome-counts genome_counts.qza \
--i-genome-lengths genome_lengths.qza \
--m-metadata-file dna_metadata.tsv \
--p-read-length 150 \
--p-min-percent-coverage 1 \
--p-min-rsquared 0.8 \
--o-cell-counts cell_counts.qza \
--o-cell-count-log cell_counts_log.qza
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
# Calculate microbial cell counts per gram of sample
count_cells_action = a_plugin.actions["count_cells"]
cell_counts_obj, cell_counts_log = count_cells_action(
fit_obj, genome_counts, genome_lengths, dna_metadata)
cell_counts_obj.save("cell_counts.qza")
cell_counts_log.save("cell_counts_log.qza")
- Generate a visualization of the cell count log.
Option 1: from the command line
# Create a visualization of the cell counts log
qiime pysyndna view-log \
-i-log cell_counts_log.qza \
--o-visualization cell_counts_log.qzv
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
# Create a visualization of the cell counts log
log_visualizer = a_plugin.visualizers["view_log"]
log_visualization = log_visualizer(cell_counts_log)
log_visualization.visualization.save("cell_counts_log.qzv")
- View the cell counts log to determine how many samples (if any) were excluded from the cell count calculations
- Generate a visualizer for the microbial cell counts per gram of sample table and examine it
- This can be done using the standard QIIME 2 commands for summarizing FeatureTables
- Characterize and analyze the microbial cell counts per gram of sample table through QIIME 2 like any other feature table of frequencies.
- Run woltka or q2-woltka to quantify microbial ORF counts
- If using woltka, the resulting count file will be in the
.biomformat - If using q2-woltka, it will be in the
.qzaQIIME artifact format
- If using woltka, the resulting count file will be in the
- Collect the gene coordinates file used by woltka/q2-woltka
- This file must be in the "WoL reannotations" format as described in the woltka gene coordinates documentation, which looks like the below:
>G000005825
1 816 2168
2 2348 3490
3 3744 3959
4 3971 5086
5 5098 5373
>G900163845
3247 3392209 3390413
3248 3393051 3392206
3249 3393938 3393048
3250 3394702 3393935
3251 3395077 3395721
- Create a tab-separated per-sample metadata file including:
- A column named
sample_nameholding the per-sample identifier used in the count files. - A column named
calc_mass_sample_aliquot_input_gcontaining the mass, in grams, of the sample in the aliquot that went into the extraction. - A column named
vol_extracted_elution_ulcontaining the volume, in uL, of elute produced by the extraction. - A column name
total_rna_concentration_ng_ulcontaining the concentration of ssRNA (in ng/uL) extracted from each sample. - A column named
total_biological_reads_r1r2containing the total number of reads (including both forward and reverse) sequenced for the sample that are not due to artifacts of library preparation.
- A column named
- Activate the QIIME 2 environment installed above
- Import the necessary inputs
- Be aware that importing the gene coordinates can take several minutes!
Option 1: from the command line
# If the microbial ORF count table is NOT already in .qza format, import it.
# Import a microbial ORF count table named "orf_counts.biom"
qiime tools import \
--input-path orf_counts.biom \
--output-path orf_counts.qza \
--type 'FeatureTable[Frequency]'
# Import an ORF coordinates file named "orf_coords.txt"
# NB: this step can take several minutes!
qiime tools import \
--input-path orf_coords.txt \
--output-path orf_coords.qza \
--type 'FeatureData[Coords]'
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
# Import necessary libraries
from qiime2 import Artifact, Metadata
from q2_types.feature_table import FeatureTable, Frequency
from q2_types.feature_data import FeatureData
from q2_pysyndna import Coords
# Import a per-sample metadata file named "rna_metadata.tsv"
rna_metadata = Metadata.load("rna_metadata.tsv")
# If the microbial ORF count table is NOT already in .qza format, import it.
# (note that if it *is* already in .qza file, one must
# instead "load" it, using Artifact.load())
# Import a microbial ORF count table named "orf_counts.biom"
orf_counts = Artifact.import_data(
FeatureTable[Frequency], 'orf_counts.biom')
orf_counts.save("orf_counts.qza")
# Import an ORF coordinates file named "orf_coords.txt"
# NB: this step can take several minutes!
orf_coords = Artifact.import_data(
FeatureData[Coords], "orf_coords.txt")
orf_coords.save("orf_coords.qza")
- Calculate microbial ORF copy counts per gram of sample
Option 1: from the command line
# Calculate microbial ORF copy counts per gram of sample
qiime pysyndna count-copies \
--i-genome_orf_counts orf_counts.qza \
--i-genome_orf_coords orf_coords.qza \
--m-metadata-file rna_metadata.tsv \
--o-copy-counts copy_counts.qza \
--o-copy-counts-log copy_counts_log.qza
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
import qiime2.sdk as sdk
# Get the q2-pysyndna plugin
pm = sdk.PluginManager()
a_plugin = pm.get_plugin(id="pysyndna")
# Calculate microbial ORF copy counts per gram of sample
count_copies_action = a_plugin.actions["count_copies"]
count_copies_obj, count_copies_log = count_copies_action(
orf_counts, orf_coords, rna_metadata)
count_copies_obj.save("copy_counts.qza")
count_copies_log.save("copy_counts_log.qza")
- Generate a visualization of the copy count log.
Option 1: from the command line
# Create a visualization of the copy counts log
qiime pysyndna view-log \
-i-log copy_counts_log.qza \
--o-visualization copy_counts_log.qzv
Option 2: using the QIIME 2 API
# Create a visualization of the copy counts log
log_visualizer = a_plugin.visualizers["view_log"]
log_visualization = log_visualizer(copy_counts_log)
log_visualization.visualization.save("copy_counts_log.qzv")
- View the copy counts log to determine how many samples (if any) were excluded from the copy count calculations
- Generate a visualizer for the microbial ORF copy counts per gram of sample table and examine it
- This can be done using the standard QIIME 2 commands for summarizing FeatureTables
- Characterize and analyze the microbial ORF copy counts per gram of sample table through QIIME 2 like any other feature table of frequencies.