-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 129
Adding an SSH target
This page explains the process of adding a new SSH target host to Warpgate and allowing users to connect to it.
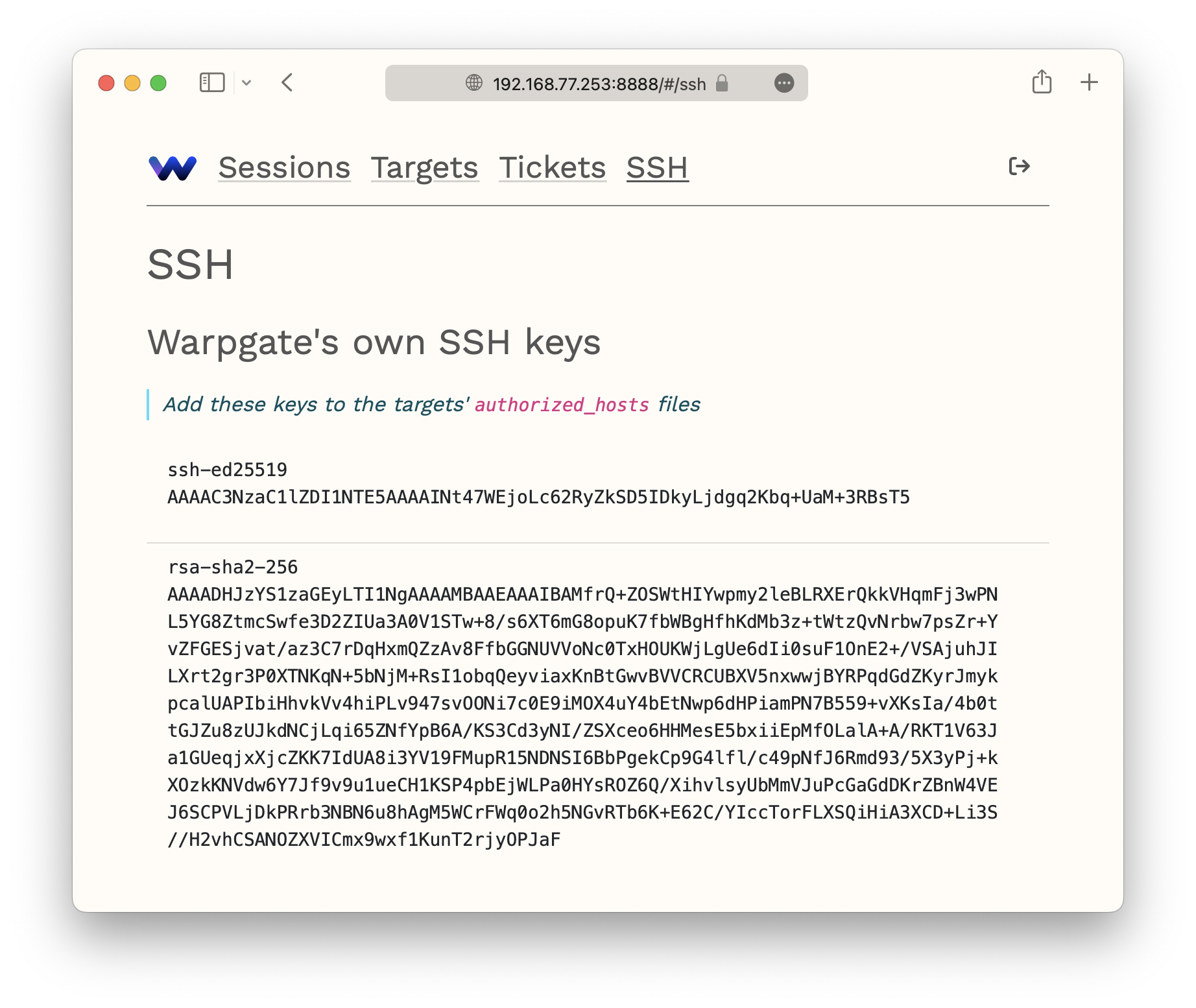
Warpgate has its own set of SSH keys which the target host must trust in order for connections to work.
You can view these keys on the SSH page of the Admin UI, or via the warpgate client-keys CLI command:
$ warpgate client-keys
13:59:41 INFO Using config: "/etc/warpgate.yaml" (users: 1, targets: 2, roles: 1)
Warpgate SSH client keys:
(add these to your target's authorized_hosts file)
ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAINt47WEjoLc62RyZkSD5IDkyLjdgq2Kbq+UaM+3RBsT5
rsa-sha2-256 AAAADHJzYS[...]
The keys are listen in the order of preference. Copy one of them and paste it at the end of the ~/.ssh/authorized_hosts file on the other side (each target host OS' user has their own authorized_hosts file and you will need to create it if it doesn't exist yet).
Although not recommended, you can use a password to authenticate against a target:
[...]
- name: my-switch
allow_roles:
- warpgate:admin
ssh:
host: 192.168.10.2
username: cisco
+ auth:
+ password: super-secret-password
[...]Isn't storing plaintext passwords unsafe?
It's not as long as the config file itself is secure. Warpgate automatically locks down the config file permissions to the bare minimum required.
Add the target host to the targets list in the Warpgate config file (default: /etc/warpgate.yaml), for example:
[...]
targets:
+ - name: my-target
+ allow_roles:
+ - "warpgate:admin"
+ ssh:
+ host: 192.168.10.20
+ username: root # optional
+ port: 22 # optional
- name: web-admin
allow_roles:
- "warpgate:admin"
web_admin: {}
users:
[...]Warpgate will automatically pick up any changes to the config file if it's valid, so give it a quick check:
$ warpgate check
14:06:56 INFO Using config: "/etc/warpgate.yaml" (users: 1, targets: 2, roles: 1)
14:06:56 INFO No problems found
The target should show up on the Targets admin UI page:
Now, fire up your favorite SSH client and try connecting to Warpgate:
- Host: the Warpgate host
- Port: the Warpgate SSH port (default: 2222)
- Username:
admin:<target-name>, in this example:admin:my-target - Password: your Warpgate admin password
When connecting for the first time, Warpgate will ask you to check and confirm the target host's SSH host key fingerprint (which you really should do).
Here's what it looks like with OpenSSH:
$ ssh admin:my-target@192.168.77.253 -p 2222
admin:my-target@192.168.77.253's password:
Warpgate Selected target: my-target
Warpgate Host key (ssh-ed25519): AAAAC3[...]
Warpgate There is no trusted ssh-ed25519 key for this host.
Warpgate Trust this key? (y/n)
✓ Warpgate connected
root ~ $
From this point on, you can use this as a normal SSH connection, including SFTP etc.
While your SSH session is running, you'll be able to see its status in the Admin UI: