| day | title | description |
|---|---|---|
10 |
Linked Lists |
Covering Singly Linked Lists, Doubly Linked Lists, and Circular Linked Lists |
A singly linked list consists of nodes, each containing data and a pointer to the next node.
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};Insertion can be done at the beginning, end, or at a specific position.
// Insert at the beginning
struct Node* insertAtBeginning(struct Node* head, int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = head;
return newNode;
}Deletion can be done from the beginning, end, or at a specific position.
// Delete from the beginning
struct Node* deleteFromBeginning(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
struct Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
free(temp);
return head;
}Traversal involves visiting each node in the list.
void traverse(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* cursor = head;
while (cursor != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->next;
}
}A doubly linked list has nodes with pointers to both the next and previous nodes.
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};Insertion in a doubly linked list requires updating both next and prev pointers.
// Insert at the beginning
struct Node* insertAtBeginning(struct Node* head, int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = head;
if (head != NULL) head->prev = newNode;
return newNode;
}Deletion in a doubly linked list involves updating both next and prev pointers.
// Delete from the beginning
struct Node* deleteFromBeginning(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
struct Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
if (head != NULL) head->prev = NULL;
free(temp);
return head;
}Traversal can be done in both forward and backward directions.
void traverseForward(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* cursor = head;
while (cursor != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->next;
}
}
void traverseBackward(struct Node* tail) {
struct Node* cursor = tail;
while (cursor != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->prev;
}
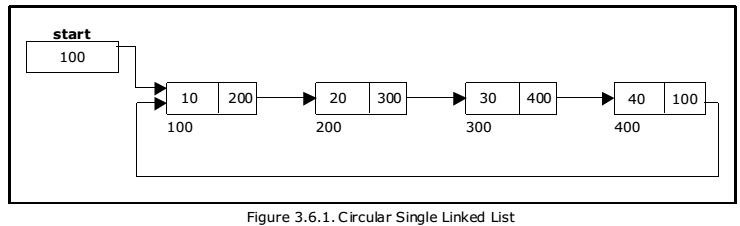
}A circular linked list connects the last node back to the first node.
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};Insertion in a circular linked list requires special handling for the last node.
// Insert at the beginning
struct Node* insertAtBeginning(struct Node* head, int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
if (head == NULL) {
newNode->next = newNode;
return newNode;
}
newNode->next = head;
struct Node* cursor = head;
while (cursor->next != head) {
cursor = cursor->next;
}
cursor->next = newNode;
return newNode;
}Deletion in a circular linked list requires updating the last node's next pointer.
// Delete from the beginning
struct Node* deleteFromBeginning(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == head) {
free(head);
return NULL;
}
struct Node* cursor = head;
while (cursor->next != head) {
cursor = cursor->next;
}
struct Node* temp = head;
head = head->next;
cursor->next = head;
free(temp);
return head;
}Traversal in a circular linked list requires stopping when we reach the first node again.
void traverse(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return;
struct Node* cursor = head;
do {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->next;
} while (cursor != head);
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node* createNode(int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int main() {
struct Node* head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(3);
struct Node* cursor = head;
while (cursor != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->next;
}
return 0;
}struct Node {
struct Node* prev
int data;
struct Node* next;
};Unlike in circular singly linked list, we don't have to traverse the whole list in order to get last position.
Just do lastNode = head->prev;
// Insert at the beginning
struct Node* insertAtBeginning(struct Node* head, int data) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
if (head == NULL) {
newNode->prev = newNode->next = newNode;
return newNode;
}
newNode->next = head;
newNode->prev = head->prev;
return newNode;
}We can use that same advantage here as well.
// Delete from the beginning
struct Node* deleteFromBeginning(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
if (head->next == head) {
free(head);
return NULL;
}
struct Node* temp = head;
head->prev->next = head->next;
head->next->prev = head->prev;
head = head->next;
free(temp);
return head;
}Traversal in a circular doubly linked list is the same as circular singly linked list. Except you can now also traverse in reverse.
void traverse(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return;
struct Node* cursor = head;
do {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->next;
} while (cursor != head);
}
void traverseReverse(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return;
struct Node* cursor = head;
do {
printf("%d ", cursor->data);
cursor = cursor->prev;
} while (cursor != head);
}