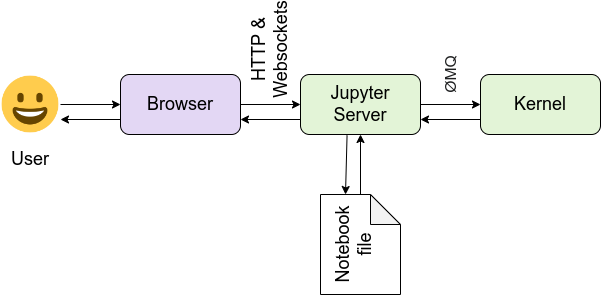
Jupyter Demo: Sample
Kernel with https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlin-jupyter
UI with https://github.com/jupyterlab/jupyterlab
- REPL tests
- basic DSL design
- Frontend Samples
- Archdoc Editor
- CodeMirror or Monaco Editor
- Parser:
marked - Math:
mathjax2
- Archdoc Server
-
Java kernel with https://github.com/twosigma/beakerx - Zeppelin Interpreter
- Jupyter Kernel Server with Kotlin
- Kotlin Jupyter Protocol Server (Socket)
- Jupyter Protocol for frontend: jmp
-
zeromq - websocket
-
- magic (%) support (ext_plugins) (%%archdoc)
-
- Markdown Parser
-
Kotlin markdown -
flexmark-java -
prosemirror-markdown
-
- Online GraphEngine
- with Mermaid
- with D3.js ?
- with Echart.js ?
- WebComponents support
DSL:
- Backend CRUD DSL
- Linter DSL
- Scanner DSL
- Architecture DSL
- Governance DSL
Graph Features:
- UML
- by extensions? like yUML, websequencediagrams ?
- UML with mermaid -[ ] custom Graph Engine
Frontend:
- Componentless Architecture with plugins
- every plugin as WebComponents
- plugin Component API design
Spike:
- Apache Calcite (for SQL parser)
- JAVAC for AST
- Janino, java compiler
- Apache Beam (for pipeline model)
- Apache Spark (for pipeline design)
Apache Spark sample
Dataset df = spark.read().json("logs.json");
df.where("age > 21")
.select("name.first").show();@file:DependsOn("org.archguard.scanner:doc-executor:2.0.0-alpha.2")
import org.archguard.dsl.*
var layer = layered {
prefixId("org.archguard")
component("controller") dependentOn component("service")
组件("service") 依赖于 组件("repository")
}Guarding like:
class(implementation "BaseParser")::name should endsWith "Parser";
class("java.util.Map") only accessed(["com.phodal.pepper.refactor.staticclass"]);
class(implementation "BaseParser")::name should not contains "Lexer";
// ========== DF with aggregation ==========
Dataset<Row> aggDF = df.groupBy("device").count();
// Print updated aggregations to console
aggDF
.writeStream()
.outputMode("complete")
.format("console")
.start();
// Have all the aggregates in an in-memory table
aggDF
.writeStream()
.queryName("aggregates") // this query name will be the table name
.outputMode("complete")
.format("memory")
.start();
spark.sql("select * from aggregates").show(); // interactively query in-memory table
libs:
KtORM sample:
val t = Employees.aliased("t")
database
.from(t)
.select(t.departmentId, avg(t.salary))
.groupBy(t.departmentId)
.having { avg(t.salary) greater 100.0 }
.forEach { row ->
println("${row.getInt(1)}:${row.getDouble(2)}")
}- setup jupyter with Kotlin: https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlin-jupyter
- with Conda
- download from https://repo.anaconda.com/
conda install -c jetbrains kotlin-jupyter-kernel
- with pip:
pip install kotlin-jupyter-kernel
- with Conda
- save with
.ipynbfor local file - try editor api ?
- analysis editor api?
- design poc editor
https://github.com/nteract/nteract is an open-source organization committed to creating fantastic interactive computing experiences that allow people to collaborate with ease.
java -jar build/distrib-build/run_kotlin_kernel/jars/kotlin-jupyter-kernel-0.11.0-100500.jar sample.json
config
{
"control_port": 50160,
"shell_port": 57503,
"transport": "tcp",
"signature_scheme": "hmac-sha256",
"stdin_port": 52597,
"hb_port": 42540,
"ip": "127.0.0.1",
"iopub_port": 40885,
"key": "a0436f6c-1916-498b-8eb9-e81ab9368e84"
}
In this section, we will explain the role of interpreters, interpreter groups and interpreter settings in Zeppelin. The concept of Zeppelin interpreters allows any language or data-processing backend to be plugged into Zeppelin. Currently, Zeppelin supports many interpreters such as Scala (with Apache Spark), Python (with Apache Spark), Spark SQL, Hive, JDBC, Markdown, Shell and so on.
A Zeppelin interpreter is a plug-in which enables Zeppelin users to use a specific language/data-processing-backend. For example, to use Scala code in Zeppelin, you would use the %spark interpreter.