A guide covering Differential Equations including the Formulas, Equations, Laws and Principles that will help you better understand the applications of Differential Equations.
Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in VSCode using this handy extension Markdown PDF.
- Differential equations: First order differential equations
- Slope fields: First order differential equations
- Euler's Method: First order differential equations
- Separable equations: First order differential equations
- Exponential models: First order differential equations
- Logistic models: First order differential equations
- Exact equations and integrating factors: First order differential equations
- Homogeneous equations: First order differential equations
- Linear homogeneous equations: Second order linear equations
- Complex and repeated roots of characteristic equation: Second order linear equations
- Method of undetermined coefficients: Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform: Laplace transform
- Properties of the Laplace transform: Laplace transform
- Laplace transform to solve a differential equation: Laplace transform
- The convolution integral
Ordinary Differential Equation | Wolfram MathWorld
Differential Equations - Wolfram|Alpha
Differential Equations | Mathematics | MIT OpenCourseWare
Differential Equations - Complete Review Course | YouTube
Differential Equations Playlist | YouTube
Introduction to Differential Equations | YouTube
Linear Systems of Differential Equations | YouTube
Linear Algebra and Differential Equations | Harvard University
Ordinary Differential Equations | Harvard University
Partial Differential Equations in Engineering Course | Stanford Online
Partial Differential Equations of Applied Mathematics Course | Stanford Online
Top Differential Equation Courses Online | Coursera
Introduction to Ordinary Differential Equations | Coursera
Differential Equations | Udemy
Top Differential Equations Courses Online | Udemy
Learn Differential Equations with Online Courses and lessons | edX
Differential Equations Courses - Engineer4Free
Differential Equations Study Resources - Course Hero
- Differential equations: First order differential equations
- Slope fields: First order differential equations
- Euler's Method: First order differential equations
- Separable equations: First order differential equations
- Exponential models: First order differential equations
- Logistic models: First order differential equations
- Exact equations and integrating factors: First order differential equations
- Homogeneous equations: First order differential equations
- Linear homogeneous equations: Second order linear equations
- Complex and repeated roots of characteristic equation: Second order linear equations
- Method of undetermined coefficients: Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform: Laplace transform
- Properties of the Laplace transform: Laplace transform
- Laplace transform to solve a differential equation: Laplace transform
- The convolution integral
Linear algebra is the math of vectors and matrices. The only prerequisite for this guide is a basic understanding of high school math concepts like numbers, variables, equations, and the fundamental arithmetic operations on real numbers: addition (denoted +), subtraction (denoted −), multiplication (denoted implicitly), and division (fractions). Also, you should also be familiar with functions that take real numbers as inputs and give real numbers as outputs, f : R → R.
Linear Algebra - Online Courses | Harvard University
Linear Algebra | MIT Open Learning Library
Top Linear Algebra Courses on Coursera
Mathematics for Machine Learning: Linear Algebra on Coursera
Top Linear Algebra Courses on Udemy
Learn Linear Algebra with Online Courses and Classes on edX
The Math of Data Science: Linear Algebra Course on edX
Linear Algebra in Twenty Five Lectures | UC Davis
Linear Algebra | UC San Diego Extension
Linear Algebra for Machine Learning | UC San Diego Extension
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Interactive Online Video | Wolfram
Linear Algebra Resources | Dartmouth
We now define the math operations for vectors. The operations we can perform on vectors ~u = (u1, u2, u3) and ~v = (v1, v2, v3) are: addition, subtraction, scaling, norm (length), dot product, and cross product:
The dot product and the cross product of two vectors can also be described in terms of the angle θ between the two vectors.
Vector Operations. Source: slideserve
Vector Operations. Source: pinterest
We denote by A the matrix as a whole and refer to its entries as aij .The mathematical operations defined for matrices are the following:
• determinant (denoted det(A) or |A|) Note that the matrix product is not a commutative operation.
Matrix Operations. Source: SDSU Physics
Check for modules that allow Matrix Operations. Source: DPS Concepts
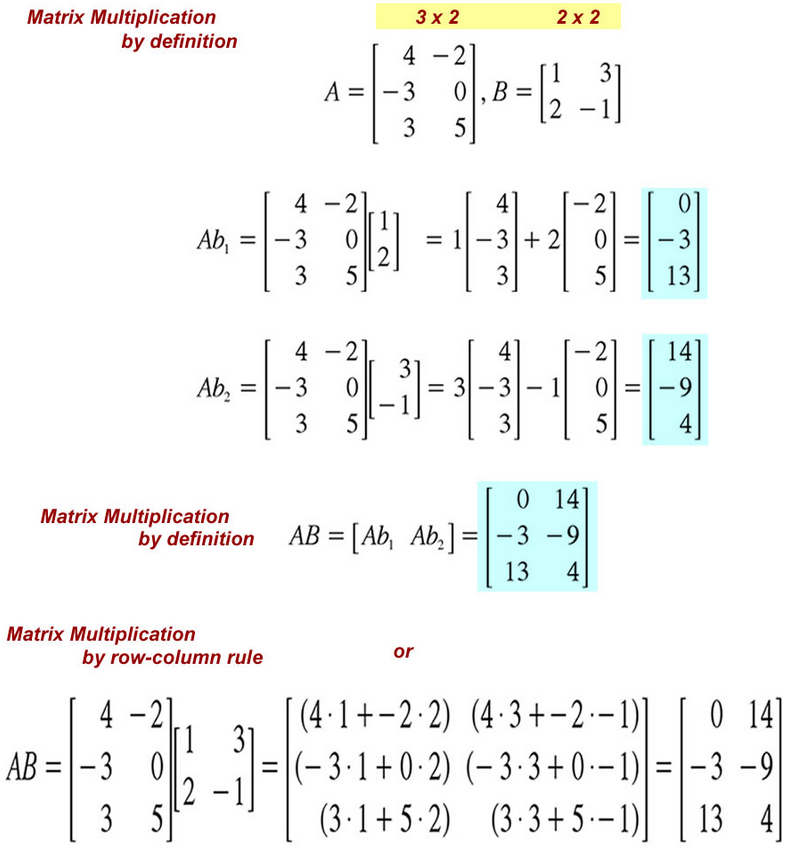
The matrix-vector product is an important special case of the matrix product.
There are two fundamentally different yet equivalent ways to interpret the matrix-vector product. In the column picture, (C), the multiplication of the
matrix A by the vector ~x produces a linear combination of the columns of the matrix: y = Ax = x1A[:,1] + x2A[:,2], where A[:,1] and A[:,2] are the first and second columns of the matrix A. In the row picture, (R), multiplication of the matrix A by the vector ~x produces a column vector with coefficients equal to the dot products of rows of the matrix with the vector ~x.
Matrix-vector product. Source: wikimedia
Matrix-vector Product. Source: mathisfun
The matrix-vector product is used to define the notion of a linear transformation, which is one of the key notions in the study of linear algebra. Multiplication by a matrix A ∈ R m×n can be thought of as computing a linear transformation TA that takes n-vectors as inputs and produces m-vectors as outputs:
Linear Transformations. Source: slideserve
Elementary matrices for linear transformations in R^2. Source:Quora
Fundamental theorem of linear algebra for Vector Spaces. Source: wikimedia
Fundamental theorem of linear algebra. Source: wolfram
System of Linear Equations by Graphing. Source: slideshare
Systems of equations as matrix equations. Source: mathisfun
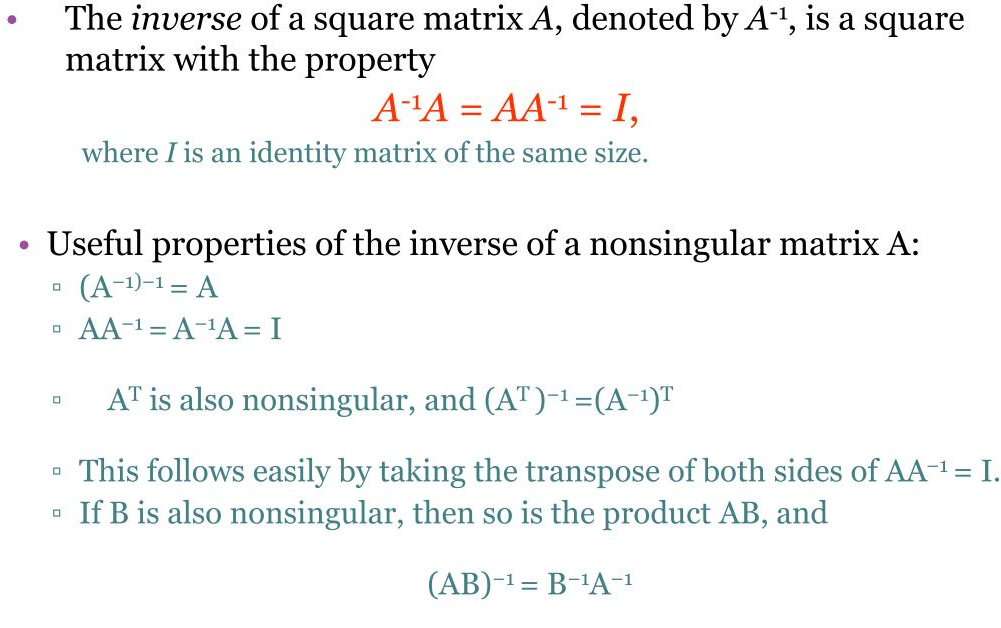
In this section we’ll look at several different approaches for computing the inverse of a matrix. The matrix inverse is unique so no matter which method we use to find the inverse, we’ll always obtain the same answer.
Inverse of 2x2 Matrix. Source: pinterest
One approach for computing the inverse is to use the Gauss–Jordan elimination procedure.
Elementray row operations. Source: YouTube
Every row operation we perform on a matrix is equivalent to a leftmultiplication by an elementary matrix.
Elementary Matrices. Source: SDSU Physics
Finding the inverse of a matrix is to use the Transpose method.
Transpose of a Matrix. Source: slideserve
In this section discuss a number of other important topics of linear algebra.
Intuitively, a basis is any set of vectors that can be used as a coordinate system for a vector space. You are certainly familiar with the standard basis for the xy-plane that is made up of two orthogonal axes: the x-axis and the y-axis.
Basis. Source: wikimedia
Change of Basis. Source: wikimedia
Matrix representations of linear transformations. Source: slideserve
The dimension of a vector space is defined as the number of vectors in a basis for that vector space. Consider the following vector space S = span{(1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0),(1, 1, 0)}. Seeing that the space is described by three vectors, we might think that S is 3-dimensional. This is not the case, however, since the three vectors are not linearly independent so they don’t form a basis for S. Two vectors are sufficient to describe any vector in S; we can write S = span{(1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0)}, and we see these two vectors are linearly independent so they form a basis and dim(S) = 2. There is a general procedure for finding a basis for a vector space. Suppose you are given a description of a vector space in terms of m vectors V = span{~v1, ~v2, . . . , ~vm} and you are asked to find a basis for V and the dimension of V. To find a basis for V, you must find a set of linearly independent vectors that span V. We can use the Gauss–Jordan elimination procedure to accomplish this task. Write the vectors ~vi as the rows of a matrix M. The vector space V corresponds to the row space of the matrix M. Next, use row operations to find the reduced row echelon form (RREF) of the matrix M. Since row operations do not change the row space of the matrix, the row space of reduced row echelon form of the matrix M is the same as the row space of the original set of vectors. The nonzero rows in the RREF of the matrix form a basis for vector space V and the numbers of nonzero rows is the dimension of V.
Basis and Dimension. Source: sliderserve
Recall the fundamental vector spaces for matrices that we defined in Section II-E: the column space C(A), the null space N (A), and the row space R(A). A standard linear algebra exam question is to give you a certain matrix A and ask you to find the dimension and a basis for each of its fundamental spaces. In the previous section we described a procedure based on Gauss–Jordan elimination which can be used “distill” a set of linearly independent vectors which form a basis for the row space R(A). We will now illustrate this procedure with an example, and also show how to use the RREF of the matrix A to find bases for C(A) and N (A).
Row space and Column space. Source: slideshare
Row space and Column space. Source: slideshare
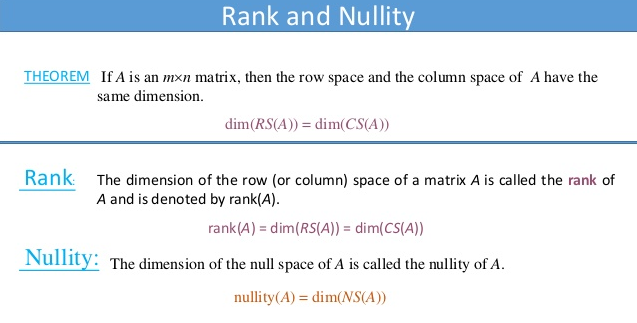
Rank and Nullity. Source: slideshare
There is an important distinction between matrices that are invertible and those that are not as formalized by the following theorem. Theorem. For an n×n matrix A, the following statements are equivalent:
Invertible Matrix theorem. Source: SDSU Physics
The determinant of a matrix, denoted det(A) or |A|, is a special way to combine the entries of a matrix that serves to check if a matrix is invertible or not.
Determinant of a Square Matrix. Source: stackexchange
Determinant of matrix. Source: onlinemathlearning
The set of eigenvectors of a matrix is a special set of input vectors for which the action of the matrix is described as a simple scaling. When a matrix is multiplied by one of its eigenvectors the output is the same eigenvector multiplied by a constant Aeλ = λeλ. The constant λ is called an eigenvalue of A.
Generalized EigenVectors. Source: YouTube
Linear regression is an approach to model the relationship between two variables by fitting a linear equation to observed data. One variable is considered to be an explanatory variable, and the other is considered to be a dependent variable.
Multiple Linear Regression. Source: Medium
MATLAB is a programming language that does numerical computing such as expressing matrix and array mathematics directly.
MATLAB and Simulink Training from MATLAB Academy
MathWorks Certification Program
MATLAB Online Courses from Udemy
MATLAB Online Courses from Coursera
MATLAB Online Courses from edX
Setting Up Git Source Control with MATLAB & Simulink
Pull, Push and Fetch Files with Git with MATLAB & Simulink
Create New Repository with MATLAB & Simulink
PRMLT is Matlab code for machine learning algorithms in the PRML book.
MATLAB Online allows to users to uilitize MATLAB and Simulink through a web browser such as Google Chrome.
Simulink is a block diagram environment for Model-Based Design. It supports simulation, automatic code generation, and continuous testing of embedded systems.
MATLAB Schemer is a MATLAB package makes it easy to change the color scheme (theme) of the MATLAB display and GUI.
LRSLibrary is a Low-Rank and Sparse Tools for Background Modeling and Subtraction in Videos. The library was designed for moving object detection in videos, but it can be also used for other computer vision and machine learning problems.
Robotics Toolbox for MATLAB provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
SEA-MAT is a collaborative effort to organize and distribute Matlab tools for the Oceanographic Community.
Gramm is a complete data visualization toolbox for Matlab. It provides an easy to use and high-level interface to produce publication-quality plots of complex data with varied statistical visualizations. Gramm is inspired by R's ggplot2 library.
hctsa is a software package for running highly comparative time-series analysis using Matlab.
Plotly is a Graphing Library for MATLAB.
YALMIP is a MATLAB toolbox for optimization modeling.
GNU Octave is a high-level interpreted language, primarily intended for numerical computations. It provides capabilities for the numerical solution of linear and nonlinear problems, and for performing other numerical experiments. It also provides extensive graphics capabilities for data visualization and manipulation.
CUDA Toolkit. Source: NVIDIA Developer CUDA
CUDA is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs. In GPU-accelerated applications, the sequential part of the workload runs on the CPU, which is optimized for single-threaded. The compute intensive portion of the application runs on thousands of GPU cores in parallel. When using CUDA, developers can program in popular languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and MATLAB.
CUDA GPU support for TensorFlow
NVIDIA Deep Learning cuDNN Documentation
NVIDIA GPU Cloud Documentation
NVIDIA NGC is a hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
NVIDIA NGC Containers is a registry that provides researchers, data scientists, and developers with simple access to a comprehensive catalog of GPU-accelerated software for AI, machine learning and HPC. These containers take full advantage of NVIDIA GPUs on-premises and in the cloud.
CUDA Toolkit is a collection of tools & libraries that provide a development environment for creating high performance GPU-accelerated applications. The CUDA Toolkit allows you can develop, optimize, and deploy your applications on GPU-accelerated embedded systems, desktop workstations, enterprise data centers, cloud-based platforms and HPC supercomputers. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ compiler, and a runtime library to build and deploy your application on major architectures including x86, Arm and POWER.
NVIDIA cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
CUDA-X HPC is a collection of libraries, tools, compilers and APIs that help developers solve the world's most challenging problems. CUDA-X HPC includes highly tuned kernels essential for high-performance computing (HPC).
NVIDIA Container Toolkit is a collection of tools & libraries that allows users to build and run GPU accelerated Docker containers. The toolkit includes a container runtime library and utilities to automatically configure containers to leverage NVIDIA GPUs.
Minkowski Engine is an auto-differentiation library for sparse tensors. It supports all standard neural network layers such as convolution, pooling, unpooling, and broadcasting operations for sparse tensors.
CUTLASS is a collection of CUDA C++ template abstractions for implementing high-performance matrix-multiplication (GEMM) at all levels and scales within CUDA. It incorporates strategies for hierarchical decomposition and data movement similar to those used to implement cuBLAS.
CUB is a cooperative primitives for CUDA C++ kernel authors.
Tensorman is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by System76.Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
Numba is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
Chainer is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using CuPy for high performance training and inference.
CuPy is an implementation of NumPy-compatible multi-dimensional array on CUDA. CuPy consists of the core multi-dimensional array class, cupy.ndarray, and many functions on it. It supports a subset of numpy.ndarray interface.
CatBoost is a fast, scalable, high performance Gradient Boosting on Decision Trees library, used for ranking, classification, regression and other machine learning tasks for Python, R, Java, C++. Supports computation on CPU and GPU.
cuDF is a GPU DataFrame library for loading, joining, aggregating, filtering, and otherwise manipulating data. cuDF provides a pandas-like API that will be familiar to data engineers & data scientists, so they can use it to easily accelerate their workflows without going into the details of CUDA programming.
cuML is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
ArrayFire is a general-purpose library that simplifies the process of developing software that targets parallel and massively-parallel architectures including CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware acceleration devices.
Thrust is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs.
AresDB is a GPU-powered real-time analytics storage and query engine. It features low query latency, high data freshness and highly efficient in-memory and on disk storage management.
Arraymancer is a tensor (N-dimensional array) project in Nim. The main focus is providing a fast and ergonomic CPU, Cuda and OpenCL ndarray library on which to build a scientific computing ecosystem.
Kintinuous is a real-time dense visual SLAM system capable of producing high quality globally consistent point and mesh reconstructions over hundreds of metres in real-time with only a low-cost commodity RGB-D sensor.
GraphVite is a general graph embedding engine, dedicated to high-speed and large-scale embedding learning in various applications.
R is an open source software environment for statistical computing and graphics. It compiles and runs on a wide variety of platforms such as Windows and MacOS.
Running R at Scale on Google Compute Engine
Learn R Programming with Online Courses and Lessons by edX
R Language Courses by Coursera
Learn R For Data Science by Udacity
RStudio is an integrated development environment for R and Python, with a console, syntax-highlighting editor that supports direct code execution, and tools for plotting, history, debugging and workspace management.
Shiny is a newer package from RStudio that makes it incredibly easy to build interactive web applications with R.
Rmarkdown is a package helps you create dynamic analysis documents that combine code, rendered output (such as figures), and prose.
Rplugin is R Language supported plugin for the IntelliJ IDE.
Plotly is an R package for creating interactive web graphics via the open source JavaScript graphing library plotly.js.
Metaflow is a Python/R library that helps scientists and engineers build and manage real-life data science projects. Metaflow was originally developed at Netflix to boost productivity of data scientists who work on a wide variety of projects from classical statistics to state-of-the-art deep learning.
Prophet is a procedure for forecasting time series data based on an additive model where non-linear trends are fit with yearly, weekly, and daily seasonality, plus holiday effects. It works best with time series that have strong seasonal effects and several seasons of historical data.
LightGBM is a gradient boosting framework that uses tree based learning algorithms, used for ranking, classification and many other machine learning tasks.
Dash is a Python framework for building analytical web applications in Python, R, Julia, and Jupyter.
MLR is Machine Learning in R.
ML workspace is an all-in-one web-based IDE specialized for machine learning and data science. It is simple to deploy and gets you started within minutes to productively built ML solutions on your own machines. ML workspace is the ultimate tool for developers preloaded with a variety of popular data science libraries (Tensorflow, PyTorch, Keras, and MXnet) and dev tools (Jupyter, VS Code, and Tensorboard) perfectly configured, optimized, and integrated.
CatBoost is a fast, scalable, high performance Gradient Boosting on Decision Trees library, used for ranking, classification, regression and other machine learning tasks for Python, R, Java, C++. Supports computation on CPU and GPU.
Plumber is a tool that allows you to create a web API by merely decorating your existing R source code with special comments.
Drake is an R-focused pipeline toolkit for reproducibility and high-performance computing.
DiagrammeR is a package you can create, modify, analyze, and visualize network graph diagrams. The output can be incorporated into R Markdown documents, integrated with Shiny web apps, converted to other graph formats, or exported as image files.
Knitr is a general-purpose literate programming engine in R, with lightweight API's designed to give users full control of the output without heavy coding work.
Broom is a tool that converts statistical analysis objects from R into tidy format.
Python is an interpreted, high-level programming language. Python is used heavily in the fields of Data Science and Machine Learning.
Python Developer’s Guide is a comprehensive resource for contributing to Python – for both new and experienced contributors. It is maintained by the same community that maintains Python.
Azure Functions Python developer guide is an introduction to developing Azure Functions using Python. The content below assumes that you've already read the Azure Functions developers guide.
CheckiO is a programming learning platform and a gamified website that teaches Python through solving code challenges and competing for the most elegant and creative solutions.
PCEP – Certified Entry-Level Python Programmer certification
PCAP – Certified Associate in Python Programming certification
PCPP – Certified Professional in Python Programming 1 certification
PCPP – Certified Professional in Python Programming 2
MTA: Introduction to Programming Using Python Certification
Getting Started with Python in Visual Studio Code
Google's Python Education Class
The Python Open Source Computer Science Degree by Forrest Knight
Intro to Python for Data Science
Learn Python with Online Courses and Classes from edX
Python Courses Online from Coursera
Python Package Index (PyPI) is a repository of software for the Python programming language. PyPI helps you find and install software developed and shared by the Python community.
PyCharm is the best IDE I've ever used. With PyCharm, you can access the command line, connect to a database, create a virtual environment, and manage your version control system all in one place, saving time by avoiding constantly switching between windows.
Python Tools for Visual Studio(PTVS) is a free, open source plugin that turns Visual Studio into a Python IDE. It supports editing, browsing, IntelliSense, mixed Python/C++ debugging, remote Linux/MacOS debugging, profiling, IPython, and web development with Django and other frameworks.
Pylance is an extension that works alongside Python in Visual Studio Code to provide performant language support. Under the hood, Pylance is powered by Pyright, Microsoft's static type checking tool.
Pyright is a fast type checker meant for large Python source bases. It can run in a “watch” mode and performs fast incremental updates when files are modified.
Django is a high-level Python Web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design.
Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries.
Web2py is an open-source web application framework written in Python allowing allows web developers to program dynamic web content. One web2py instance can run multiple web sites using different databases.
AWS Chalice is a framework for writing serverless apps in python. It allows you to quickly create and deploy applications that use AWS Lambda.
Tornado is a Python web framework and asynchronous networking library. Tornado uses a non-blocking network I/O, which can scale to tens of thousands of open connections.
HTTPie is a command line HTTP client that makes CLI interaction with web services as easy as possible. HTTPie is designed for testing, debugging, and generally interacting with APIs & HTTP servers.
Scrapy is a fast high-level web crawling and web scraping framework, used to crawl websites and extract structured data from their pages. It can be used for a wide range of purposes, from data mining to monitoring and automated testing.
Sentry is a service that helps you monitor and fix crashes in realtime. The server is in Python, but it contains a full API for sending events from any language, in any application.
Pipenv is a tool that aims to bring the best of all packaging worlds (bundler, composer, npm, cargo, yarn, etc.) to the Python world.
Python Fire is a library for automatically generating command line interfaces (CLIs) from absolutely any Python object.
Bottle is a fast, simple and lightweight WSGI micro web-framework for Python. It is distributed as a single file module and has no dependencies other than the Python Standard Library.
CherryPy is a minimalist Python object-oriented HTTP web framework.
Sanic is a Python 3.6+ web server and web framework that's written to go fast.
Pyramid is a small and fast open source Python web framework. It makes real-world web application development and deployment more fun and more productive.
TurboGears is a hybrid web framework able to act both as a Full Stack framework or as a Microframework.
Falcon is a reliable, high-performance Python web framework for building large-scale app backends and microservices with support for MongoDB, Pluggable Applications and autogenerated Admin.
Neural Network Intelligence(NNI) is an open source AutoML toolkit for automate machine learning lifecycle, including Feature Engineering, Neural Architecture Search, Model Compression and Hyperparameter Tuning.
Dash is a popular Python framework for building ML & data science web apps for Python, R, Julia, and Jupyter.
Luigi is a Python module that helps you build complex pipelines of batch jobs. It handles dependency resolution, workflow management, visualization etc. It also comes with Hadoop support built-in.
Locust is an easy to use, scriptable and scalable performance testing tool.
spaCy is a library for advanced Natural Language Processing in Python and Cython.
NumPy is the fundamental package needed for scientific computing with Python.
Pillow is a friendly PIL(Python Imaging Library) fork.
IPython is a command shell for interactive computing in multiple programming languages, originally developed for the Python programming language, that offers enhanced introspection, rich media, additional shell syntax, tab completion, and rich history.
GraphLab Create is a Python library, backed by a C++ engine, for quickly building large-scale, high-performance machine learning models.
Pandas is a fast, powerful, and easy to use open source data structrures, data analysis and manipulation tool, built on top of the Python programming language.
PuLP is an Linear Programming modeler written in python. PuLP can generate LP files and call on use highly optimized solvers, GLPK, COIN CLP/CBC, CPLEX, and GUROBI, to solve these linear problems.
Matplotlib is a 2D plotting library for creating static, animated, and interactive visualizations in Python. Matplotlib produces publication-quality figures in a variety of hardcopy formats and interactive environments across platforms.
Scikit-Learn is a simple and efficient tool for data mining and data analysis. It is built on NumPy,SciPy, and mathplotlib.
Julia is a high-level, high-performance dynamic language for technical computing. Julia programs compile to efficient native code for multiple platforms via LLVM.
JuliaHub contains over 4,000 Julia packages for use by the community.
DataFrames Tutorial using Jupyter Notebooks
JuliaPro is a free and fast way to setup Julia for individual researchers, engineers, scientists, quants, traders, economists, students and others. Julia developers can build better software quicker and easier while benefiting from Julia's unparalleled high performance. It includes 2600+ open source packages or from a curated list of 250+ JuliaPro packages. Curated packages are tested, documented and supported by Julia Computing.
Juno is a powerful, free IDE based on Atom for the Julia language.
Debugger.jl is the Julia debuggin tool.
Profile (Stdlib) is a module provides tools to help developers improve the performance of their code. When used, it takes measurements on running code, and produces output that helps you understand how much time is spent on individual line's.
Revise.jl allows you to modify code and use the changes without restarting Julia. With Revise, you can be in the middle of a session and then update packages, switch git branches, and/or edit the source code in the editor of your choice; any changes will typically be incorporated into the very next command you issue from the REPL. This can save you the overhead of restarting Julia, loading packages, and waiting for code to JIT-compile.
JuliaGPU is a Github organization created to unify the many packages for programming GPUs in Julia. With its high-level syntax and flexible compiler, Julia is well positioned to productively program hardware accelerators like GPUs without sacrificing performance.
IJulia.jl is the Julia kernel for Jupyter.
AWS.jl is a Julia interface for Amazon Web Services.
CUDA.jl is a package for the main programming interface for working with NVIDIA CUDA GPUs using Julia. It features a user-friendly array abstraction, a compiler for writing CUDA kernels in Julia, and wrappers for various CUDA libraries.
XLA.jl is a package for compiling Julia to XLA for Tensor Processing Unit(TPU).
Nanosoldier.jl is a package for running JuliaCI services on MIT's Nanosoldier cluster.
Julia for VSCode is a powerful extension for the Julia language.
JuMP.jl is a domain-specific modeling language for mathematical optimization embedded in Julia.
Optim.jl is a univariate and multivariate optimization in Julia.
RCall.jl is a package that allows you to call R functions from Julia.
JavaCall.jl is a package that allows you to call Java functions from Julia.
PyCall.jl is a package that allows you to call Python functions from Julia.
MXNet.jl is the Apache MXNet Julia package. MXNet.jl brings flexible and efficient GPU computing and state-of-art deep learning to Julia.
Knet is the Koç University deep learning framework implemented in Julia by Deniz Yuret and collaborators. It supports GPU operation and automatic differentiation using dynamic computational graphs for models defined in plain Julia.
Distributions.jl is a Julia package for probability distributions and associated functions.
DataFrames.jl is a tool for working with tabular data in Julia.
Flux.jl is an elegant approach to machine learning. It's a 100% pure-Julia stack, and provides lightweight abstractions on top of Julia's native GPU and AD support.
IRTools.jl is a simple and flexible IR format, expressive enough to work with both lowered and typed Julia code, as well as external IRs.
Cassette.jl is a Julia package that provides a mechanism for dynamically injecting code transformation passes into Julia’s just-in-time (JIT) compilation cycle, enabling post hoc analysis and modification of "Cassette-unaware" Julia programs without requiring manual source annotation or refactoring of the target code.
- If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a Pull Request.
Distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License.