将多个小查询批处理为单个大查询可以是一种有用的优化。请编写一个名为 QueryBatcher 的类来实现这个功能。
它的构造函数应接受两个参数:
- 一个异步函数
queryMultiple,它接受一个字符串键的数组作为输入。它将返回一个与输入数组长度相同的值数组。每个索引对应于与input[i]相关联的值。可以假设该异步函数永远不会被拒绝。 - 一个以毫秒为单位的节流时间
t。
该类有一个方法:
async getValue(key):接受一个字符串键,并返回一个解析后的字符串值。传递给此函数的键值最终应传递给queryMultiple函数。在t毫秒内不应连续调用queryMultiple。第一次调用getValue时,应立即使用该单个键调用queryMultiple。如果在t毫秒后再次调用了getValue,则所有传递的键应传递给queryMultiple,并返回最终结果。可以假设传递给该方法的每个键都是唯一的。
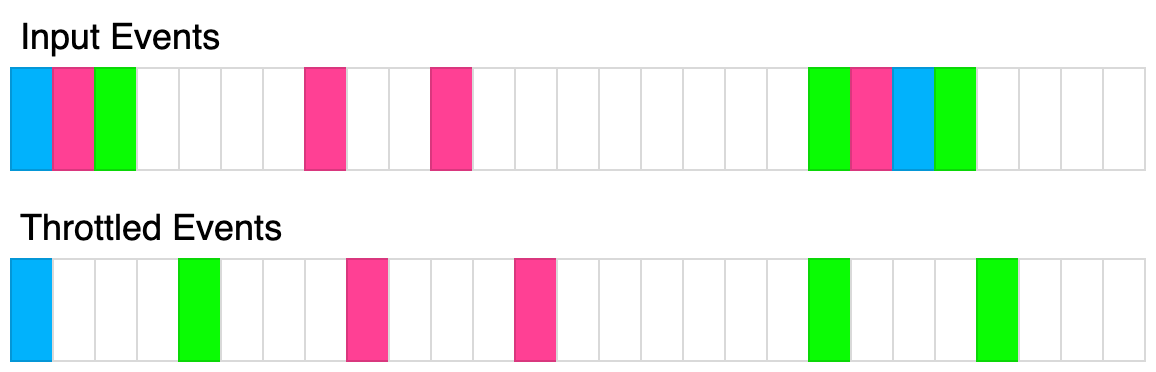
下图说明了节流算法的工作原理。每个矩形代表 100毫秒。节流时间为 400毫秒。
示例 1:
输入:
queryMultiple = async function(keys) {
return keys.map(key => key + '!');
}
t = 100
calls = [
{"key": "a", "time": 10},
{"key": "b", "time": 20},
{"key": "c", "time": 30}
]
输出:[
{"resolved": "a!", "time": 10},
{"resolved": "b!", "time": 110},
{"resolved": "c!", "time": 110}
]
解释:
const batcher = new QueryBatcher(queryMultiple, 100);
setTimeout(() => batcher.getValue('a'), 10); // "a!" at t=10ms
setTimeout(() => batcher.getValue('b'), 20); // "b!" at t=110ms
setTimeout(() => batcher.getValue('c'), 30); // "c!" at t=110ms
queryMultiple 简单地给键添加了"!"。
在 t=10ms 时,调用 getValue('a'),立即调用 queryMultiple(['a']) 并立即返回结果。
在 t=20ms 时,调用 getValue('b'),但查询需要等待。
在 t=30ms 时,调用 getValue('c'),但查询需要等待。
在 t=110ms 时,调用 queryMultiple(['b', 'c']) 并立即返回结果。
示例 2;
输入:
queryMultiple = async function(keys) {
await new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, 100));
return keys.map(key => key + '!');
}
t = 100
calls = [
{"key": "a", "time": 10},
{"key": "b", "time": 20},
{"key": "c", "time": 30}
]
输出:[
{"resolved": "a!", "time": 110},
{"resolved": "b!", "time": 210},
{"resolved": "c!", "time": 210}
]
解释:
这个例子与示例 1 相同,只是在 queryMultiple 中有一个 100ms 的延迟。结果也相同,只是 promise 的解析时间延迟了 100ms。
示例 3:
输入:
queryMultiple = async function(keys) {
await new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, keys.length * 100));
return keys.map(key => key + '!');
}
t = 100
calls = [
{"key": "a", "time": 10},
{"key": "b", "time": 20},
{"key": "c", "time": 30},
{"key": "d", "time": 40},
{"key": "e", "time": 250}
{"key": "f", "time": 300}
]
输出:[
{"resolved":"a!","time":110},
{"resolved":"e!","time":350},
{"resolved":"b!","time":410},
{"resolved":"c!","time":410},
{"resolved":"d!","time":410},
{"resolved":"f!","time":450}
]
解释:
在 t=10ms 时,调用 queryMultiple(['a']) ,在 t=110ms 时解析。
在 t=110ms 时,调用 queryMultiple(['b', 'c', 'd']) ,在 t=410ms 时解析。
在 t=250ms 时,调用 queryMultiple(['e']) ,在 t=350ms 时解析。
在 t=350ms 时,调用 queryMultiple(['f']) ,在 t=450ms 时解析。
提示:
0 <= t <= 10000 <= calls.length <= 101 <= key.length <= 100所有的键值都是唯一的