The idea is to create a device connected to the internet capable of measuring the electrical consumption of a three-phase line and keeping a historical data to optimize energy consumption
- Arduino UNO
- CT Sensor YHDC
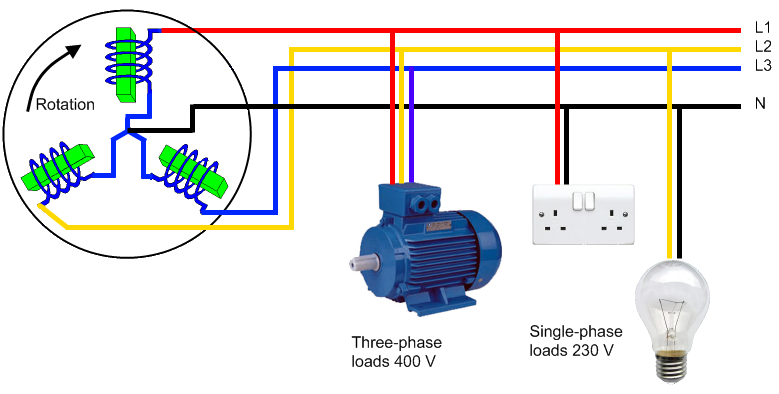
Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by electrical grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads. A three-wire three-phase circuit is usually more economical than an equivalent two-wire single-phase circuit at the same line to ground voltage because it uses less conductor material to transmit a given amount of electrical power. Polyphase power systems were independently invented by Galileo Ferraris, Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky, Jonas Wenström, John Hopkinson and Nikola Tesla in the late 1880s.
In a symmetric three-phase power supply system, three conductors each carry an alternating current of the same frequency and voltage amplitude relative to a common reference but with a phase difference of one third of a cycle between each. The common reference is usually connected to ground and often to a current-carrying conductor called the neutral. Due to the phase difference, the voltage on any conductor reaches its peak at one third of a cycle after one of the other conductors and one third of a cycle before the remaining conductor. This phase delay gives constant power transfer to a balanced linear load. It also makes it possible to produce a rotating magnetic field in an electric motor and generate other phase arrangements using transformers (for instance, a two phase system using a Scott-T transformer). The amplitude of the voltage difference between two phases is 3 {\sqrt {3}} (1.732...) times the amplitude of the voltage of the individual phases. The symmetric three-phase systems described here are simply referred to as three-phase systems because, although it is possible to design and implement asymmetric three-phase power systems (i.e., with unequal voltages or phase shifts), they are not used in practice because they lack the most important advantages of symmetric systems. In a three-phase system feeding a balanced and linear load, the sum of the instantaneous currents of the three conductors is zero. In other words, the current in each conductor is equal in magnitude to the sum of the currents in the other two, but with the opposite sign. The return path for the current in any phase conductor is the other two phase conductors.