-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 39
FAQ
- Why clifm?
- Numbers?
- Clear the screen
- Bookmarks
- Search/filter files
- Files selection
- Opening applications
- Color schemes
- File previews
- Aliases
People often asks how does clifm compare to other file managers. The answer is simple: it doesn't. And here's why.
Clifm is not so much about features (though it provides quite a lot of them), but about design, about the way in which you interact with your file system.
Most terminal file managers out there (if not all) are built/designed using the TUI principles, much like Midnight Commander or Ranger. But clifm is built based on the CLI principles: do not navigate through a big menu of files, just type it!, exactly as you do in your shell, but easier and faster.
Clifm does not need to be better. It's just different! 😉
For more information see our introductory section.
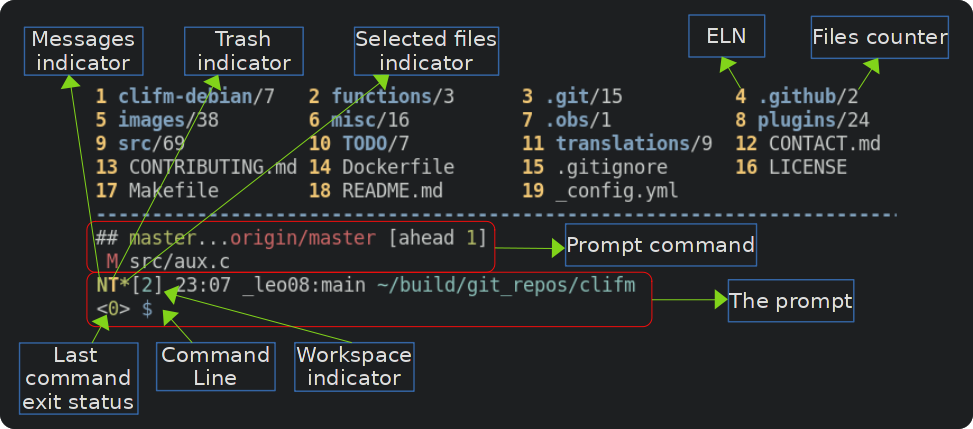
ELN: It stands for Entry List Number. Each entry in the files list has its own number, which can be used as a shortcut to corresponding file. For example, to print file properties of the file whose ELN is 12 you can enter p 12 (the actual file name will be suggested next to the ELN; just press Right to accept the suggestion). In the same way, to change to a directory or to open a file (with the default associated application) just enter its ELN.
Files counter: The amount of files contained by a given directory
Workspace indicator: Clifm provides up to 8 workspaces, each with its own independent path. To switch workspaces use the ws command. Example: ws 2 (to switch to the second workspace). Alt-[1-4] is also available.
To clear the screen just enter rf (. will also do the trick). You can also press Enter (on an empty line) or Ctrl-l.
Use the bm command as follows: bm add FILENAME BOOKMARK_NAME, say bm add important_dir/ dir, in which case the directory important_dir will be bookmarked as dir. Then you can access your bookmark either via bm dir or b:dir.
Note that you can operate on your bookmarks as if there where any other file. For example, to select the bookmark named dir use the s command: s b:dir.
To list available bookmarks just enter bm or type b:<TAB> (or bm <TAB>).
Absolutely. You can filter files by name, MIME type, and file type. A few easy examples:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
=<TAB> |
List all file types in the current directory |
=l<TAB> |
List all symbolic links in the current directory |
@<TAB> |
List all MIME types in the current directory |
@image<TAB> |
List all files whose MIME type matches image in the current directory |
*.pdf<TAB> |
List all file names ending with .pdf
|
/file* |
Print a list of all file names starting with file in the current directory |
For more information consult the file filters and the files search sections.
Easy. Just use the s command. Examples:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
s *.c |
Select files with .c extension |
s 1-12 |
Select files whose ELN's are 1 through 12 (the first 12 files) |
s t:pdf |
Select all files tagged as pdf
|
s *.c 1-12 t:pdf |
All of the above at once |
List selected files as follows: enter sb or type s:<TAB>.
To deselect files use the ds command: ds * to deselect all files, or ds <TAB> to deselect selectively.
To operate on selected files use the sel or s: keywords. For example: p s: to print file properties of all selected files. Type s:<TAB> to operate on selected files selectively.
See the files selection page for more information.
Let's say you want to open PDF files with Okular. The procedure is quite straitghtforward:
- Open the Mimelist file, where opening applications are defined:
mm edit(or F6). - Search for the PDF section and place Okular as the first opening application:
X:.*/pdf$:okular;...
For more information see the resource opener section.
Contributed by theRoboxx
Either via the command line (--color-scheme=NAME), permanent via the ColorScheme option in the main configuration file, or temporary for preview purposes using the cs command, for instance,
cs mytheme
Enter cs (or cs <TAB>) to get a list of available color schemes.
By default, clifm ships several themes, though more can be found in our colors repository.
For more details and custom theming visit the wiki.
Use the alias import command. Example:
alias import ~/.bashrcSee the aliases section for more details.
Yes. If running in fzf-mode (default if fzf is installed):
- Use the view command: enter
viewor press Alt+-. - You can also just press TAB to browse files in the current directory, including previews.
For image previews consult the image previews section.
🤷♀️ The answer you're looking for isn't here? Please request it to be added to this FAQ page.
⬆ Top
📌 Wiki Home
⚡ CliFM Home

What is clifm?
Is it for me?
Main design and goals
Dependencies
Installation
Interface
Getting help
Configuration file
Command line options
Commands
Keybindings
FAQ
ELN (entry list number)
Navigation
Basic file operations
Opening files
Sorting files
Filtering files
Selection
Search
Bookmarks
Trash
Archives
File details/Long view
Basic usage examples
Workspaces
Directory jumper
Resource opener (file launcher)
Actions (plugins)
Autocommands
Profiles
Aliases
The prompt
TAB completion (with fzf integration)
Auto-suggestions
Syntax highlighting
File tags
File names cleaner
Fastback and backdir
Remote file systems management
Light mode
Read-only mode
Stealth mode (incognito)
Disk usage analyzer mode
Desktop notifications
Environment
Files
Security
Tiling WM's and terminal multiplexers
FZF mode for TAB completion
File/image previews
Bulk operations
Archiving
Virtual directories
cp/mv progress bar
Send files to Android device
Git integration
Wildcards and REGEX
Multiple instances
Icons
Plugins
Customization
Custom MIME types
CD on quit
Files picker
Files lister (ls-mode)
stat(1) replacement
Subshell notification