ToggleX is a flexible and powerful feature flag management library for .NET applications. It allows developers to enable or disable features in their application dynamically based on certain conditions, without deploying new code. Which makes it useful for controlling beta features, conducting A/B testing, rolling out features incrementally, or temporarily disabling certain functionalities in production environments.
- Dynamic Feature Management: Toggle features on or off based on conditions
- Customizable Context: Users can define their own feature context classes to determine feature eligibility
- Μultiple Feature Sources: Supports JSON-based configuration for feature flag management
- Integration with ASP.NET Core: Easily integrates with ASP.NET Core applications via Dependency Injection and Action Filters
The core functionality of the ToggleX library revolves around managing feature flags based on conditions defined within feature configuration files (such as JSON files). The library allows you to:
- Define Features: Features are enabled or disabled based on specific conditions
- Use Context: Conditions for enabling/disabling features can depend on user-specific or application-specific context (e.g., user role, user location, or other custom data)
- Evaluate Conditions: Conditions can be evaluated dynamically using expressions (e.g., evaluating whether a user has access to a certain feature)
The core components of the library are:
FeatureManager: The main component that checks whether a feature is enabled or not based on providedFeatureProvider: Provides the feature flag configuration. This can be a JSON provider, or other custom providersFeatureContext: A base context class that can be implemented by the user to represent various data points needed to evaluate conditions for a feature flag
You can install the ToggleX library via NuGet Package Manager or .NET CLI.
dotnet add package ToggleX
Name: The name of the feature flagIsEnabled: A boolean value indicating if the feature is enabled or disabledDependsOn: A list of other feature flags that this feature depends on. The feature will only be enabled if all the dependencies are enabled.Rules: A list of conditions that further define when the feature flag should be enabled, based on the context provided. Each rule has:Condition: A condition expression that evaluates whether the feature should be enabled (e.g.UserRole == 'Admin')IsEnabled: A boolean value indicating whether the feature should be enabled
[
{
"Name": "AdvancedSearch",
"IsEnabled": true,
"DependsOn": ["SearchEngine"],
"Rules": [
{
"Condition": "UserRole == 'Admin' && UserId == 42 && UserLocation == 'GR'",
"IsEnabled": true
}
]
},
{
"Name": "SearchEngine",
"IsEnabled": true,
"DependsOn": []
}
]In your Program.cs or Startup.cs, register the FeatureManager (in this case using JsonFeatureProvider):
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton(new FeatureManager(new JsonFeatureProvider("features.json"));
}
}Imagine you have the same JSON configuration as above in our example. After registering the FeatureManager, you might want to create a custom context class:
public class CustomFeatureContext : IFeatureContext
{
public CustomFeatureContext(string userRole, int userId, string userLocation)
{
UserRole = userRole;
UserId = userId;
UserLocation = userLocation;
}
public string UserRole { get; set; }
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string UserLocation { get; set; }
}Make sure to also register it in your services:
builder.Services.AddScoped<CustomFeatureContext>(provider => new CustomFeatureContext("Admin", 42, "GR"));Then, you might want to create your own custom attribute:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Class)]
public class FeatureFlagAttribute : Attribute, IActionFilter
{
private readonly string _featureName;
private readonly Type _featureContextType;
public FeatureFlagAttribute(string featureName, Type featureContextType)
{
_featureName = featureName;
_featureContextType = featureContextType;
}
public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
var featureManager = context.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetService<FeatureManager>();
try
{
IFeatureContext featureContext = (IFeatureContext)context.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetRequiredService(_featureContextType);
var isFeatureEnabled = featureManager.IsFeatureEnabled(_featureName, featureContext);
if (!isFeatureEnabled)
{
context.Result = new ContentResult
{
Content = "Feature is disabled..\n",
StatusCode = 403
};
}
}
catch (FeatureEvaluationException ex)
{
var requestDetails = GetRequestDetails(context.HttpContext.Request);
Log.Error($"on request: {requestDetails} \n{ex.Message}");
context.Result = new ContentResult
{
Content = "Feature is disabled.\n",
StatusCode = 403
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
public void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext context) { }
}Which then can be used in ANY Class or Method:
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
[FeatureFlag("AdvancedSearch", typeof(CustomFeatureContext))]
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}The ToggleX library includes detailed error handling for various situations where feature evaluation might fail. Below are examples of common error scenarios, as well as how they will be represented in the application:
This error occurs when the conditions defined for a feature flag do not match the current context. For example, if a feature flag is enabled only for users with a specific role or location, but the current context doesn't match, the evaluation will fail
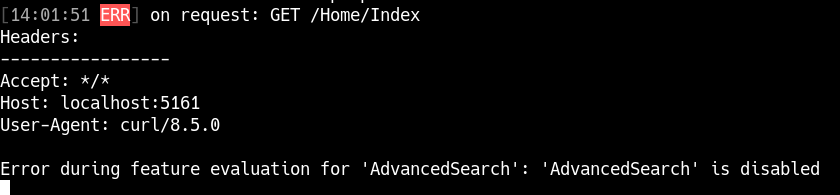
This error occurs when a feature flag is explicitly disabled in the configuration but the application attempts to evaluate it as if it's enabled
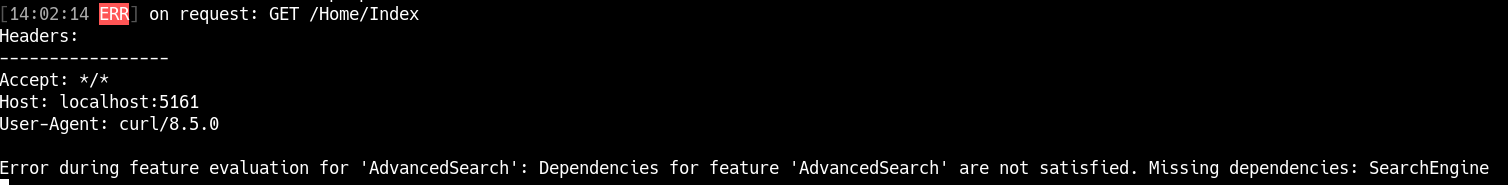
This error occurs when a feature has dependencies (e.g., other features that must be enabled for this one to work) and those dependencies are not satisfied. For example, if the AdvancedSearch feature requires a SearchEngine feature to be enabled, but SearchEngine is disabled, the evaluation will fail
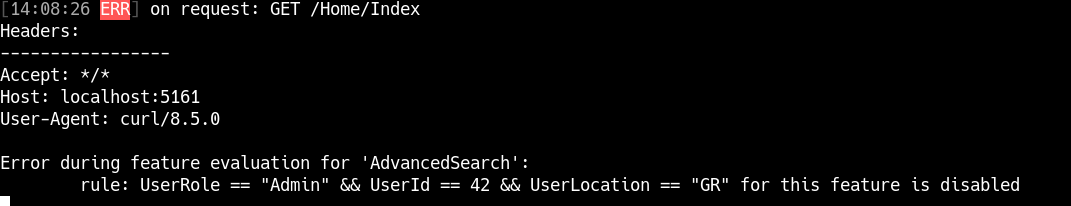
This error occurs when a feature rule is explicitly disabled in the configuration. For example, a feature flag may be designed to be dynamically enabled/disabled based on business logic, and the rule itself could be disabled under certain circumstances.