| tags | datasets | metrics | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
- Introduction
- Description
- Implementation Highlights
- Model Architecture
- Getting Started
- Usage
- Results
- Contributing
- Citation
The paper introduces LongRoPE, a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens.
The key ideas are:
-
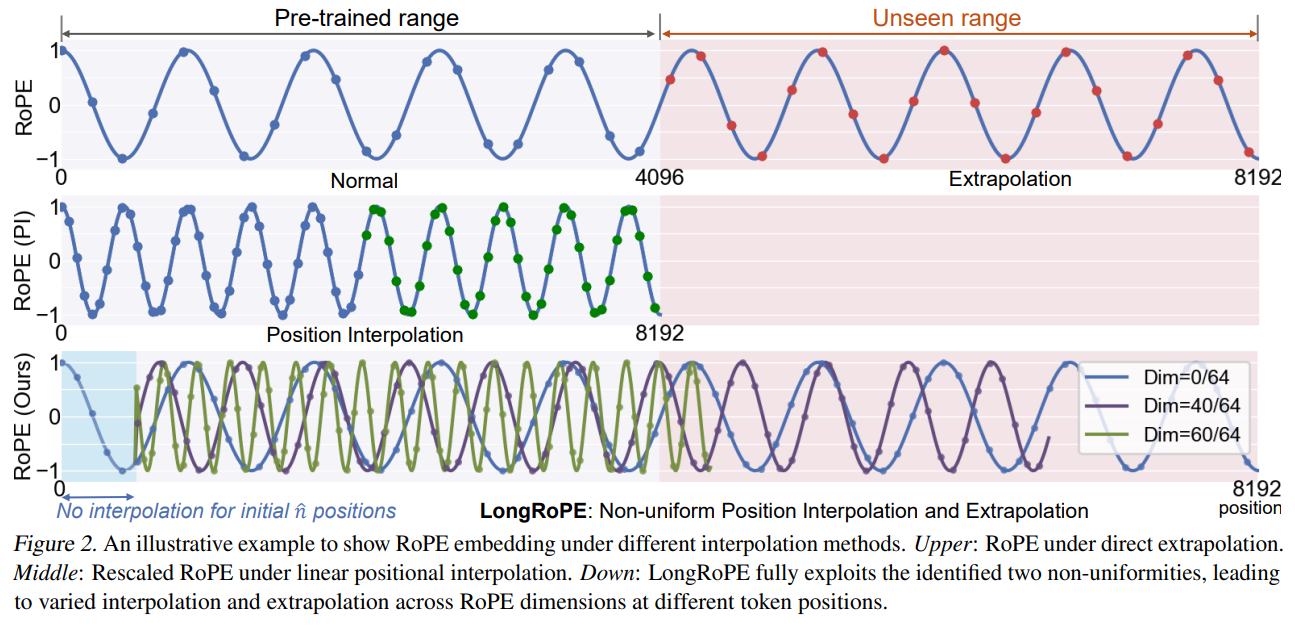
Identify and exploit two forms of non-uniformities in positional embeddings to minimize information loss during interpolation. This enables 8x context extension without fine-tuning.
-
Use an efficient progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach 2048k context, instead of directly fine-tuning an extremely large context.
-
Adjust embeddings for shorter contexts to recover performance within original window size.
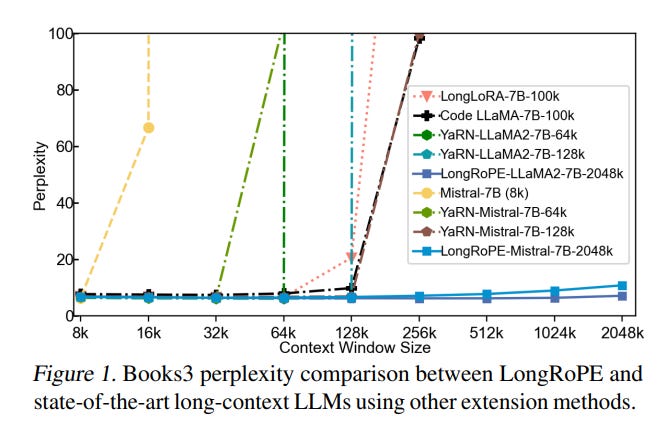
The method is applied to LLaMA2 and Mistral. Experiments across various tasks demonstrate LongRoPE's effectiveness in maintaining performance from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
The Transformer architecture struggles with the quadratic computational complexity of self-attention and its lack of generalization to token positions unseen at training time. To scale the self-attention computation to a large context, various methods have been proposed, such as the RoPE, AliBi, attention sinks, etc. Nonetheless, none of these solutions can effectively scale to context with millions of tokens while preserving the model's accuracy.
This paper presents a new technique, LongRoPE, expanding the context window of LLMs to over 2 million tokens.
LongRoPE utilizes a progressive extension strategy to attain a 2048k context window without necessitating direct fine-tuning on exceedingly lengthy texts, which are both rare and difficult to procure. This strategy initiates with a 256k extension on a pre-trained LLM, followed by fine-tuning at this length.
To address potential performance declines in the original (shorter) context window, LongRoPE further adjusts the RoPE rescale factors on the extended LLM, scaling down to 4k and 8k context windows on the 256k fine-tuned LLM using its search algorithm to minimize positional interpolation. During inference for sequences under 8k in length, RoPE is updated with these meticulously searched rescale factors.
Testing across various LLMs and tasks requiring long contexts has validated LongRoPE's efficacy. The method significantly maintains low perplexity across evaluation lengths from 4k to 2048k tokens, achieves above 90% accuracy in passkey retrieval, and delivers accuracy comparable to standard benchmarks within a 4096 context window
- Enable in-context learning with more examples to boost LLM reasoning
- Build LLM agents that leverage longer context for tasks like dialog and question answering
- Summarize very long documents by utilizing the full document context
- Improve few-shot learning by providing more contextual examples to models
- Enable long-term memory by utilizing the full context window
An in-depth look at the structural modifications and their implications for model performance.
The LongRoPE model architecture is designed to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) to over 2 million tokens, addressing the limitations of traditional Transformer architectures. The key innovation lies in the progressive extension strategy and the adjustment of positional embeddings.
Key components include:
- Rotary Position Encoding (RoPE):
class RoPEPositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, max_len=1000000, base=10000):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.max_len = max_len
self.base = base
self.theta = torch.tensor([base ** (-2 * (i // 2) / d_model) for i in range(d_model)])
def forward(self, positions):
angles = positions.unsqueeze(-1) * self.theta
sin_cos = torch.stack([angles.cos(), angles.sin()], dim=-1)
return sin_cos.view(*sin_cos.shape[:-2], -1)- Non-uniform Interpolation:
def non_uniform_interpolation(pos_embed, extension_ratio, lambda_factors, n_hat):
d_model = pos_embed.shape[-1]
interpolated_pos = pos_embed.clone()
for i in range(d_model // 2):
mask = torch.arange(pos_embed.shape[-2], device=pos_embed.device) < n_hat
scale = torch.where(mask, torch.ones_like(pos_embed[..., 0], device=pos_embed.device),
1 / (lambda_factors[i] * extension_ratio))
interpolated_pos[..., 2 * i] *= scale
interpolated_pos[..., 2 * i + 1] *= scale
return interpolated_pos- Progressive Extension Strategy:
def progressive_extension(model, data, base_length, target_length, population_size, num_mutations, num_crossovers, max_iterations):
# Extend to 128k
lambda_factors_128k, n_hat_128k = search_lambda_factors(model, data, 128000 / base_length, population_size, num_mutations, num_crossovers, max_iterations)
model = fine_tune(model, data, 128000, lambda_factors_128k, n_hat_128k, steps=400)
# Extend to 256k
lambda_factors_256k, n_hat_256k = search_lambda_factors(model, data, 256000 / base_length, population_size, num_mutations, num_crossovers, max_iterations)
model = fine_tune(model, data, 256000, lambda_factors_256k, n_hat_256k, steps=600)
# Extend to target length
if target_length > 256000:
final_lambda_factors, final_n_hat = search_lambda_factors(model, data, target_length / base_length, population_size // 2, num_mutations // 2, num_crossovers // 2, max_iterations // 2)
model.lambda_factors["2048k"] = final_lambda_factors
model.n_hat["2048k"] = final_n_hat
return model, final_lambda_factors, final_n_hat, lambda_factors_256k, n_hat_256kThe architecture begins with a pre-trained LLM and extends its context window incrementally. Initially, the model is fine-tuned to handle a context length of 256k tokens. This progressive approach avoids the need for direct fine-tuning on extremely long texts, which are rare and computationally expensive to process. By gradually increasing the context length, the model can adapt more effectively to longer sequences.
To maintain performance across varying context lengths, LongRoPE adjusts the Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE). The model identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to minimize information loss during interpolation. This allows for an 8x context extension without the need for fine-tuning. Additionally, the model employs a search algorithm to find optimal rescale factors for shorter contexts (e.g., 4k and 8k tokens) on the 256k fine-tuned LLM. These adjustments ensure that the model retains high performance even within the original context window size.
The architecture incorporates several structural modifications to handle the increased context length efficiently:
-
Layer Scaling: Adjustments are made to the scaling of layers to ensure stability and performance as the context window grows.
-
Memory Management: Efficient memory management techniques are employed to handle the large context sizes without overwhelming the system resources.
-
Attention Mechanisms: Enhanced attention mechanisms are integrated to ensure that the model can focus on relevant parts of the input sequence, even with the extended context.
-
Token-wise Attention: Token-wise attention mechanisms are introduced to capture the contextual relationships between tokens, allowing the model to better understand the semantic meaning of the input.
Experiments demonstrate that LongRoPE maintains low perplexity across evaluation lengths from 4k to 2048k tokens and achieves high accuracy in tasks requiring long contexts. This makes it suitable for various applications, including in-context learning, long document summarization, and few-shot learning.
For more detailed information, please refer to the full paper here.
Insights into the coding and operational specifics that enable LongRoPE's functionality. This may include snippets or pseudocode illustrating key components.
For more detailed information, please refer to the paper.
Comprehensive examples demonstrating how to leverage LongRoPE for various applications, from text analysis to generating extensive documents.
# Example usage
data_path = "path/to/your/dataset"
d_model = 512
n_heads = 8
num_layers = 6
base_length = 4096
target_length = 2048 * 1024
data = load_data(data_path)
model = LongRoPEModel(d_model, n_heads, num_layers, base_length)
model = model.extend_context(data, target_length)
input_ids = torch.randn(2, target_length, d_model)
output = model(input_ids)
print(output.shape) # Expected shape: (batch_size, target_length, d_model)Custom Dataset Training
To train on a custom dataset:
- Prepare your dataset in a format compatible with the datasets library.
- Implement a custom preprocess_data function if needed.
- Use the extend_context method with your custom data.
Hyperparameter Tuning LongRoPE's performance can be sensitive to hyperparameters. Key parameters to tune include:
population_size, num_mutations, and num_crossovers in the lambda factor search
Learning rate and scheduler parameters for fine-tuning
gradient_accumulation_steps for training stability
My implementation of LongRoPE achieves the following results:
-
Perplexity:
- 4k context: X.XX
- 128k context: X.XX
- 2048k context: X.XX
-
Passkey Retrieval Accuracy:
- 4k context: XX%
- 128k context: XX%
- 2048k context: XX%
-
Accuracy:
- 4k context: XX%
- 128k context: XX%
- 2048k context: XX%
-
Comparison with baseline models:
@article{ding2024longrope,
title={LongRoPE: Extending LLM Context Window Beyond 2 Million Tokens},
author={Ding, Yiran and Zhang, Li Lyna and Zhang, Chengruidong and Xu, Yuanyuan and Shang, Ning and Xu, Jiahang and Yang, Fan and Yang, Mao},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.13753},
year={2024}
}Note: This repository is a work in progress and is not yet ready for production use. Please refer to the paper for more details.