-
Why you need to map an array ?
The
Array.map()method allows us to iterate over an array and modify its elements using a callback function. The callback function will then be executed on each of the array's elements, returning a new array as the result.In React, we use map to modify an array to list of JSX by adding a certain HTML elements to each element of an array. Generally, data is in the form of an array/an array of objects. To render this array/array of objects most of the time we modify the data using
map. -
Why we need keys during mapping an array ?
Keyshelp React to identify items which have changed, added, or removed. It should be given to the elements inside the array to give the elements a stable unique identity.In React, during mapping if we do not pass key it raises a warning on the browser. If the data does not have an id, which is unusual, we have to find a way to create a unique identifier for each element when we map it.
-
What is the importance of destructuring your code ?
Destructuring is a feature of JavaScript that allows you to extract values from arrays or objects and assign them to variables in a concise and convenient way. It can help you organize your code and make it simpler, modular, more readable, and reusable.
for examples,
- Array destructuring: You can use square brackets [] to assign values from an array to variables. For example:
const foo = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
const [red, yellow, green] = foo;
console.log(red); // "one"
console.log(yellow); // "two"
console.log(green); // "three"- Object destructuring: You can use curly braces {} to assign values from an object to variables. For example:
let person = { firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Doe' };
let { firstName, lastName } = person;
console.log(firstName); // "John"
console.log(lastName); // "Doe"-
Does destructuring make your code clean and easy to read ?
Yes, destructuring can make your code clean and easy to read by reducing the amount of code you need to write and making it clear what values you are using from arrays or objects. For example, instead of writing:
let person = { firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Doe' };
let firstName = person.firstName;
let lastName = person.lastName;You can write:
let person = { firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Doe' };
let { firstName, lastName } = person;This way, you can avoid repeating yourself and make your code more concise.
-
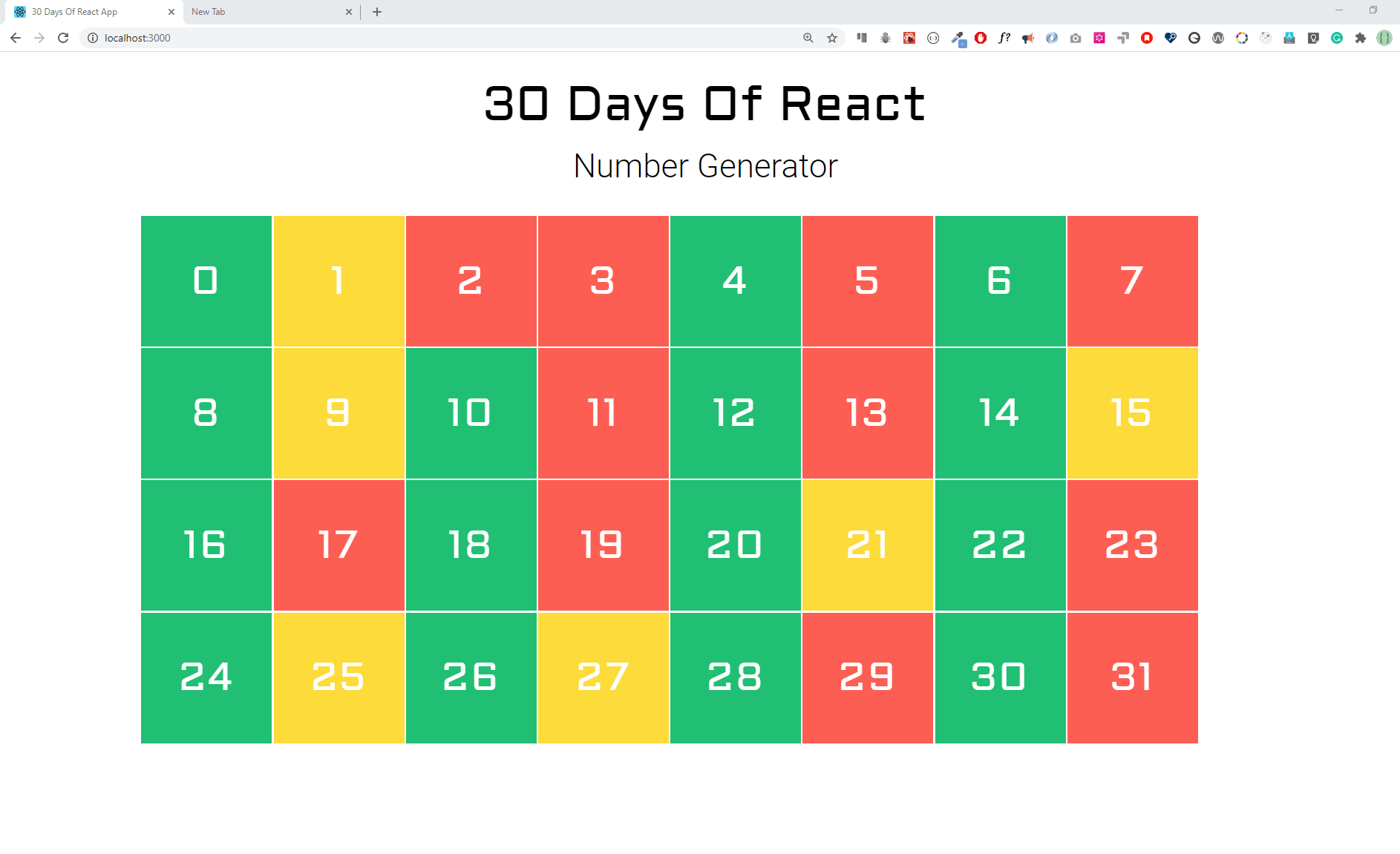
In the following design, evens are green, odds are yellow and prime numbers are red. Build the following colors using React component
Solution:
./src/Exercises/NumberGenerator.jsimport React from 'react'; import { randomUUID } from '../helper'; import './NumberGenerator.scss'; /** * A simple Javascript program to check Prime number, using recursion * * @param {*} n is a Number * @returns true if n is prime, otherwise false */ function isPrime(n, i = 2) { if (n <= 2) return n == 2; if (n % i == 0) return false; if (i * i > n) return true; return isPrime(n, i + 1); } /** * A simple Javascript program to check for even or odd * * @param {*} n is a Number * @returns true if n is even, otherwise false */ function isEven(n) { return n % 2 == 0; } // NumberedBox Component const NumberedBox = ({ text, color }) => { return ( <div className="numbered-box text-center col-3 col-md-auto" style={{ backgroundColor: color }}> {text} </div> ); }; // Section Header Component const SectionTitle = ({ heading, subHeading, text = '' }) => ( <div className="section-title text-center"> <h1 className="mono-h1">{heading}</h1> <p className="mt-3 fw-light fs-2">{subHeading}</p> </div> ); // NumberGenerator Component const NumberGenerator = ({ number = 32 }) => { const numberOfItems = Array.from({ length: number }, (_, i) => i); return ( <div className="section-wrapper py-4"> <SectionTitle heading="30 Days of React" subHeading="Number Generator" /> <div className="pt-2"> <div className="d-grid numbered-box-wrapper"> {numberOfItems.map((index) => { if (isPrime(index)) { return <NumberedBox key={randomUUID()} text={index} color="#FD5E53" />; } else if (isEven(index)) { return <NumberedBox key={randomUUID()} text={index} color="#20BF73" />; } else { return <NumberedBox key={randomUUID()} text={index} color="#FCDB3A" />; } })} </div> </div> </div> ); }; export default NumberGenerator;
-
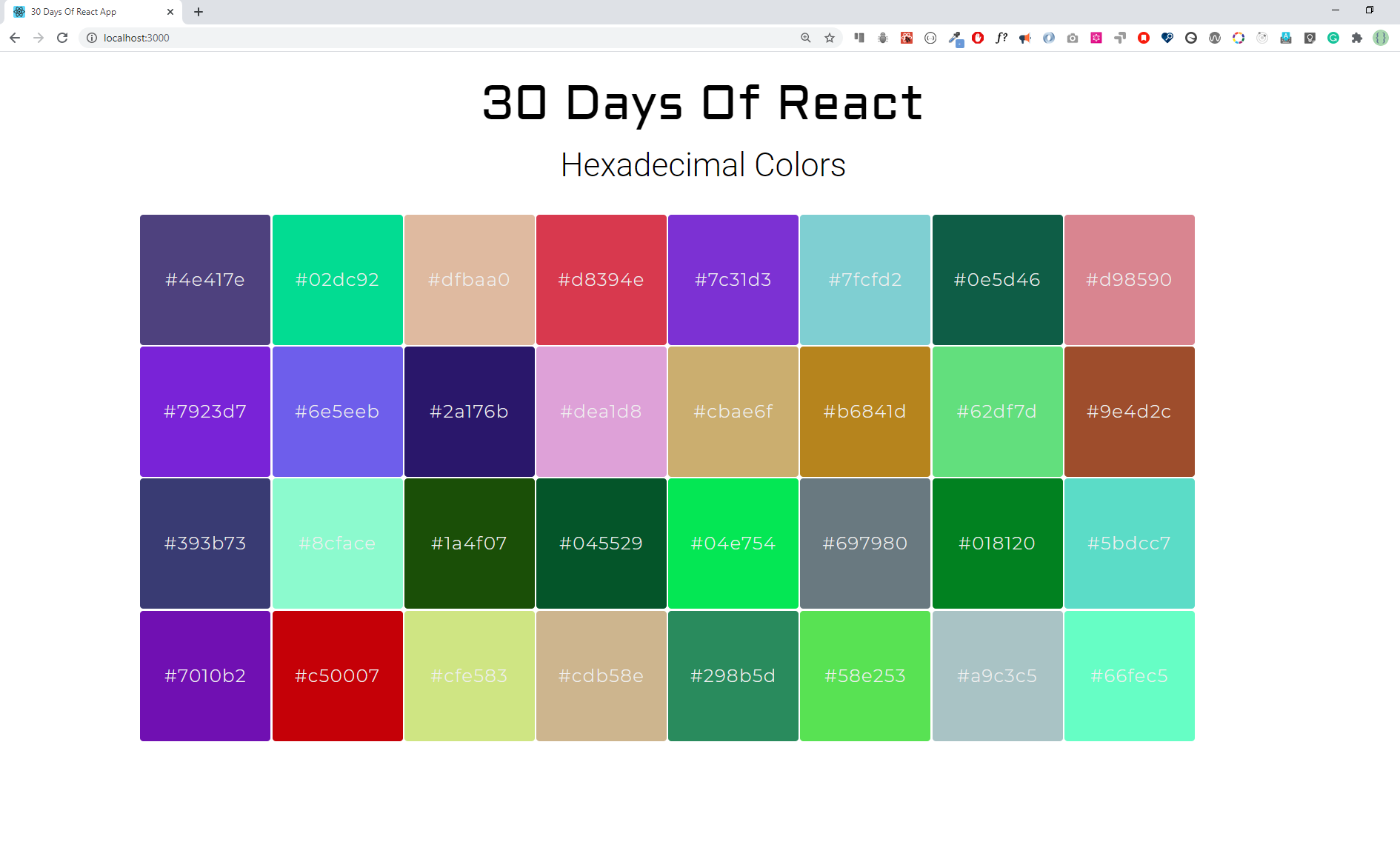
Create the following hexadecimal colors using React component
Solution:
./src/Exercises/HexColorGenerator.jsimport React from 'react'; import { randomUUID } from '../helper'; /** * A function generate a number of hexadecimal codes and returns a array. * * @param {*} total length of array * @returns hexArray consisting hexadecimal codes */ const randomHexColors = (total = 5) => { const hexArray = []; for (let index = 0; index < total; index++) { const color = '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * (0xffffff + 1)) .toString(16) .padStart(6, '0') // in case the number is too small to fill .toUpperCase(); hexArray.push(color); } return hexArray; }; // Section Header Component const SectionTitle = ({ heading, subHeading, text = '' }) => ( <div className="section-title text-center"> <h1 className="mono-h1">{heading}</h1> <p className="mt-3 fw-light fs-2">{subHeading}</p> </div> ); // HexColorGenerator Component (Main) const HexColorGenerator = ({ totalHex }) => { const coloredBox = randomHexColors(totalHex).map((hex, index) => ( <div key={randomUUID()} style={{ backgroundColor: hex, color: '#fff' }} className="border border-1 rounded-1 border-light d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center fs-4 fw-lighter p-4" > {hex} </div> )); return ( <div className="section-wrapper py-4"> <SectionTitle heading="30 Days of React" subHeading="Hexadecimal colors" /> <div className="pt-2 d-grid colored-box-wrapper">{coloredBox}</div> </div> ); }; export default HexColorGenerator;
-
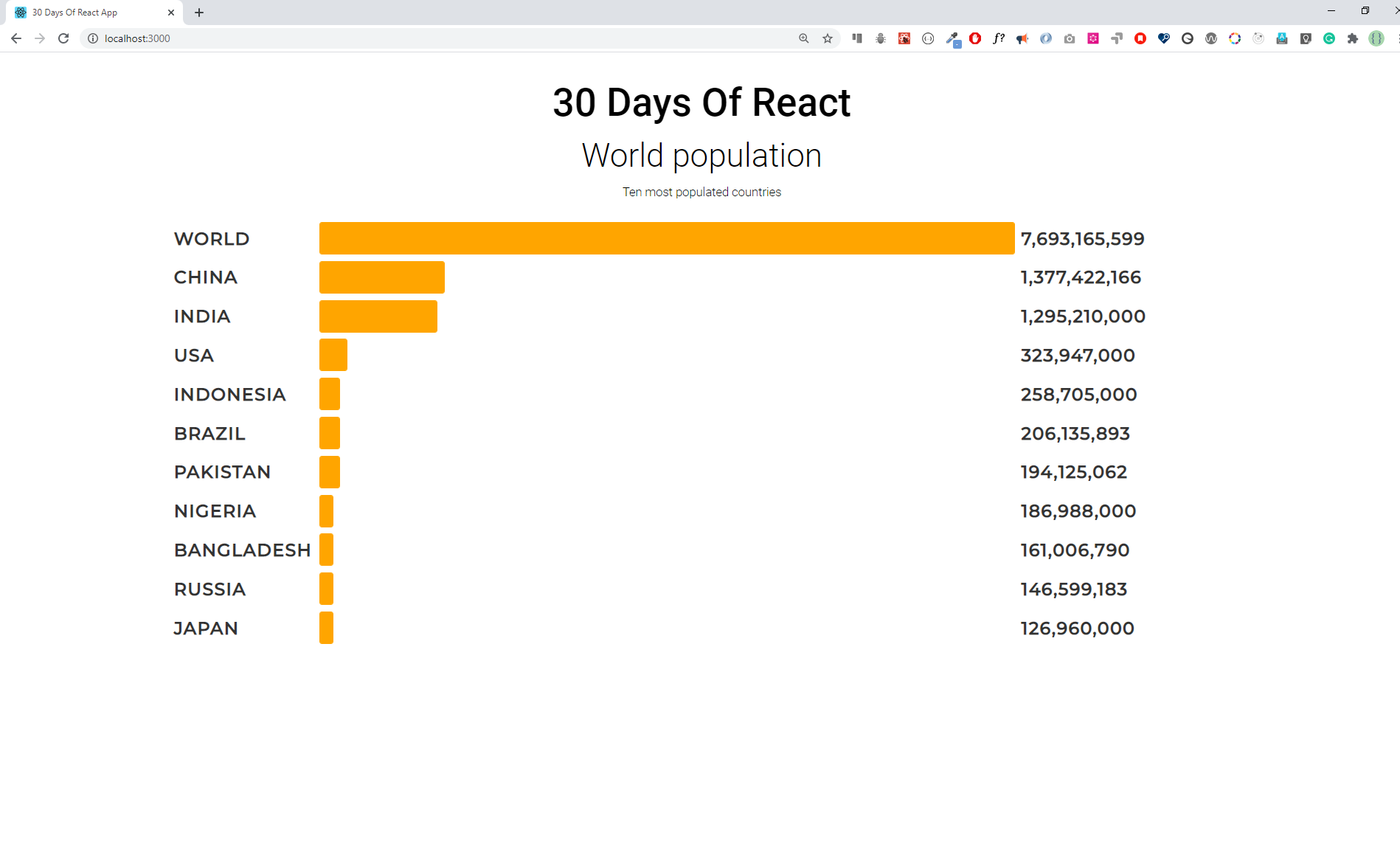
Make the following bar group using the given data
Solution:
./src/Exercises/WorldPopulation.jsimport React from 'react'; import { randomUUID } from '../helper'; import { allCountries } from './data'; import './WorldPopulation.scss'; const topTenPopulatedCountries = allCountries.sort((a, b) => b.population - a.population).slice(0, 10); const worldPopulation = allCountries.map((country) => country.population).reduce((curr, sum) => curr + sum); // Section Header Component const SectionTitle = ({ heading, subHeading, text = '' }) => ( <div className="section-title text-center"> <h1 className="display-3 fw-medium">{heading}</h1> <p className="m-0 mt-2 fw-light display-5">{subHeading}</p> <p className="m-0 mt-1 fw-light">{text}</p> </div> ); const topCountryList = topTenPopulatedCountries.map((country) => { return ( <div className="d-grid population-graph-item mb-2" key={randomUUID()}> <div className="label fw-medium text-uppercase">{country.name}</div> <progress className="progress-bar" value={country.population} max={worldPopulation}></progress> <div className="number fw-medium">{country.population}</div> </div> ); }); // World Population Component (Graph) const WorldPopulation = (props) => { return ( <div className="section-wrapper py-4"> <SectionTitle heading="30 Days of React" subHeading="World Population" text="Ten most populated countries" /> <div className="pt-3 population-graph-wrapper"> <div className="d-grid population-graph-item mb-2"> <div className="label fw-medium text-uppercase">World</div> <progress className="progress-bar" value={worldPopulation} max={worldPopulation}></progress> <div className="number fw-medium">{worldPopulation}</div> </div> {topCountryList} </div> </div> ); }; export default WorldPopulation;