forked from geocompx/geocompr
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
Copy pathREADME.Rmd
357 lines (261 loc) · 17.9 KB
/
README.Rmd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
---
output: github_document
---
<!-- README.md is generated from README.Rmd. Please edit that file - rmarkdown::render('README.Rmd', output_format = 'github_document', output_file = 'README.md') -->
```{r, echo = FALSE}
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
fig.path = "figures/"
)
is_online = curl::has_internet()
```
# Geocomputation with R
<!-- badges: start -->
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/geocompx/geocompr/main?urlpath=rstudio)
[](https://rstudio.cloud/project/1642300)
[](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/actions)
[](https://github.com/geocompx/docker/)
[](https://discord.gg/PMztXYgNxp)
[](https://github.com/codespaces/new?hide_repo_select=true&ref=main&repo=84222786&machine=basicLinux32gb&devcontainer_path=.devcontainer.json&location=WestEurope)
<!-- [](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/84222786) -->
<!-- badges: end -->
## Introduction
This repository hosts the code underlying Geocomputation with R, a book by [Robin Lovelace](https://www.robinlovelace.net/), [Jakub Nowosad](https://jakubnowosad.com/), and [Jannes Muenchow](https://github.com/jannes-m).
If you find the contents useful, please [cite it](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/raw/main/CITATION.bib) as follows:
> Lovelace, Robin, Jakub Nowosad and Jannes Muenchow (2019). Geocomputation with R. The R Series. CRC Press.
The first version of the book has been published by [CRC Press](https://www.crcpress.com/9781138304512) in the [R Series](https://www.routledge.com/Chapman--HallCRC-The-R-Series/book-series/CRCTHERSER) and can be viewed online at [bookdown.org](https://bookdown.org/robinlovelace/geocompr/).
Read the latest version at [r.geocompx.org](https://r.geocompx.org/).
### Note: we are actively working on the Second Edition 🏗
<details>
<summary>Summary of the changes</summary>
Since commencing work on the Second Edition in September 2021 much has changed, including:
- Replacement of `raster` with `terra` in Chapters 1 to 7 (see commits related to this update [here](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/search?q=terra&type=commits))
- Update of Chapter 7 to include mention alternative ways or reading-in OSM data in [#656](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/pull/656)
- Refactor build settings so the book builds on Docker images in the [geocompr/docker](https://github.com/geocompr/docker) repo
- Improve the experience of using the book in Binder (ideal for trying out the code before installing or updating the necessary R packages), as documented in issue [#691](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/issues/691) (thanks to [yuvipanda](https://github.com/yuvipanda))
- Improved communication of binary spatial predicates in Chapter 4 (see [#675](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/pull/675))
- New section on the links between subsetting and clipping (see [#698](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/pull/698)) in Chapter 5
- New [section](https://r.geocompx.org/spatial-operations.html#de-9im-strings) on the dimensionally extended 9 intersection model (DE-9IM)
- New [chapter](https://r.geocompx.org/raster-vector.html) on raster-vector interactions split out from Chapter 5
- New [section](https://r.geocompx.org/spatial-class.html#the-sfheaders-package) on the **sfheaders** package
- New [section](https://r.geocompx.org/spatial-class.html#s2) in Chapter 2 on spherical geometry engines and the **s2** package
- Replacement of code based on the old **mlr** package with code based on the new **mlr3** package, as described in a huge [pull request](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/pull/771)
<!-- Todo: update this bullet point (Rl 2021-11) -->
<!-- - Next issue -->
<!-- Todo: add news file? (RL 2021-11) -->
<!-- See NEWS.md for a summary of the changes. -->
See [https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/compare/1.9...main](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/compare/1.9...main#files_bucket) for a continuously updated summary of the changes to date.
At the time of writing (April 2022) there have been more than 10k lines of code/prose added, lots of refactoring!
[](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/compare/1.9...main)
</details>
Contributions at this stage are very welcome.
## Contributing
We encourage contributions on any part of the book, including:
- improvements to the text, e.g. clarifying unclear sentences, fixing typos (see guidance from [Yihui Xie](https://yihui.org/en/2013/06/fix-typo-in-documentation/));
- changes to the code, e.g. to do things in a more efficient way;
- suggestions on content (see the project's [issue tracker](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/issues));
- improvements to and alternative approaches in the Geocompr solutions booklet hosted at [r.geocompx.org/solutions](https://r.geocompx.org/solutions) (see a blog post on how to update solutions in files such as [_01-ex.Rmd](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/blob/main/_01-ex.Rmd) [here](https://geocompr.github.io/post/2022/geocompr-solutions/))
See [our-style.md](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/blob/main/misc/our-style.md) for the book's style.
```{r contributors, include=FALSE}
contributors = source("code/list-contributors.R")[[1]]
# save for future reference:
readr::write_csv(contributors, "extdata/contributors.csv")
# table view:
# knitr::kable(contributors, caption = "Contributors to Geocomputation with R")
# text view
c_txt = contributors$name
c_url = contributors$link
c_rmd = paste0("[", c_txt, "](", c_url, ")")
contributors_text = paste0(c_rmd, collapse = ", ")
```
Many thanks to all contributors to the book so far via GitHub (this list will update automatically): `r contributors_text`.
During the project we aim to contribute 'upstream' to the packages that make geocomputation with R possible.
This impact is recorded in [`our-impact.csv`](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/blob/main/misc/our-impact.csv).
## Downloading the source code
The recommended way to get the source code underlying Geocomputation with R on your computer is by cloning the repo.
You can can that on any computer with [Git](https://github.com/git-guides/install-git) installed with the following command:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr.git
```
An alternative approach, which we recommend for people who want to contribute to open source projects hosted on GitHub, is to install the [`gh` CLI tool](https://github.com/cli/cli#installation).
From there cloning a fork of the source code, that you can change and share (including with Pull Requests to improve the book), can be done with the following command:
```bash
gh repo fork geocompx/geocompr # (gh repo clone geocompx/geocompr # also works)
```
Both of those methods require you to have Git installed.
If not, you can download the book's source code from the URL https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/archive/refs/heads/main.zip .
Download/unzip the source code from the R command line to increase reproducibility and reduce time spent clicking around:
```{r dl-unzip}
#| eval=FALSE
u = "https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/archive/refs/heads/main.zip"
f = basename(u)
download.file(u, f) # download the file
unzip(f) # unzip it
file.rename(f, "geocompr") # rename the directory
rstudioapi::openProject("geococompr") # or open the folder in vscode / other IDE
```
## Reproducing the book in R/RStudio/VS Code
To ease reproducibility, we created the `geocompkg` package.
Install it with the following commands:
```{r readme-install-github}
#| eval=FALSE
install.packages("remotes")
# To reproduce the first Part (chapters 1 to 8):
remotes::install_github("geocompx/geocompkg")
```
Installing `geocompkg` will also install core packages required for reproducing **Part 1 of the book** (chapters 1 to 8).
Note: you may also need to install [system dependencies](https://github.com/r-spatial/sf#installing) if you're running Linux (recommended) or Mac operating systems.
You also need to have the [**remotes**](https://github.com/r-lib/remotes/) package installed:
To reproduce book **in its entirety**, run the following command (which installs additional 'Suggests' packages, this may take some time to run!):
```{r readme-install-github-2, message=FALSE, results='hide'}
#| eval=FALSE
# Install packages to fully reproduce book (may take several minutes):
options(repos = c(
geocompx = 'https://geocompx.r-universe.dev',
cran = 'https://cloud.r-project.org'
))
# From geocompx.r-universe.dev (recommended):
install.packages("geocompkg", dependencies = TRUE)
# Alternatively from GitHub:
remotes::install_github("geocompr/geocompkg", dependencies = TRUE)
```
You need a recent version of the GDAL, GEOS, PROJ and udunits libraries installed for this to work on Mac and Linux.
See the **sf** package's [README](https://github.com/r-spatial/sf) for information on that.
After the dependencies have been installed you should be able to build and view a local version the book with:
```{r readme-render-book}
#| eval=FALSE
# Change this depending on where you have the book code stored:
rstudioapi::openProject("~/Downloads/geocompr")
# or code /location/of/geocompr in the system terminal
# or cd /location/of/geocompr then R in the system terminal, then:
bookdown::render_book("index.Rmd") # to build the book
browseURL("_book/index.html") # to view it
# Or, to serve a live preview the book and observe impact of changes:
bookdown::serve_book()
```
<!-- The code associated with each chapter is saved in the `code/chapters/` folder. -->
<!-- `source("code/chapters/07-transport.R")` runs run the code chunks in chapter 7, for example. -->
<!-- These R scripts are generated with the follow command which wraps `knitr::purl()`: -->
```{r gen-code, results='hide', echo=FALSE}
#| eval=FALSE
geocompkg:::generate_chapter_code()
```
## Geocompr in a devcontainer
A great feature of VS Code is [devcontainers](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/containers), which allow you to develop in an isolated Docker container.
If you have VS Code and the necessary dependencies installed on your computer, you can build Geocomputation with R in a devcontainer as shown below (see [#873](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/issues/873) for details):

## Geocompr in Binder
For many people the quickest way to get started with Geocomputation with R is in your web browser via Binder.
To see an interactive RStudio Server instance click on the following button, which will open [mybinder.org](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/geocompx/geocompr/main?urlpath=rstudio) with an R installation that has all the dependencies needed to reproduce the book:
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/geocompx/geocompr/main?urlpath=rstudio)
You can also have a play with the repo in RStudio Cloud by clicking on this link (requires log-in):
[](https://rstudio.cloud/project/1642300)
## Geocomputation with R in a Docker container
To ease reproducibility we have made Docker images available, at [geocompr/geocompr](https://hub.docker.com/r/geocompr/geocompr/) on DockerHub.
These images allow you to explore Geocomputation with R in a virtual machine that has up-to-date dependencies.
After you have [installed docker](https://www.docker.com/products/container-runtime/) and set-it up on [your computer](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/) you can start RStudio Server without a password (see the [Rocker project](https://www.rocker-project.org/use/managing_users/) for info on how to add a password and other security steps for public-facing servers):
```sh
docker run -p 8787:8787 -e DISABLE_AUTH=TRUE geocompr/geocompr
```
If it worked you should be able to open-up RStudio server by opening a browser and navigating to
http://localhost:8787/ resulting in an up-to-date version of R and RStudio running in a container.
Start a plain R session running:
```sh
docker run -it geocompr/geocompr R
```
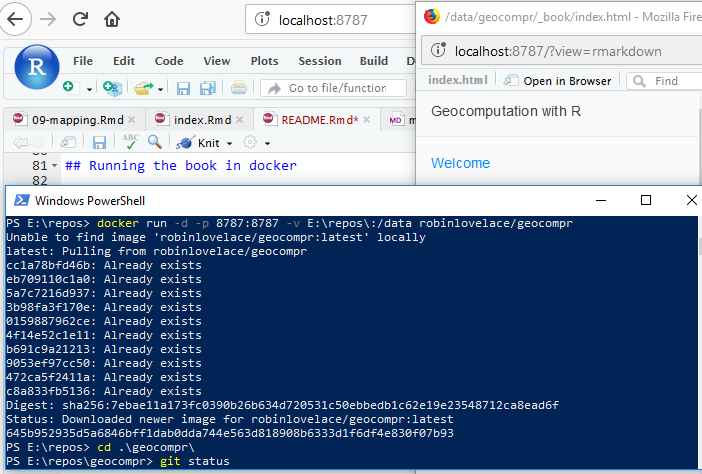
If you see something like this after following the steps above, congratulations: it worked!
See [github.com/rocker-org](https://github.com/rocker-org/rocker/wiki/Using-the-RStudio-image#running-rstudio-server) for more info.
If you want to call QGIS from R, you can use the `qgis` tag, by running the following command for example (which also shows how to set a password and use a different port on localhost):
```
docker run -d -p 8799:8787 -e USERID=$UID -e PASSWORD=strongpass -v $(pwd):/home/rstudio/geocompr geocompx/geocompr:qgis
```
From this point to *build* the book you can open projects in the `geocompr` directory from the project box in the top-right hand corner, and knit `index.Rmd` with the little `knit` button above the the RStudio script panel (`Ctl+Shift+B` should do the same job).
See the [geocompr/docker](https://github.com/geocompr/docker#geocomputation-with-r-in-docker) repo for details, including how to share volumes between your computer and the Docker image, for using geographic R packages on your own data and for information on available tags.
## Reproducing this README
To reduce the book's dependencies, scripts to be run infrequently to generate input for the book are run on creation of this README.
The additional packages required for this can be installed as follows:
```{r extra-pkgs, message=FALSE, eval=FALSE}
source("code/extra-pkgs.R")
```
With these additional dependencies installed, you should be able to run the following scripts, which create content for the book, that we've removed from the main book build to reduce package dependencies and the book's build time:
```{r source-readme, eval=FALSE}
source("code/01-cranlogs.R")
source("code/sf-revdep.R")
source("code/09-urban-animation.R")
source("code/09-map-pkgs.R")
```
Note: the `.Rproj` file is configured to build a website not a single page.
To reproduce this [README](https://github.com/geocompx/geocompr/blob/main/README.Rmd) use the following command:
```{r render-book, eval=FALSE}
rmarkdown::render("README.Rmd", output_format = "github_document", output_file = "README.md")
```
```{r scripts, eval=FALSE, echo=FALSE}
# We aim to make every script in the `code` folder reproducible.
# To check they can all be reproduced run the following:
# Aim: test reproducibility of scripts
script_names = list.files("code", full.names = T)
avoid = "pkgs|anim|us|saga|sliver|tsp|parti|polycent|cv|svm|data|location|eco|rf|cran|hex"
dontrun = grepl(avoid, script_names)
script_names = script_names[!dontrun]
counter = 0
for(i in script_names[45:length(script_names)]) {
counter = counter + 1
print(paste0("Script number ", counter, ": ", i))
source(i)
}
```
<!-- ## Book statistics -->
<!-- An indication of the book's progress over time is illustrated below (to be updated roughly every week as the book progresses). -->
```{r gen-stats, echo=FALSE, message=FALSE, warning=FALSE, eval=FALSE}
# source("code/generate-chapter-code.R")
book_stats = readr::read_csv("extdata/word-count-time.csv",
col_types=('iiDd'))
# to prevent excessive chapter count
if (Sys.Date() > max(book_stats$date) + 5) {
book_stats_new = geocompkg:::generate_book_stats()
book_stats = bind_rows(book_stats, book_stats_new)
readr::write_csv(book_stats, "extdata/word-count-time.csv")
}
book_stats = dplyr::filter(book_stats, chapter <= 15)
library(ggplot2)
book_stats$chapter = formatC(book_stats$chapter, width = 2, format = "d", flag = "0")
book_stats$chapter = fct_rev(as.factor(book_stats$chapter))
book_stats$n_pages = book_stats$n_words / 300
```
```{r bookstats, warning=FALSE, echo=FALSE, fig.width=8, fig.height=5, eval=FALSE}
ggplot(book_stats) +
geom_area(aes(date, n_pages, fill = chapter), position = "stack") +
ylab("Estimated number of pages") +
xlab("Date") +
scale_x_date(date_breaks = "2 month",
limits = c(min(book_stats$date), as.Date("2018-10-01")),
date_labels = "%b %Y") +
coord_cartesian(ylim = c(0, 350))
```
<!-- Book statistics: estimated number of pages per chapter over time. -->
## Citations
To cite packages used in this book we use code from [Efficient R Programming](https://csgillespie.github.io/efficientR/):
```{r gen-cite, warning=FALSE}
# geocompkg:::generate_citations()
```
This generates .bib and .csv files containing the packages.
The current of packages used can be read-in as follows:
```{r pkg_df, message=FALSE}
pkg_df = readr::read_csv("extdata/package_list.csv")
```
Other citations are stored online using Zotero.
If you would like to add to the references, please use Zotero, join the [open group](https://www.zotero.org/groups/418217/energy-and-transport) add your citation to the open [geocompr library](https://www.zotero.org/groups/418217/energy-and-transport/items/collectionKey/9K6FRP6N).
We use the following citation key format:
```
[auth:lower]_[veryshorttitle:lower]_[year]
```
This can be set from inside Zotero desktop with the Better Bibtex plugin installed (see [github.com/retorquere/zotero-better-bibtex](https://github.com/retorquere/zotero-better-bibtex)) by selecting the following menu options (with the shortcut `Alt+E` followed by `N`), and as illustrated in the figure below:
```
Edit > Preferences > Better Bibtex
```

Zotero settings: these are useful if you want to add references.
When you export the citations as a .bib file from Zotero, use the `Better BibTex` (not `BibLaTeX`) format.
We use Zotero because it is a powerful open source reference manager that integrates well with citation tools in VS Code and RStudio.