|
|---|
| >->->-> This is a development branch. Features here may be experimental and not fully stable. <-<-<-<-< |
ASK stands for Auxiliary Source of Knowledge. ASK was developed by Auxiliarist Drew Wilkins as a proof of concept to make it easier for Auxiliarists and prospective members to find Auxiliary-related information. Powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI), ASK searches over 300 Coast Guard Auxiliary references to find answers directly from authoritative sources.
ASK stems from the need for easier ways to find official information. Auxiliarists are surrounded by a growing amount of policy and procedure info necessary to guide their actions. However, accessing these resources is not straight-forward. The bulk of it is stowed away in PDFs scattered across various platforms, making it cumbersome to located and search. Furthermore, outdated and region-specific info can be misconstrued as applicable.
Since 2008, Auxiliary missions types have grown 36%. The Auxiliary now manages over 120 competencies and 377 tasks requiring over 245 Auxiliary-related policy documents to support. That’s almost 9000 pages of Auxiliary policies. In some cases, currency requires familiarity with eight or more policy documents, which creates an obstacle to skills development and readiness.
ASK makes it easier to find Auxiliary-related information. It takes a user’s question, examines the public USCG Auxiliary documents and then answers the question in natural language using AI.
ASK's mission is to provide members efficient, accurate, and easy access to the authoritative source of knowledge on any topic in the Auxiliary.
-
Policy Compliance: ASK helps members understand and adhere to policy and helps the organization transition to new policies. For example, a member can find the policy changes affecting their competency.
-
New Member Onboarding: ASK gives new members a convenient access to answers or to ask a question they may be hesitatnt to ask in person. For example, a new member can ask questions that might make them “feel stupid” to ask in person. A supportive and informative “first ninety days” sets the foundation for a productive and engaged member.
-
Training Support: ASK provides personalized learning for trainees. It can compare and contrast terms or create custom quizzes, with ASK grading the results
-
In-the-Field Mission Support: ASK is field-ready. Auxiliarists can access crucial documents during mission execution, enhancing Auxiliarist performance efficiency and decision-making.
-
Language Access: ASK translates queries and results into foreign languages which helps the USCG fulfill its requirements under Executive Order 13166, “Improving Access to Services for Persons with Limited English Proficiency”
ASK is available to try here
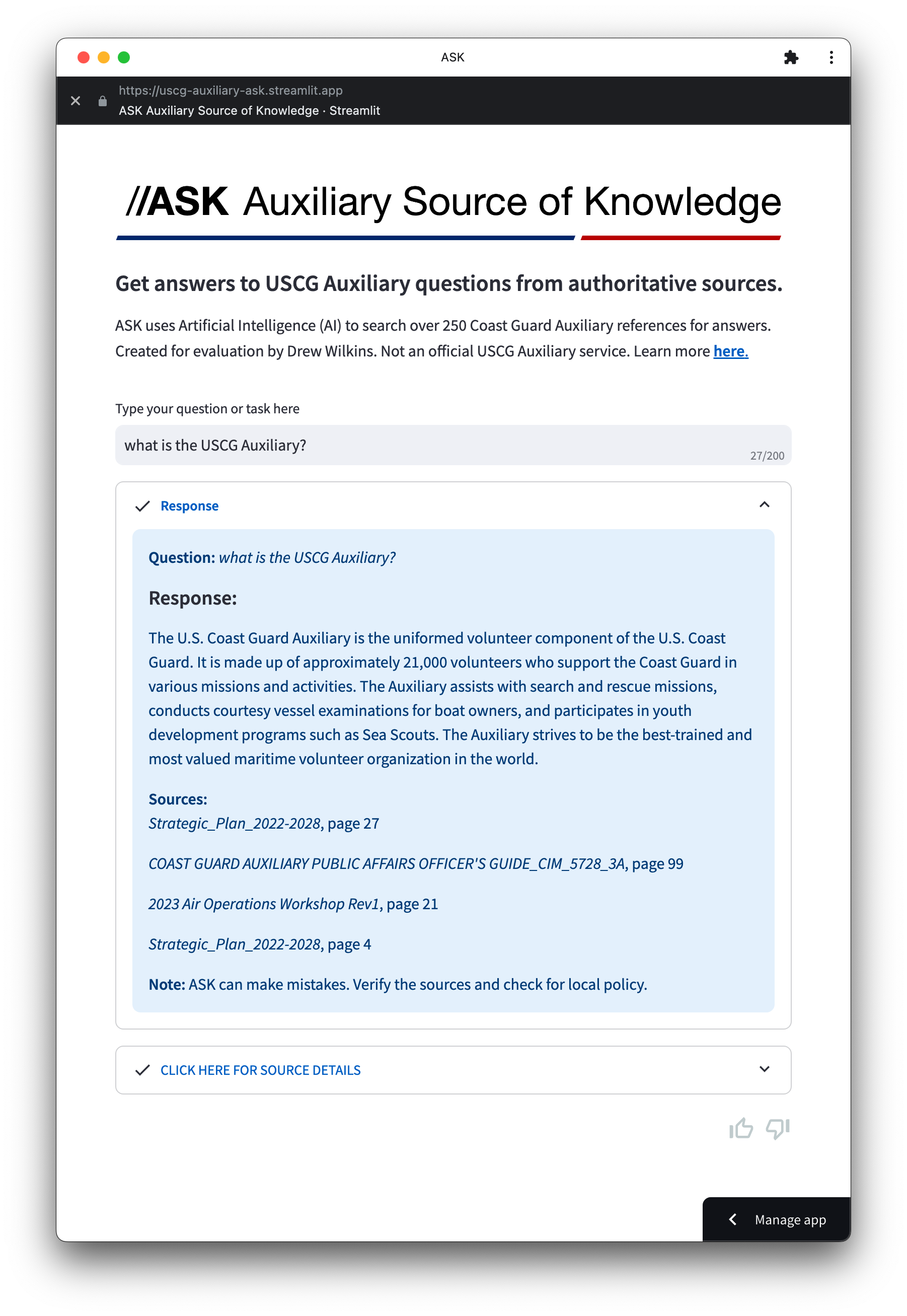
Generative AI Document Search brings together two capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI): the powerful information retrieval of a search engine with text generation ability of a Generative AI operating within a controlled organizational environment. Generative AI Document Search overcomes limitations of both by utilizing retrieved information from existing data, ensuring that the answers provided are not only contextually appropriate but also substantiated by credible sources. It works by taking a user’s question from a search bar, retrieving related information from a pre-defined library of USCG reference documents, and then generating a detailed response back to the user that includes the source citations.
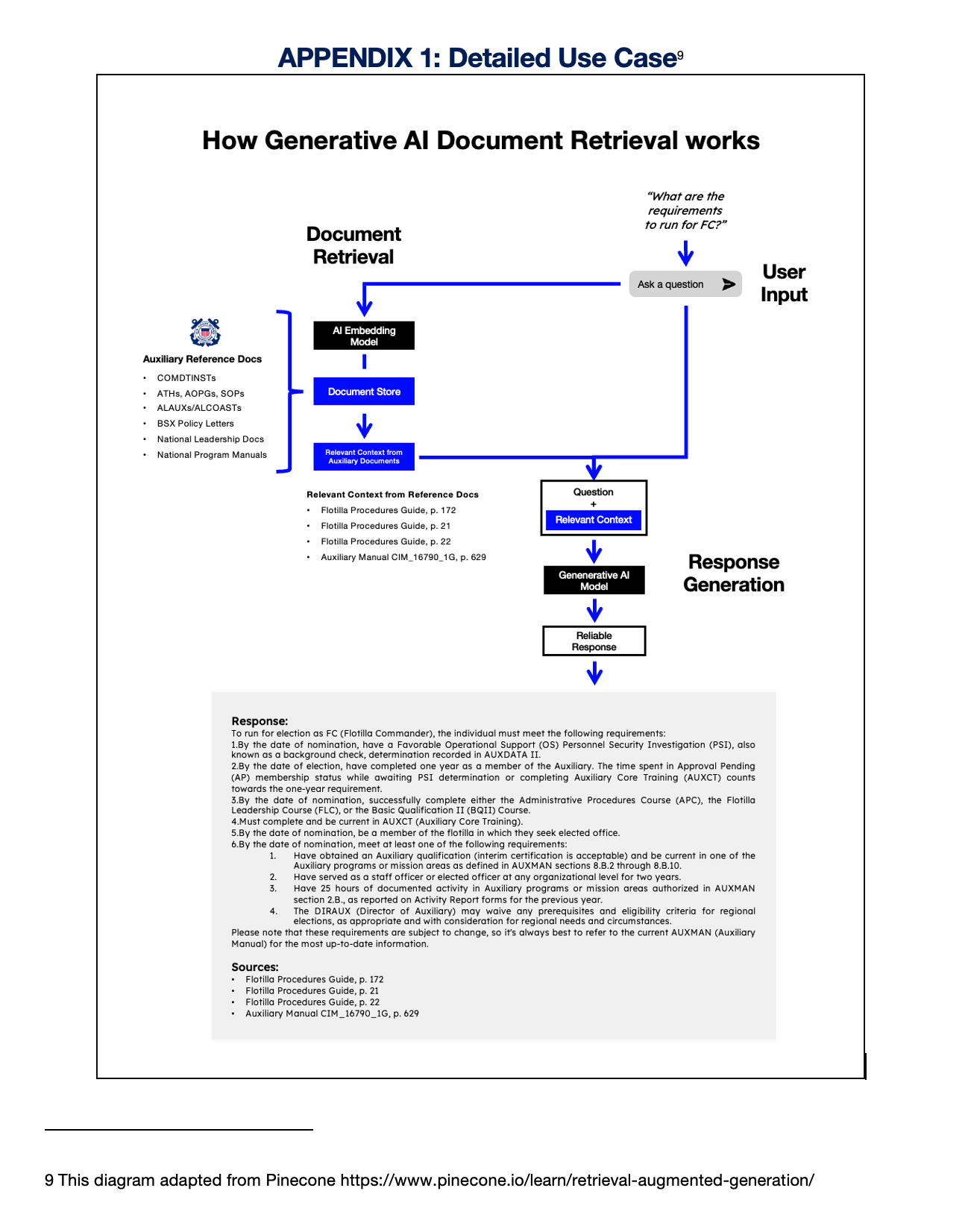
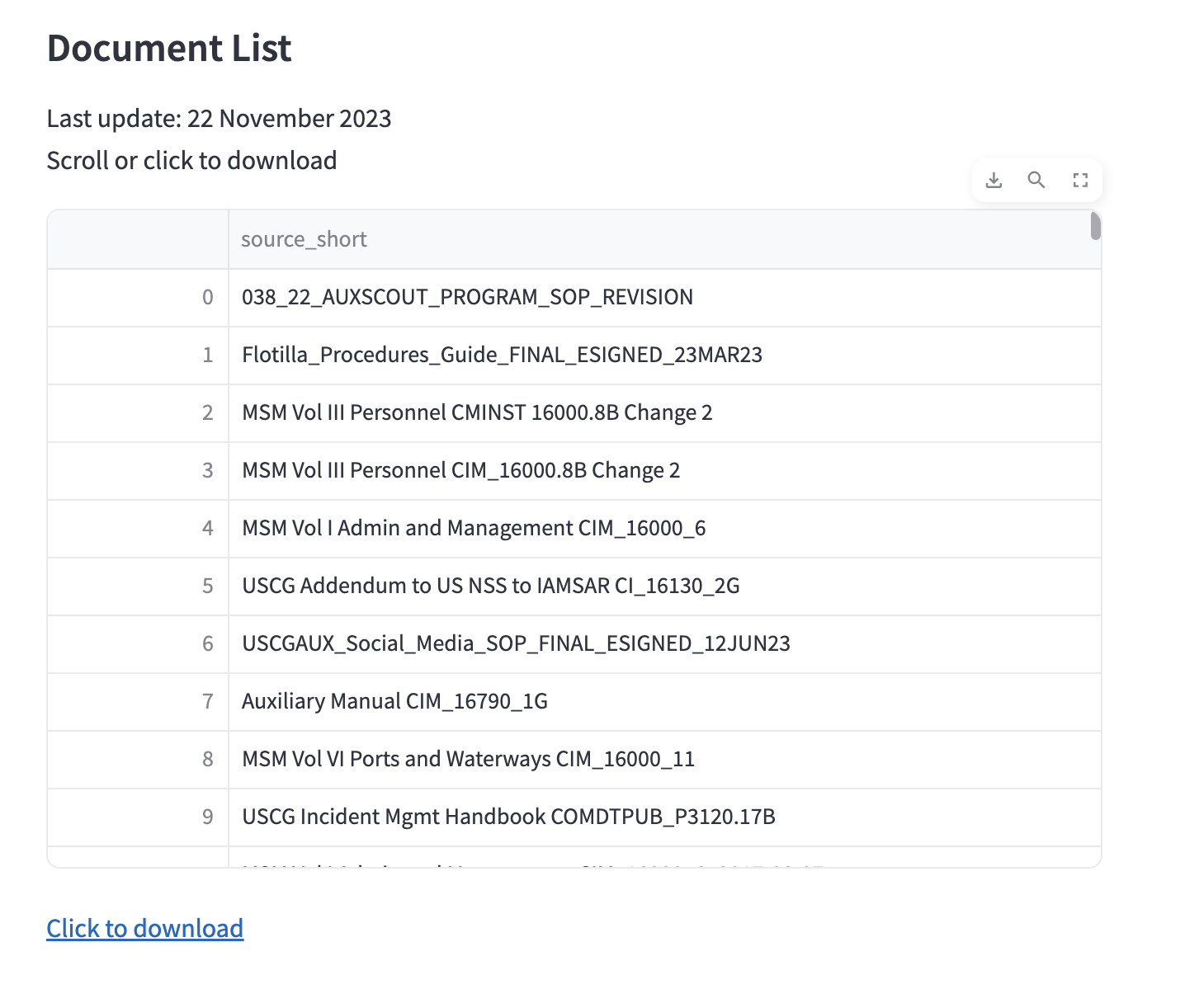
ASK is loaded with over 250 national documents (over 8000 pages). The app includes a searchable list of documents in its information section. Click image to visit.
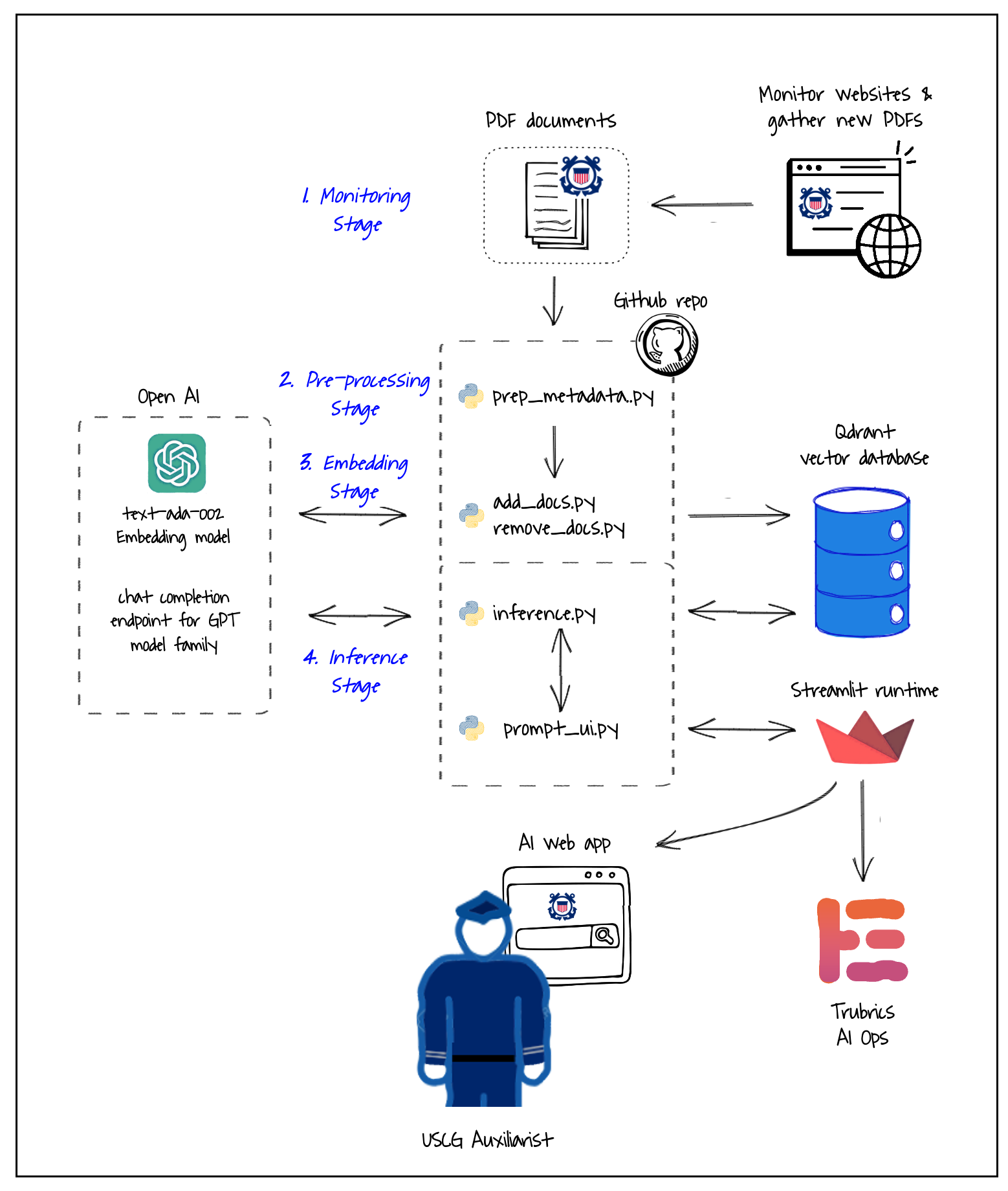
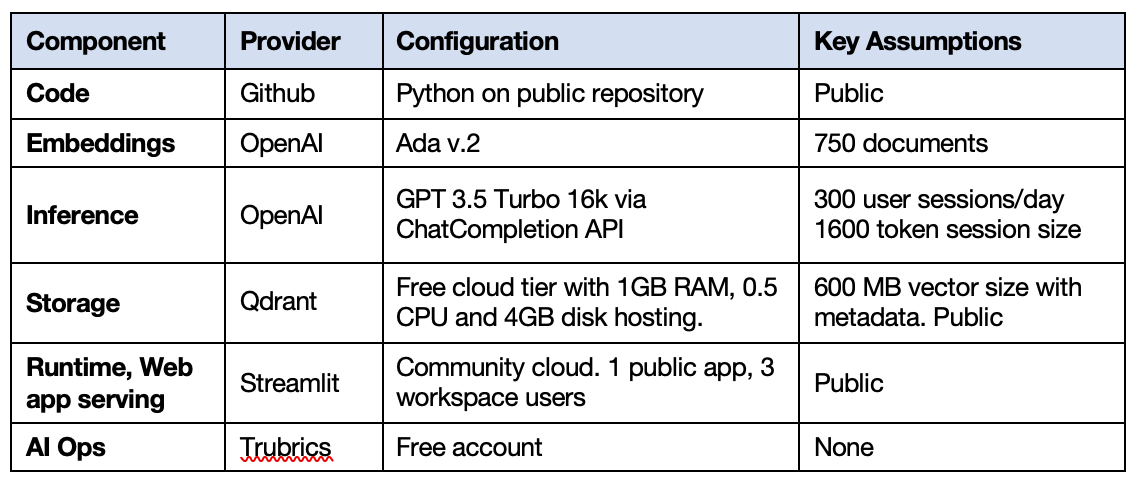
ASK relies on five core components: a python codebase, a Gen AI model, vector database, a runtime environment, and a Web app server. It has been designed to take advantage of open-source to allow continued innovation and to keep costs low.
The main components of the solution are:
-
Codebase: written by me in Python 3.8.10 using open source licenses. Version control is via a public git repository located at _https://github.com/drew-wks/ASK. Development workflow is notated here.
-
Embedding model: Embeddings are generated using OpenAI Ada v.2 which is providing state of the art (SOTA) embeddings at the time of this writing. The model is accessed from the code via API. Alternatives exist and may provide superior results or same for less cost. More on this embedding can be found here: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/embeddings/what-are-embeddings
-
Storage: Qdrant open-source vector database cluster hosted on AWS. The proof of concept utilizes 300 MB of file storage (186 MB payload of pdfs plus 100 MB for the vectors, metadata, index and swap files). The recommended configuration is for 600 MB to hold all policy documents in the Auxiliary.
-
Inference model: OpenAI ChatGPT 3.5 series via API. Chat history is currently turned off as it doesn’t seem to be needed and minimizes per-request costs. More information on this API is located at https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/gpt/chat-completions-api
-
Runtime environment, Web app server, front end: All provided by Streamlit framework and cloud turns the Python script by rendering it as a web app.
Two additional components simplify system development and management:
-
LangChain: An open-source integration framework for Gen AI models which integrates the components in the Gen AI pipeline and makes it easy to change the ingestion approach, model or vector database as requirement change or opportunities arise. This is essential since generative AI technology is advancing quickly.
-
AI Ops: Trubrics monitoring and optimization for machine learning models. It collects the queries and responses, parameters and token usage , and direct user feedback and provides an administrative dashboard for monitoring performance.
The following configuration was specified for the proof of concept. This proposal recommends using it for the first-year launch of ASK.
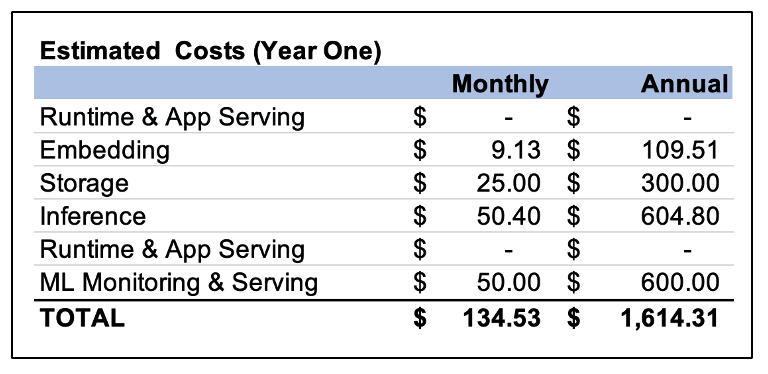
Estimated year one costs are given below based on the recommended configuration. Primary cost drivers are usage and storage. All costs are monthly subscriptions. There is no deployment cost since the prototype has already been built and can be moved to production using volunteers.
The streamlit app is a multi-page app with the TOC hidden. Streamlit runs off of ui.py. rag.py contains most of the retrieval and inference code.
Efforts were taken to free up as much screen real estate as possible for small mobile screens. This includes:
- Creating a rich info area located on a separate page of a multipage app and hiding the TOC
- Linking to other pages with a hyperlink rather than a button that takes up vertical space
- Adjustments to page header and footer
- Replacing Streamlit header with st.status
- Removing instructional text after query is submitted to make room for response (using st.empty)
Other features
- OpenAI down triggers a user warning
- Warning is displayed if OpenAI quota is exceeded and I need to pay for more credits
Testing
- Development workflow is notated here.
- Additional testing is conducted using /test, test.py, just_streamlit_text.py
- Clone the repository
- Open the project in VS Code.
- Set up your local environment and python interpreter
- Add your streamlit secrets into .secrets.toml
- Select the ui.py file
- Go to the "Run and Debug" panel in VS Code (Ctrl+Shift+D or Cmd+Shift+D).
- Select "Run Streamlit App" and press the green play button to start
- The Streamlit user interface will load in the default browser
-
- To run the tests, install pytest