diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 64a7071bc..f3bd9041a 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@
The goal of SeedSigner is to lower the cost and complexity of Bitcoin multi-signature wallet use. To accomplish this goal, SeedSigner offers anyone the opportunity to build a verifiably air-gapped, stateless Bitcoin signing device using inexpensive, publicly available hardware components (usually < $50). SeedSigner helps users save with Bitcoin by assisting with trustless private key generation and multi-signature wallet setup, and helps users transact with Bitcoin via a secure, air-gapped QR-exchange signing model.
-Additional information about the project can be found at [seedsigner.com](https://seedsigner.com).
+Additional information about the project can be found at [SeedSigner.com](https://seedsigner.com).
You can follow [@SeedSigner](https://twitter.com/SeedSigner) on Twitter for the latest project news and developments.
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ If you have specific questions about the project, our [Telegram Group](https://t
### Considerations:
* Built for compatibility with Specter Desktop, Sparrow, and BlueWallet Vaults
* Device takes up to 60 seconds to boot before menu appears (be patient!)
-* Always test your setup before transfering larger amounts of bitcoin (try testnet first!)
+* Always test your setup before transferring larger amounts of bitcoin (try Testnet first!)
* Taproot not quite yet supported
* Slightly rotating the screen clockwise or counter-clockwise should resolve lighting/glare issues
* If you think SeedSigner adds value to the Bitcoin ecosystem, please help us spread the word! (tweets, pics, videos, etc.)
@@ -77,60 +77,176 @@ Notes:
# Software Installation
-## Special Note on Minimizing Trust
+## A Special Note On Minimizing Trust
As is the nature of pre-packaged software downloads, downloading and using the prepared SeedSigner release images means implicitly placing trust in the individual preparing those images; in our project the release images are prepared and signed by the eponymous creator of the project, SeedSigner "the person". That individual is additionally the only person in possession of the PGP keys that are used to sign the release images.
However, one of the many advantages of the open source software model is that the need for this kind of trust can be negated by our users' ability to (1) review the project's source code and (2) assemble the operating image necessary to use the software themselves. From our project's inception, instructions to build a SeedSigner operating image (using precisely the same process that is used to create the prepared release images) have been made availabile. We have put a lot of thought and work into making these instructions easy to understand and follow, even for less technical users. These instructions can be found [here](docs/manual_installation.md).
## Downloading the Software
-The quickest and easiest way to install the software is to download the most recent "seedsigner_X_X_X.zip" file in the [software releases](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases) section of this repository.
+
+Download the current Version (0.6.0) software image that is compatible with your Raspberry Pi Hardware:
+| The small-sized Raspberry Pi Hardware models (the ZERO's) | | The large-sized Raspberry Pi Hardware models (Full size) |
+|--- |--- |--- |
+| [SeedSigner software for the Pi Zero **V1.3**](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner_os.0.6.0.pi0.img "Download the ...pi0.img file") | | [SeedSigner software for the Raspberry Pi 4 Model B](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner_os.0.6.0.pi4.img "Download the ...pi4.img file") |
+| [SeedSigner software for the Pi Zero W or Pi Zero WH](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner_os.0.6.0.pi0.img "Download the ...pi0.img file") | | [SeedSigner software for the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner_os.0.6.0.pi02w.img "Download the ...pi02w.img file") |
+| [SeedSigner software for the Pi Zero **2** W (The "Pi Zero **TWO** W")](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner_os.0.6.0.pi02w.img "Download the ...pi02w.img file") | | [SeedSigner software for the Raspberry Pi 2 Model B ](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner_os.0.6.0.pi2.img "Download the ...pi2.img file")
This is not the file for a Pi **ZERO** 2.
That hardware is a different chipset and motherboard. |
-After downloading the .zip file, extract the seedsigner .img file, and write it to a MicroSD card (at least 4GB in size or larger). Then install the MicroSD in the assembled hardware and off you go.
+Note: If you have physically removed the WiFi component from your board, you will still use the image file of the original(un-modified) hardware. (Our files are compiled/based on the *processor* architecture.)
-## Verifying the Software
-You can verify the data integrity and authenticity of the latest release with as little as three commands. This process assumes that you know [how to navigate on a terminal](https://terminalcheatsheet.com/guides/navigate-terminal) and have navigated to the folder where you have these four relevant files present: (This will most likely be your Downloads folder.)
+**also download** these 2 signature verification files to the same folder
+[The Plaintext manifest file](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner.0.6.0.sha256)
+[The Signature of the manifest file](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases/download/0.6.0/seedsigner.0.6.0.sha256.sig)
-* seedsigner_pubkey.gpg (from the main folder of this repo)
-* seedsigner_0_4_6.img.zip (from the software release)
-* seedsigner_0_4_6.img.zip.sha256 (from the software release)
-* seedsigner_0_4_6.img.zip.sha256.sig (from the software release)
+Users familiar with older versions of the SeedSigner software might be surprised with how fast their software downloads now are, because since version 0.6.0 the software image files are now 100x smaller! Each image file is now under 42 Megabytes so your downloads and verifications will be very quick now (and might even seem *too* quick)!
-**Note:** The specific version number of the files in your folder might not match the above exactly, but their overall format and amount should be the same.
+Once the files have all finished downloading, follow the steps below to verify the download before continuing on to write the software onto a MicroSD card. Next, insert the MicroSD into your assembled hardware and connect the USB power. Allow about 45 seconds for our logo to appear, and then you can begin using your SeedSigner!
+
+[Our previous software versions are available here](https://github.com/SeedSigner/seedsigner/releases). Choose a specific version and then expand the *Assets* sub-heading to display the .img file binary and also the 2 associated signature files. **Note:** The prior version files will have lower numbers than the scripts and examples provided in this document, but the naming format will be the same, so you can edit them as required for signature verification etc.
+
+
+## Verifying that the downloaded files are authentic (optional but highly recommended!)
+
+You can quickly verify that the software you just downloaded is both authentic and unaltered, by following these instructions.
+We assume you are running the commands from a computer where both [GPG](https://gnupg.org/download/index.html) and [shasum](https://command-not-found.com/shasum) are already installed, and that you also know [how to navigate on a terminal](https://terminalcheatsheet.com/guides/navigate-terminal).
+
+
+### Step 1. Verify that the signature (.sig) file is genuine:
+
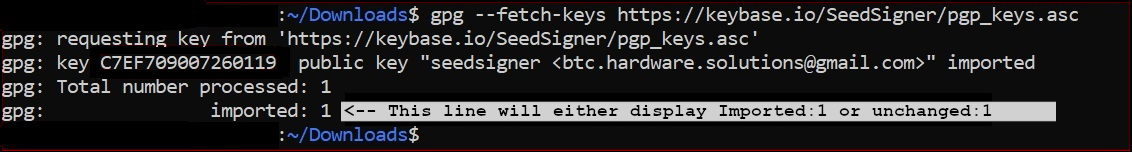
+Run GPG's *fetch-keys* command to import the SeedSigner projects public key from the popular online keyserver called *Keybase.io*, into your computers *keychain*.
-This process also assumes you are running the commands from a system where both [GPG](https://gnupg.org/download/index.html) and [shasum](https://command-not-found.com/shasum) are installed and working.
-First make sure that the public key is present in your keychain:
```
-gpg --import seedsigner_pubkey.gpg
+gpg --fetch-keys https://keybase.io/seedsigner/pgp_keys.asc
```
-This command will import the public key, or return:
+The result should confirm that 1 key was *either* imported or updated. *Ignore* any key ID's or email addresses shown.
+
+
+
+Next, you will run the *verify* command on the signature (.sig) file. (*Verify* must be run from inside the same folder that you downloaded the files into earlier. The `*`'s in this command will auto-fill the version from your current folder, so it should be copied and pasted as-is.)
```
-key <...> not changed
+gpg --verify seedsigner.0.6.*.sha256.sig
```
-Now you can verify the authenticity of the small text file containing the release's SHA256 hash with the command:
-```
-gpg --verify seedsigner_0_*_*.img.zip.sha256.sig
+When the verify command completes successfully, it should display output like this:
+
+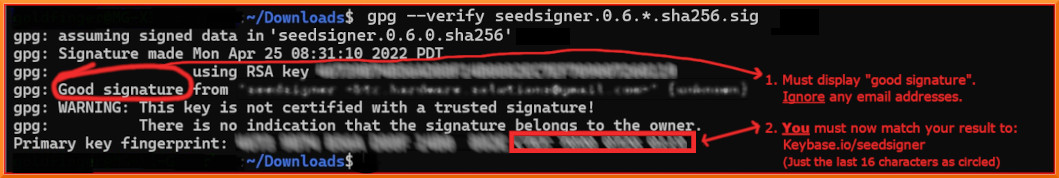
+The result must display "**Good signature**". Ignore any email addresses - *only* matching Key fingerprints count here. Stop immediately if it displays "*Bad signature*"!
+
+
+On the *last* output line, look at your *rightmost* 16 characters (the 4 blocks of 4).
+**Crucially, we must now check WHO that Primary key fingerprint /ID belongs to.** We will start by looking at Keybase.io to see if it is the *SeedSigner project* 's public key or not.
+
+ About the warning message:
+ Since you are about to match the outputted fingerprint/ID against the proofs at Keybase.io/SeedSigner, and thereby confirm who the pubkey really belongs to-, you can safely ignore this warning message:
+
```
-**Note:** The `*`s in the command above allow the terminal to auto-populate the command with the version number you have in the folder you are in. It should be copied and pasted as is.
+> WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature!
+> There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner.
+ ```
+
+
+
+ More about how the verify command works:
+
+The verify command will attempt to decrypt the signature file (sha256.sig) by trying each public key already imported into your computer. If the public key we just imported (via fetch-keys), manages to: (a) successfully decrypt the .sig file , and (b), that result matches exactly to the clear-text equivalent (.sha256) of the .sig file, then its "a good signature"!
+
+Crucially, we must still manually check who *exactly* owns the Key ID which gave us that "Good signature". Thats what the warning message means- Who does the matching key really belong to? We will start by looking at keybase.io to see if it is "The SeedSigner project"'s public Key or not.
+Note that it is the file hashes of .sig and .sha256 that *verify* compares, not their raw contents.
+
+
+
+
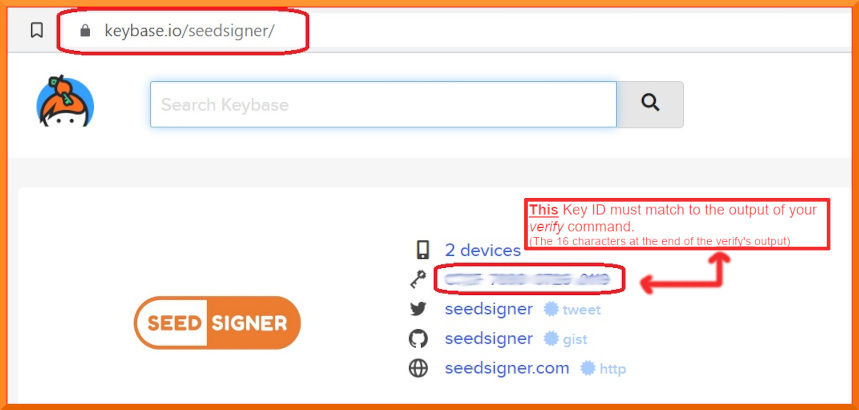
+Now to determine ***who*** the Public key ID belongs to: Goto [Keybase.io/SeedSigner](https://keybase.io/seedsigner)
+
+
+
+
-The reponse to this command should include the text:
+**You must now *manually* compare: The 16 character fingerprint ID (as circled in red above) to, those *rightmost* 16 characters from your *verify* command.**
+
+**If they match exactly, then you have successfully confirmed that your .sig file is authentically from the SeedSigner Project!**
+
+
+Learn more about how keybase.io helps you check that someone (online) is who they say they are:
+
+Keybase.io allows you to independently verify that the public key saved on Keybase.io, is both authentic and that it belongs to the organization it claims to represent.
+ Keybase has already checked the three pubkey file locations cryptographically when they were saved there. You can further verify the key publications if you would like:
+
+ - *via Keybase*: By clicking on any of the three blue badges to see that the "proof" was published at that location. (The blue badge marked as tweet, is in the most human-readable form and it is also a bi-directional link on Twitter)
+or,
+ - *without keybase (out-of-band)*: By using these 3 links directly: [Twitter](https://twitter.com/SeedSigner/status/1530555252373704707), [Github](https://gist.github.com/SeedSigner/5936fa1219b07e28a3672385b605b5d2) and [SeedSigner.com](https://seedsigner.com/keybase.txt). This method can be used if you would like to make an even deeper, independent inspection without relying on Keybase at all, or if the Keybase.io site is no longer valid or it is removed entirely.
+
+Once you have used one of these methods, you will know if the Public Key stored on Keybase, is genuinely from the SeedSinger Project or not.
+
+
+
+If the two ID's do *not* match, then you must stop here immediately. Do not continue. Contact us for assistance in the Telegram group address above.
+
+
+
+### Step 2. Verifying that the *software images/binaries* are genuine
+
+Now that you have confirmed that you do have the real SeedSigner Project's Public Key (ie the 16 characters match) - you can return to your terminal window. Running the *shasum* command, is the final verification step and will confirm (via file hashing) that the software code/image files, were also not altered since publication, or even during your download process.
+(Prior to version 0.6.0 , your verify command will check the .zip file which contains the binary files.)
+
+ **On Linux or OSX:** Run this command
```
-Good signature from "seedsigner " [unknown]
+shasum -a 256 --ignore-missing --check seedsigner.0.6.*.sha256
```
-The previous command validates that aforementioned small text file was signed using the private key that matches the published public key associated with the project (an early timestamped record of this public/private key's creation can be found in this [tweet](https://twitter.com/SeedSigner/status/1389617642286329856?s=20)).
-The last step is to make sure the .zip file that you've downloaded, and that contains the released software, is a perfect match to the software that was published by the holder of the private key in the last step. The command for this step is:
+**On Windows (inside Powershell):** Run this command
```
-shasum -a 256 -c seedsigner_0_*_*.img.zip.sha256
+CertUtil -hashfile seedsigner.0.6.0.sha256 SHA256 | findstr /v "hash"
```
-The reponse to this command should include the text:
+On Windows, you must then manually compare the resulting file hash value to the corresponding hash value shown inside the .SHA256 cleartext file.
+
+
+Wait up to 30 seconds for the command to complete, and it should display:
```
-seedsigner_0_4_6.img.zip: OK
+seedsigner_os.0.6.x[Your_Pi_Model_For_Example:pi02w].img: OK
```
+**If you receive the "OK" message** for your **seedsigner_os.0.6.x.[Your_Pi_Model_For_Example:pi02w].img file**, as shown above, then your verification is fully complete!
+**All of your downloaded files have now been confirmed as both authentic and unaltered!** You can proceed to create/write your MicroSD card😄😄 !!
+
+If your file result shows "FAILED", then you must stop here immediately. Do not continue. Contact us for assistance at the Telegram group address above.
+
+
+
+Please recognize that this process can only validate the software to the extent that the entity that first published the key is an honest actor, and their private key is not compromised or somehow being used by a malicious actor.
+
+
+
+
+## Writing the software onto your MicroSD card
+
+To write the SeedSigner software onto your MicroSD card, there are a few options available:
+| Application | Description | Platform and official Source |
+|--------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| Balena Etcher | The application is called Etcher, and the company that wrote it is called Balena. Hence *Etcher by Balena* or *Balena Etcher* | [Available for Windows, Mac and Linux](https://www.balena.io/etcher#download-etcher) |
+| Raspberry Pi Imager | Produced by the Raspberry Pi organization. | [Available for Windows, Mac and Linux](https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/) |
+| DD Command Line Utility | Built-in to Linux and MacOS, the DD (Data Duplicator) is a tool for advanced users. If not used carefully it can accidentally format the incorrect disk! | Built-in to Linux and MacOS |
+
+Be sure to download the software from the genuine publisher.
+Either of the Etcher or Pi Imager software is recommended. Some SeedSigner users have reported a better experience with one or the other. So, if the one application doesn’t work well for your particular machine, then please try the other one.
+
+### **General Considerations:**
+The writing and verify steps are very quick from version 0.6.0 upwards, so please pay close attention to your screen.
+Make sure to set any write-protection physical slider on the MicroSD Card Adapter to UN-locked.
+You also don’t need to pre-format the MicroSD beforehand. You *dont* need to unzip any .zip file beforehand.
+Current Etcher and Pi Imager software will perform a verify action (by default) to make sure the card was written successfully! Watching for that verify step to complete successfully can save you a lot of headaches if you later need to troubleshoot issues where your SeedSigner device doesn’t boot up at power on.
+Writing the MicroSd card is also known as flashing.
+It will overwrite everything on the MicroSD card.
+If the one application fails for you, then please try again using our other recommended application.
+Advanced users may want to try the Linux/MacOS *DD* command instead of using Etcher or Pi Imager, however, a reminder is given that DD can overwrite the wrong disk if you are not careful !
+#### **Specific considerations for Windows users:**
+Use the Pi imager software as your first choice on Windows. Windows can sometimes flag the writing of a MicroSD as risky behaviour and hence it may prevent this activity. If this happens, your writing/flashing will fail, hang or wont even begin, in which case you should to try to run the Etcher/Pi-Imager app "As administrator", (right-click and choose that option). It can also be blocked by windows security in some cases, so If you have the (non-default) *Controlled Folder Access* option set to active, try turning that *off* temporarily.
+
+
-There are other steps you can take to verify the software, including examining the hash value in the .sha256 text file, but this one has been documented here because it seems the simplest for most people to follow. Please recognize that this process can only validate the software to the extent that the entity that first published the key is an honest actor, and assumes the private key has remained uncompromised and is not being used by a malicious actor.
---------------
@@ -154,7 +270,7 @@ The upper and lower portions of the enclosure can be printed using a standard FD
* [Lil Pill](https://cults3d.com/en/3d-model/gadget/lil-pill-seedsigner-case) by @_CyberNomad
* [OrangeSurf Case](https://github.com/orangesurf/orangesurf-seedsigner-case) by @OrangeSurfBTC
-* [PS4 Seedsigner](https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:5363525) by @Silexperience
+* [PS4 SeedSigner](https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:5363525) by @Silexperience
* [OpenPill Faceplate](https://www.printables.com/en/model/179924-seedsigner-open-pill-cover-plates-digital-cross-jo) by @Revetuzo
* [Waveshare CoverPlate](https://cults3d.com/en/3d-model/various/seedsigner-coverplate-for-waveshare-1-3-inch-lcd-hat-with-240x240-pixel-display) by @Adathome1