In addition to new RoamJS Query Builder components, this extension enhances Roam's native querying experience by providing features such as an intuitive UI for creating and editing queries, sorting and randomizing query results, and displaying more context in these results.
In a block, type {{qb}}.
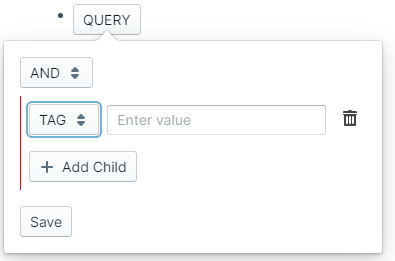
Similar to date picker, there will be an overlay that appears next to the QUERY button. After specifying different query components that you're interested in searching, hit save to insert the query syntax into the block.
The overlay is fully keyboard accessible. Each input is focusable and you can tab and shift+tab through them. For the query component dropdown, you could use the following key strokes to navigate:
- Arrow Up/Arrow Down - Navigate Options
- Enter - Open Dropdown
- a - Select 'AND'
- o - Select 'OR'
- b - Select 'BETWEEN'
- t - Select 'TAG'
- n - Select 'NOT'
On any deletable component, you could hit ctrl+Backspace or cmd+Backspace to delete the icon. Hitting enter on the save button will output the query into the block.
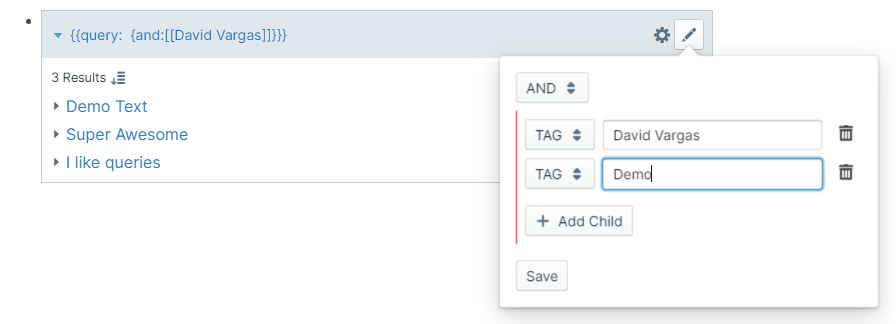
There will also be an edit button rendered on any existing query. Clicking the edit icon will overlay the builder to edit the existing query!
The legacy Query Tools extension was merged with this one to bring all native query manipulation features under Query Builder. These features could be configured within the Roam Depot Settings for Query Builder.
Default Sort- The default sorting all native queries in your graph should useSort Blocks- If set to 'True', sort the query results by blocks instead of pages.Context- The default value for Context for all queries. See below.
On expanded queries, there will be a sort icon that appears next to the results text. Clicking on the sort icon will make a sort menu visible to the user.
To persist a particular sort on a query, create a block on the page with the text Default Sort. Nest the value under that block.
To configure sorting by blocks on a single query instead of on all queries in your DB, add a block that says Sort Blocks as a child to the specific query.
Here are the options you can sort by:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Sort By Created Date | This will sort all the query results in ascending order that the page was created. |
| Sort By Created Date Descending | This will sort all the query results in descending order that the page was created. |
| Sort By Daily Note | This will sort all the query results in ascending order by Daily Note, followed by created date of non-daily note pages. |
| Sort By Daily Note Descending | This will sort all the query results in descending order by Daily Note, followed by created date of non-daily note pages. |
| Sort By Edited Date | This will sort all the query results in ascending order that the page was last edited. |
| Sort By Edited Date Descending | This will sort all the query results in descending order that the page was last edited. |
| Sort By Page Title | This will sort all the query results in ascending alphabetical order of the page title. |
| Sort By Page Title Descending | This will sort all the query results in descending alphabetical order of the page title. |
| Sort By Word Count | This will sort all the query results in ascending order of the word count. |
| Sort By Word Count Descending | This will sort all the query results in descending order of the word count. |
Sometimes we have queries with hundreds of results and want to return a random element from that query. Returning random results from multiple queries could lead to serendipitous connections. To return a random result from a query, add a block that says Random as a child of the query. Nest the value representing the number of random results you'd like returned from the query.
By default, query results only display the most nested block in the result. To display more context in a given query, add a block that says Context as a child block of the query. Set the value to the number of levels you'd like displayed, or Top to display full context, as a child of this Context block.
By default, query results display the query logic itself for the label. To display an alias for the given query, add a block that says Alias as a child block of the query, with the value of the alias nested below that.