We want to provide you a few examples of languages created with YAJCo. You can download them and try them out.
Download all examples: https://github.com/kpi-tuke/yajco-examples/archive/master.zip
You can use any Java IDE with support for Maven. Examples have been tested in
- IntelliJ IDEA
- Netbeans
- Eclipse
We recommend using IntelliJ IDEA as Netbeans has problems with generated sources and sometimes cannot provide them for error checking. Even when build and run is OK in Netbeans, project report fictious Netbeans errors. So you can use even Netbeans, but need to ignore errors. Eclipse is OK as long as you know how to run Maven builds in it.
If you experience some problems running these examples, please do clean and build first and than run. With some specific IntelliJ IDEA settings it is required to do run two times in row and you need to use our provided run main class configuration.
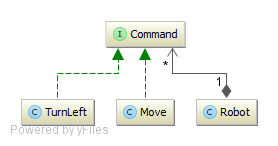
Directory: yajco-example-simpleRobot
Very simple example for manipulating robot. Robot takes 2 types of commands:
- Move
- Turn left Execution of each command is displayed with message to standard output.
This language example serves as simple example of multiple language concepts with simple concrete syntax and semantics. It is possible to use abstract classes and interfaces as points of extensions as is uses class Command.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
begin
move
turn-left
move
end
Execution result:
going straight
turning left
going straight
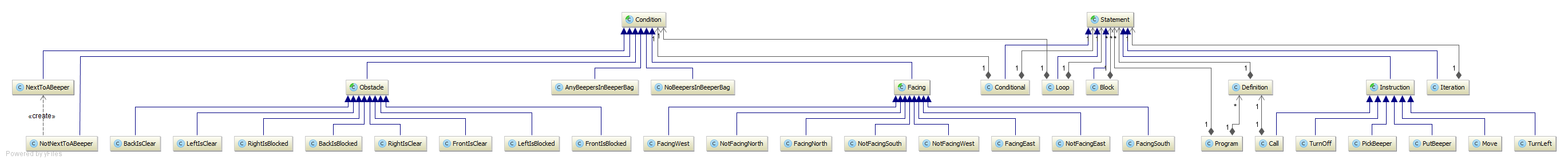
Directory: yajco-example-robotKarel
Complex example containing Robot Karel language as explained in http://mormegil.wz.cz/prog/karel/prog_doc.htm
Overview of all classes used for language specification is displayed in next image. As you can see it pretty complex example. It supports even creation of new named definitions of instructions.
Result of execution is actual evaluation of instructions in provided world. Before each evaluation of instruction state of the world and robot is displayed in console.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
Map:
*******
*o o*
* o *
* K *
*******
Instructions:
BEGINNING-OF-PROGRAM
DEFINE TURNRIGHT AS
ITERATE 3 TIMES
TURNLEFT
BEGINNING-OF-EXECUTION
MOVE
TURNRIGHT
MOVE
PICKBEEPER
TURNLEFT
MOVE
TURNOFF
END-OF-EXECUTION
END-OF-PROGRAM
Execution result:
*******
*o o*
* o *
* A *
*******
Karel: posX=3, posY=3, direction=NORTH, beepers=0
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.Move
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* Ao *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=3, posY=2, direction=NORTH, beepers=0
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.TurnLeft
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* <o *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=3, posY=2, direction=WEST, beepers=0
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.TurnLeft
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* Vo *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=3, posY=2, direction=SOUTH, beepers=0
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.TurnLeft
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* >o *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=3, posY=2, direction=EAST, beepers=0
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.Move
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* > *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=4, posY=2, direction=EAST, beepers=0
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.PickBeeper
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* > *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=4, posY=2, direction=EAST, beepers=1
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.TurnLeft
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o o*
* A *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=4, posY=2, direction=NORTH, beepers=1
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.Move
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*******
*o Ao*
* *
* K *
*******
Karel: posX=4, posY=1, direction=NORTH, beepers=1
Executing: yajco.robot.karel.model.instruction.TurnOff
*******
*o Ao*
* *
* K *
*******
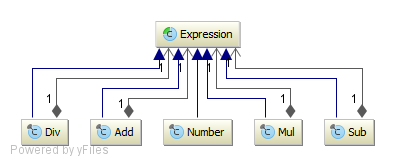
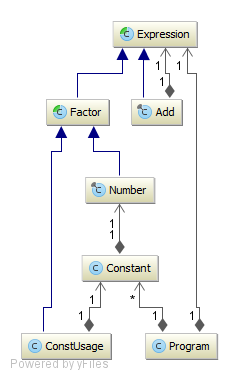
Directory: yajco-example-mathExpressions
Language for writing simple mathematical expressions consisting of:
- addition
- reduction
- multiplication
- division (integer)
- parenthesis
Result of each sentence of this language is evaluation of mathematical expression and it provides result. Such language could be used as module for any other language requiring support of mathematical expression.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
(1+6/2)*30
Execution result:
Result for '(1+6/2)*30' is: 120
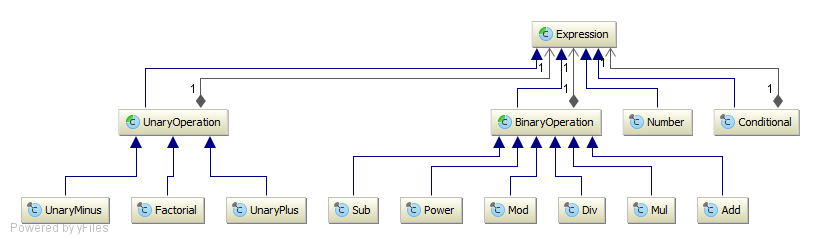
Directory: yajco-example-extMathExpressions
Language similar to previous language of mathematical expressions. Contains more mathematical operations and provides example for automatically generated Printer included in YAJCo tool.
Result of execution is evaluation of expression in form of mathematical value. As result we also print parsed sentence with automatically generated printer. Language supports parenthesis, therefore printer uses parenthesis in all possible places (of course, it would be nice to make printer more sophisticated :-))
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
2 ^ 3 * -7
Execution result:
Result: -56
Printer output:
((( 2) \^( 3)) \*( -( 7)))
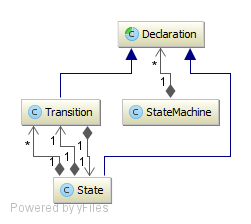
Directory: yajco-example-stateMachine
State machine is common in computer science. We have created language to describe state machines. It is possible to specify states and transitions between states. This example is a simple example for usage of identifiers and references in form of a language pattern, as YAJCo provides special annotations for this functionality.
Result of execution of a language sentence is summary of described state machine with information about incoming and outcoming transitions for each state.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
state Ready;
state Running;
state Unsafe;
trans a : Ready -> Running;
trans b : Running -> Ready;
trans c : Running -> Unsafe;
trans d : Unsafe -> Running;
Execution result:
state Ready [outgoingTrans: a ; incomingTrans: b ];
state Running [outgoingTrans: b c ; incomingTrans: a d ];
state Unsafe [outgoingTrans: d ; incomingTrans: c ];
trans a:Ready->Running;
trans b:Running->Ready;
trans c:Running->Unsafe;
trans d:Unsafe->Running;
Directory: yajco-example-deskNielsen
Language for description of simple expressions with constants.
Result of execution is transformation to instruction set and once again we display automatically generated printer output.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
print x + y + 3 + 2 where x = 1, y = 2
Execution result:
--------------------- PROGRAM RESULT ---------------------
PUSH 2
PUSH 3
PUSH 2
PUSH 1
ADD
ADD
ADD
--------------------- PRINTER OUTPUT ---------------------
print(((( x) +( y)) +( 3)) +( 2)) where x = 1, y = 2
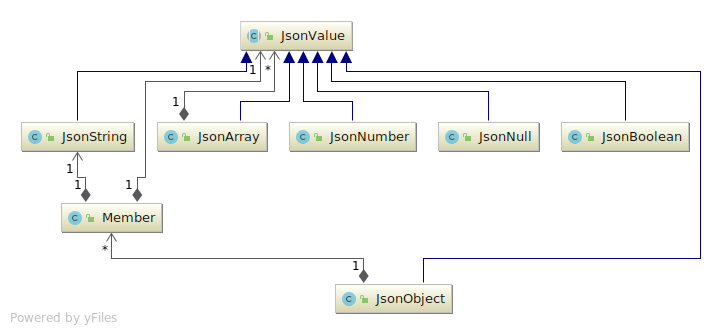
Directory: yajco-example-json
Parser for JSON format. Created by one of our bachelor student as part of YAJCo usage study.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
{
"id": 444,
"gender": "male",
"name": "John Bell",
"active": true,
"age": 345,
"hobbies": ["skiing","sleeping"]
}
Result is internal model of parsed JSON.
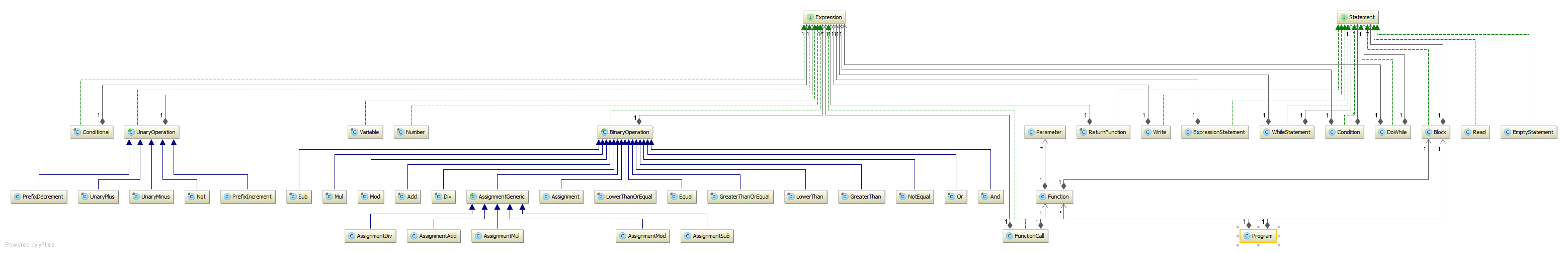
Directory: yajco-example-imperativeLang
Generic imperative programming language with support for named functions, blocks, iterations, variables. This language proves wide possibilities of YAJCo tool. It can be complex for understanding, but presents almost all functions possible in YAJCo.
Result of execution can be almost anything written in sentence. It is possible to evaluate mathematical or logical expression, write strings, call functions.
Model (class diagram):
Sentence example:
abs(x) {
return x < 0 ? - x : x;
}
{
i = -10;
while ( i <= 10 ) {
write abs(i);
i = i + 1;
}
}
Execution result:
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{i=11}